 “Genus Cannabis belong to family Cannabaceae and is traditionally used as medicinal plant against many diseases notably asthma, malaria, treatment of skin diseases, diabetes and headache. The plant Cannabis sativa L. is flowering and an annual herbaceous plant located to eastern Asia but now of cosmopolitan distribution due to extensive cultivation.
“Genus Cannabis belong to family Cannabaceae and is traditionally used as medicinal plant against many diseases notably asthma, malaria, treatment of skin diseases, diabetes and headache. The plant Cannabis sativa L. is flowering and an annual herbaceous plant located to eastern Asia but now of cosmopolitan distribution due to extensive cultivation.
Aim of the study: The aim of review is to provide a complete evaluation of the botanical, ethnological and chemical aspects of Cannabis sativa L., and its importance in pharmacological studies.
Results and discussions: This article briefly reviews the botany, traditional knowledge, pharmacological and therapeutic application of the plant C. sativa. This is an attempt to compile and document information about the chemical constituent, pharmacological and therapeutic effects of C. sativa as important herbal drug due to its safety and effectiveness. Studies have revealed its use as anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-cancer, anti-inflammatory and improving testicular function in rats. Consumption of C. sativa is greater in all over the world among all other drugs of abuse in its various forms such as marijuana, hashish and cannabis oil. The study of herbal medicine spans the knowledge of biology, history, source, physical and chemical nature, and mechanism of action, traditional, medicinal and therapeutic use of drug. This article also provide knowledge about macroscopically and microscopically characters of Cannabis sativa with geographical sources. The wellknown cannabinoids are Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), Cannabidiol (CBD) and Cannabichromene (CBC) and their pharmacological properties and importance have been extensively studied. Hence, efforts are required to establish and validate evidence regarding safety and practices of Ayurveda medicines.
Conclusion: Thes studies will help in expanding the current therapeutic potential of C. sativa and it also provide a strong support to its future clinical use as herbal medicines having safe in use with no side effects.”

 “Studies have reported changes in the endocannabinoid system in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), playing a role in the pathophysiology of AD. Cannabinoids have been shown to have neuroprotective properties, reduce neuroinflammation, and enhance neurogenesis. Evidence suggests that the utilization of marijuana products containing both tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) or CBD alone have been effective and safe for use in older people with agitation associated with dementia.
“Studies have reported changes in the endocannabinoid system in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), playing a role in the pathophysiology of AD. Cannabinoids have been shown to have neuroprotective properties, reduce neuroinflammation, and enhance neurogenesis. Evidence suggests that the utilization of marijuana products containing both tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) or CBD alone have been effective and safe for use in older people with agitation associated with dementia. “The seed of the hemp plant (Cannabis sativa L.) has been revered as a nutritional resource in Old World Cultures. This has been confirmed by contemporary science wherein hempseed oil (HSO) was found to exhibit a desirable ratio of omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) considered optimal for human nutrition. HSO also contains gamma-linoleic acid (GLA) and non-psychoactive cannabinoids, which further contribute to its’ potential bioactive properties. Herein, we present the kinetics of the thermal stability of these nutraceutical compounds in HSO, in the presence of various antioxidants (e.g. butylated hydroxytoluene, alpha-tocopherol, and ascorbyl palmitate). We focussed on oxidative changes in fatty acid profile and acidic cannabinoid stability when HSO was heated at different temperatures (25 °C to 85 °C) for upto 24 h. The fatty acid composition was evaluated using both GC/MS and 1H-NMR, and the cannabinoids profile of HSO was obtained using both HPLC-UV and HPLC/MS methods. The predicted half-life (DT50) for omega-6 and omega-3 PUFAs in HSO at 25 °C was about 3 and 5 days, respectively; while that at 85 °C was about 7 and 5 hours respectively, with respective activation energies (Ea) being 54.78 ± 2.36 and 45.02 ± 2.87 kJ/mol. Analysis of the conjugated diene hydroperoxides (CDH) and p-Anisidine value (p-AV) revealed that the addition of antioxidants significantly (p < 0.05) limited lipid peroxidation of HSO in samples incubated at 25-85 °C for 24 h. Antioxidants reduced the degradation constant (k) of PUFAs in HSO by upto 79%. This corresponded to a significant (p < 0.05) increase in color stability and pigment retention (chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids) of heated HSO. Regarding the decarboxylation kinetics of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) in HSO, at both 70 °C and 85 °C, CBDA decarboxylation led to predominantly cannabidiol (CBD) production. The half-life of CBDA decarboxylation (originally 4 days) could be increased to about 17 days using tocopherol as an antioxidant. We propose that determining acidic cannabinoids decarboxylation kinetics is a useful marker to measure the shelf-life of HSO. The results from the study will be useful for researchers looking into the thermal treatment of hempseed oil as a functional food product, and those interested in the decarboxylation kinetics of the acidic cannabinoids.”
