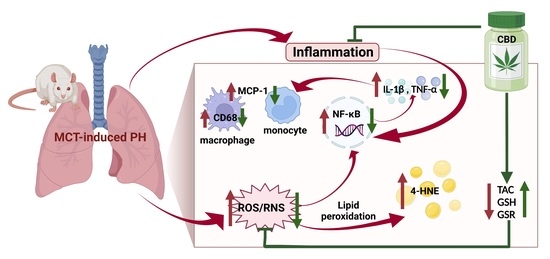
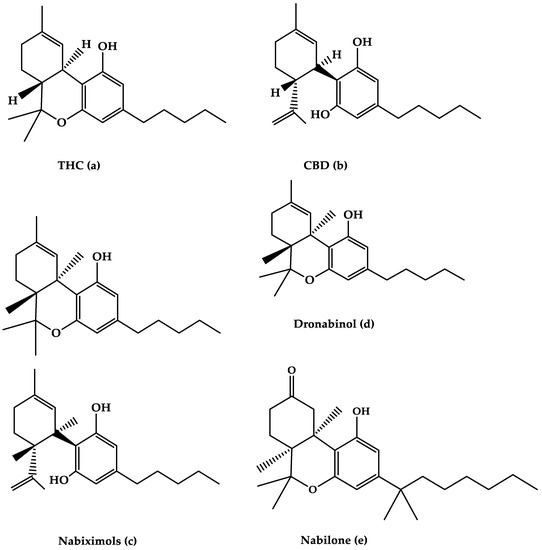
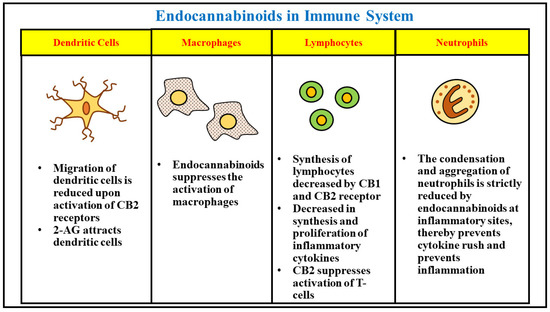
“Background: Even though the Cannabis plant has been used to treat nausea for millennia, few studies have measured real-time effects of common and commercially available cannabis-based products.
Study: Using the Releaf App, 886 people completed 2220 cannabis self-administration sessions intended to treat nausea between June 6, 2016 and July 8, 2019. They recorded the characteristics of self-administered cannabis products and baseline symptom intensity levels before tracking real-time changes in the intensity of their nausea.
Results: By 1 hour postconsumption, 96.4% of people had experienced symptom relief with an average symptom intensity reduction of -3.85 points on a 0 to 10 visual analog scale (SD=2.45, d=1.85, P<0.001). Symptom relief was statistically significant at 5 minutes and increased with time. Among product characteristics, flower and concentrates yielded the strongest, yet similar results; products labeled as Cannabis indica underperformed those labeled as Cannabis sativa or hybrid; and joints were associated with greater symptom relief than pipes or vaporizers. In sessions using flower, higher tetrahydrocannbinol and lower cannabidiol were generally associated with greater symptom relief (eg, within 5 min).
Conclusions: The findings suggest that the vast majority of patients self-selecting into cannabis use for treatment of nausea likely experience relief within a relative short duration of time, but the level of antiemetic effect varies with the characteristics of the cannabis products consumed in vivo. Future research should focus on longer term symptom relief, including nausea-free intervals and dosing frequency; the risks of consumption of medical cannabis, especially among high-risk populations, such as pregnant women and children; and potential interactions between cannabis, conventional antiemetics, other medications, food, tobacco, alcohol, and street drugs among specific patient populations.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35258504/