“Objectives: To assess the motivation of cancer survivors to consume medical cannabis and to assess the patterns of use, perceived efficacy, as well as side and adverse effects.
“Objectives: To assess the motivation of cancer survivors to consume medical cannabis and to assess the patterns of use, perceived efficacy, as well as side and adverse effects.
Results: The mean monthly dosage of cannabis consumed was 42.4 grams; 95.8% of respondents reported not consuming cannabis regularly before being diagnosed with cancer; the most common way of administration was smoking, and most of the participants reported taking cannabis throughout the day. The most common symptoms for which participants took medical cannabis were pain (n = 169, 88.9%), sleeping disorder (n = 144, 75.8%) and anxiety (n = 79, 41.6%). Twenty patients (10.5%) reported on mild side (or adverse) effects.
Conclusions: This study indicates that cancer survivors may indeed consume cannabis for symptom relief, and not merely for recreational purposes. Although our findings point to perceived safety and efficacy of medical cannabis for cancer survivors, more research is needed to study the adequate role that cannabis may have for treating symptoms associated with cancer survivorship.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33197667/
“In conclusion, despite the many challenges and uncertainties, cannabis is being slowly diffused into healthcare. Survivors who have ongoing symptoms as a result of their prior treatments should be carefully assessed as to whether there is a medical need for which cannabis may be helpful. Indeed, patients and physicians should establish and maintain a therapeutic alliance in which medical needs and potential treatments, including medical cannabis, are honestly discussed and mutually considered and agreed upon.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0965229920318598?via%3Dihub

 “The COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 is a deadly disease afflicting millions. The pandemic continues affecting population due to nonavailability of drugs and vaccines. The pathogenesis and complications of infection mainly involve hyperimmune-inflammatory responses. Thus, therapeutic strategies rely on repurposing of drugs aimed at reducing infectivity and inflammation and modulate immunity favourably.
“The COVID-19 pandemic caused by SARS-CoV-2 is a deadly disease afflicting millions. The pandemic continues affecting population due to nonavailability of drugs and vaccines. The pathogenesis and complications of infection mainly involve hyperimmune-inflammatory responses. Thus, therapeutic strategies rely on repurposing of drugs aimed at reducing infectivity and inflammation and modulate immunity favourably.
 “Background: Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is characterized by progressive deterioration in behaviors, executive function and/or language. The behavioral variant (Bv) is characterized by disinhibition and obsessive/compulsive behaviors. These symptoms are sometimes resistant to medications. This series examines patients suffering with treatment-resistant Bv-FTD who were prescribed cannabinoid and related compounds for other indications.
“Background: Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is characterized by progressive deterioration in behaviors, executive function and/or language. The behavioral variant (Bv) is characterized by disinhibition and obsessive/compulsive behaviors. These symptoms are sometimes resistant to medications. This series examines patients suffering with treatment-resistant Bv-FTD who were prescribed cannabinoid and related compounds for other indications. “The increasing legalization of Cannabis for recreational and medicinal purposes in the United States has spurred renewed interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids (CBs) for human disease.
“The increasing legalization of Cannabis for recreational and medicinal purposes in the United States has spurred renewed interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabinoids (CBs) for human disease. “The ability of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) inflorescence extract to counteract lipid oxidation was studied in stripped linseed oil.
“The ability of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) inflorescence extract to counteract lipid oxidation was studied in stripped linseed oil.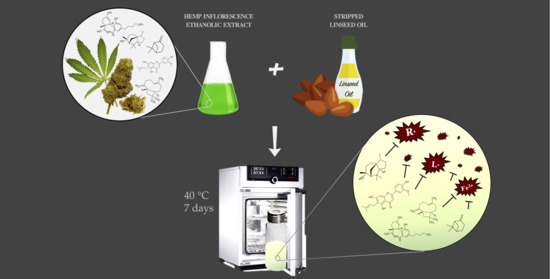
 “Cannabis has been used as a medicine for millennia. Prohibition in the mid-20th century precluded early scientific investigation.
“Cannabis has been used as a medicine for millennia. Prohibition in the mid-20th century precluded early scientific investigation. “Medical cannabis and individual cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), are receiving growing attention in both the media and the scientific literature. The Cannabis plant, however, produces over 100 different cannabinoids, and cannabigerol (CBG) serves as the precursor molecule for the most abundant phytocannabinoids.
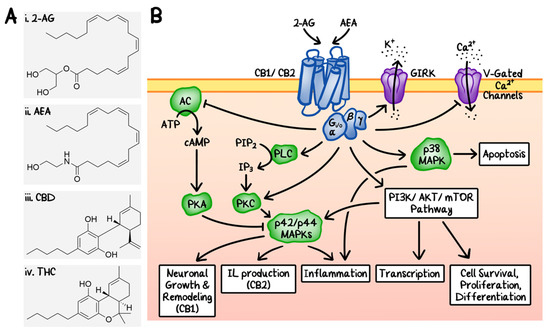
“Medical cannabis and individual cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), are receiving growing attention in both the media and the scientific literature. The Cannabis plant, however, produces over 100 different cannabinoids, and cannabigerol (CBG) serves as the precursor molecule for the most abundant phytocannabinoids. “The endocannabinoid (eCB) system encompasses the eCBs anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, their anabolic/catabolic enzymes, and the cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Its expansion to include several eCB-like lipid mediators, their metabolic enzymes, and their molecular targets, forms the endocannabinoidome (eCBome).
“The endocannabinoid (eCB) system encompasses the eCBs anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, their anabolic/catabolic enzymes, and the cannabinoid CB1 and CB2 receptors. Its expansion to include several eCB-like lipid mediators, their metabolic enzymes, and their molecular targets, forms the endocannabinoidome (eCBome). “Recently, cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), have been the subject of intensive research and heavy scrutiny. Cannabinoids encompass a wide array of organic molecules, including those that are physiologically produced in humans, synthesized in laboratories, and extracted primarily from the Cannabis sativa plant. These organic molecules share similarities in their chemical structures as well as in their protein binding profiles. However, pronounced differences do exist in their mechanisms of action and clinical applications, which will be briefly compared and contrasted in this review. The mechanism of action of CBD and its potential applications in cancer therapy will be the major focus of this review article.”
“Recently, cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), have been the subject of intensive research and heavy scrutiny. Cannabinoids encompass a wide array of organic molecules, including those that are physiologically produced in humans, synthesized in laboratories, and extracted primarily from the Cannabis sativa plant. These organic molecules share similarities in their chemical structures as well as in their protein binding profiles. However, pronounced differences do exist in their mechanisms of action and clinical applications, which will be briefly compared and contrasted in this review. The mechanism of action of CBD and its potential applications in cancer therapy will be the major focus of this review article.”