“The seed of the hemp plant (Cannabis sativa L.) has been revered as a nutritional resource in Old World Cultures. This has been confirmed by contemporary science wherein hempseed oil (HSO) was found to exhibit a desirable ratio of omega-6 and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) considered optimal for human nutrition. HSO also contains gamma-linoleic acid (GLA) and non-psychoactive cannabinoids, which further contribute to its’ potential bioactive properties. Herein, we present the kinetics of the thermal stability of these nutraceutical compounds in HSO, in the presence of various antioxidants (e.g. butylated hydroxytoluene, alpha-tocopherol, and ascorbyl palmitate). We focussed on oxidative changes in fatty acid profile and acidic cannabinoid stability when HSO was heated at different temperatures (25 °C to 85 °C) for upto 24 h. The fatty acid composition was evaluated using both GC/MS and 1H-NMR, and the cannabinoids profile of HSO was obtained using both HPLC-UV and HPLC/MS methods. The predicted half-life (DT50) for omega-6 and omega-3 PUFAs in HSO at 25 °C was about 3 and 5 days, respectively; while that at 85 °C was about 7 and 5 hours respectively, with respective activation energies (Ea) being 54.78 ± 2.36 and 45.02 ± 2.87 kJ/mol. Analysis of the conjugated diene hydroperoxides (CDH) and p-Anisidine value (p-AV) revealed that the addition of antioxidants significantly (p < 0.05) limited lipid peroxidation of HSO in samples incubated at 25-85 °C for 24 h. Antioxidants reduced the degradation constant (k) of PUFAs in HSO by upto 79%. This corresponded to a significant (p < 0.05) increase in color stability and pigment retention (chlorophyll a, chlorophyll b and carotenoids) of heated HSO. Regarding the decarboxylation kinetics of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) in HSO, at both 70 °C and 85 °C, CBDA decarboxylation led to predominantly cannabidiol (CBD) production. The half-life of CBDA decarboxylation (originally 4 days) could be increased to about 17 days using tocopherol as an antioxidant. We propose that determining acidic cannabinoids decarboxylation kinetics is a useful marker to measure the shelf-life of HSO. The results from the study will be useful for researchers looking into the thermal treatment of hempseed oil as a functional food product, and those interested in the decarboxylation kinetics of the acidic cannabinoids.” “The efficacy of cannabidiol (CBD) with and without concomitant clobazam (CLB) was evaluated in stratified analyses of four large randomized controlled trials, two in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and two in Dravet syndrome.
“The efficacy of cannabidiol (CBD) with and without concomitant clobazam (CLB) was evaluated in stratified analyses of four large randomized controlled trials, two in Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and two in Dravet syndrome. “The Cannabis plant contains numerous components, including cannabinoids and other active molecules. The phyto-cannabinoid activity is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Cannabinoids affect the nervous system and play significant roles in the regulation of the immune system.
“The Cannabis plant contains numerous components, including cannabinoids and other active molecules. The phyto-cannabinoid activity is mediated by the endocannabinoid system. Cannabinoids affect the nervous system and play significant roles in the regulation of the immune system.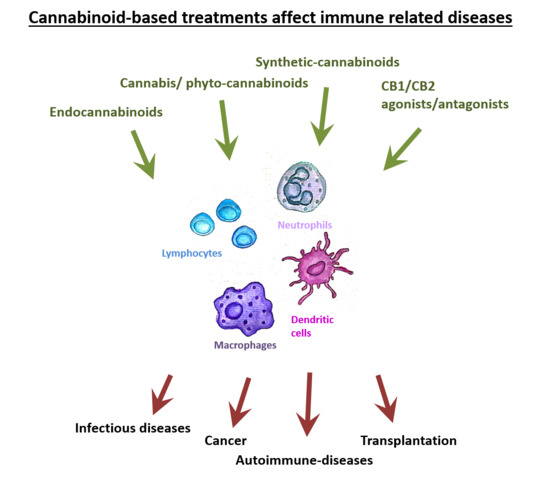
 “Current antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are undesirable for many reasons including the inability to reduce seizures in certain types of epilepsy, such as Dravet syndrome (DS) where in one-third of patients does not respond to current AEDs, and severe adverse effects that are frequently experienced by patients.
“Current antiepileptic drugs (AEDs) are undesirable for many reasons including the inability to reduce seizures in certain types of epilepsy, such as Dravet syndrome (DS) where in one-third of patients does not respond to current AEDs, and severe adverse effects that are frequently experienced by patients. “Objective: To determine whether cannabis may reduce HIV-related persistent inflammation, we evaluated the relationship of cannabis use in people with HIV (PWH) to inflammatory cytokines in CSF and blood plasma.
“Objective: To determine whether cannabis may reduce HIV-related persistent inflammation, we evaluated the relationship of cannabis use in people with HIV (PWH) to inflammatory cytokines in CSF and blood plasma.
 “Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical
“Attenuating emesis elicited by both disease and medical treatments of disease remains a critical  “Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an often chronic condition for which currently available medications have limited efficacy.
“Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is an often chronic condition for which currently available medications have limited efficacy.