 “The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
“The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
In addition to regulating physiological processes, the ECS directly influences anxiety, feeding behaviour/appetite, emotional behaviour, depression, nervous functions, neurogenesis, neuroprotection, reward, cognition, learning, memory, pain sensation, fertility, pregnancy, and pre-and post-natal development.
The ECS is also involved in several pathophysiological diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. In recent years, genetic and pharmacological manipulation of the ECS has gained significant interest in medicine, research, and drug discovery and development.
The distribution of the components of the ECS system throughout the body, and the physiological/pathophysiological role of the ECS-signalling pathways in many diseases, all offer promising opportunities for the development of novel cannabinergic, cannabimimetic, and cannabinoid-based therapeutic drugs that genetically or pharmacologically modulate the ECS via inhibition of metabolic pathways and/or agonism or antagonism of the receptors of the ECS. This modulation results in the differential expression/activity of the components of the ECS that may be beneficial in the treatment of a number of diseases.
This manuscript in-depth review will investigate the potential of the ECS in the treatment of various diseases, and to put forth the suggestion that many of these secondary metabolites of Cannabis sativa L. (hereafter referred to as “C. sativa L.” or “medical cannabis”), may also have potential as lead compounds in the development of cannabinoid-based pharmaceuticals for a variety of diseases.”
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/17/9472

 “Obesity-related insulin resistance (IR) and attenuated brain insulin signaling are significant risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders, e.g., Alzheimer’s disease. IR and type 2 diabetes correlate with an increased concentration of sphingolipids, a class of lipids that play an essential structural role in cellular membranes and cell signaling pathways.
“Obesity-related insulin resistance (IR) and attenuated brain insulin signaling are significant risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders, e.g., Alzheimer’s disease. IR and type 2 diabetes correlate with an increased concentration of sphingolipids, a class of lipids that play an essential structural role in cellular membranes and cell signaling pathways. “Introduction:
“Introduction: 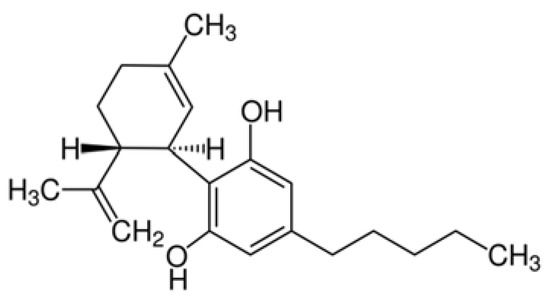
 “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by structural damage, death, and functional disruption of cholinergic neurons (ChNs) as a result of intracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, extracellular neuritic plaques, and hyperphosphorylation of protein tau (p-Tau) overtime.
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is characterized by structural damage, death, and functional disruption of cholinergic neurons (ChNs) as a result of intracellular amyloid-β (Aβ) aggregation, extracellular neuritic plaques, and hyperphosphorylation of protein tau (p-Tau) overtime. “Background: Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is characterized by progressive deterioration in behaviors, executive function and/or language. The behavioral variant (Bv) is characterized by disinhibition and obsessive/compulsive behaviors. These symptoms are sometimes resistant to medications. This series examines patients suffering with treatment-resistant Bv-FTD who were prescribed cannabinoid and related compounds for other indications.
“Background: Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is characterized by progressive deterioration in behaviors, executive function and/or language. The behavioral variant (Bv) is characterized by disinhibition and obsessive/compulsive behaviors. These symptoms are sometimes resistant to medications. This series examines patients suffering with treatment-resistant Bv-FTD who were prescribed cannabinoid and related compounds for other indications. “The aberrant accumulation of disease-specific protein aggregates accompanying cognitive decline is a pathological hallmark of age-associated neurological disorders, also termed as proteinopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis.
“The aberrant accumulation of disease-specific protein aggregates accompanying cognitive decline is a pathological hallmark of age-associated neurological disorders, also termed as proteinopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown. “Background: Older adults (≥50 years) represent the fastest-growing population of people who use cannabis, potentially due to the increasing promotion of cannabis as medicine by dispensaries and cannabis websites. Given healthy aging and cannabis use are both associated with cognitive decline, it is important to establish the effects of cannabis on cognition in healthy aging.
“Background: Older adults (≥50 years) represent the fastest-growing population of people who use cannabis, potentially due to the increasing promotion of cannabis as medicine by dispensaries and cannabis websites. Given healthy aging and cannabis use are both associated with cognitive decline, it is important to establish the effects of cannabis on cognition in healthy aging. “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a central nervous system disease characterized by dementia, which has now become a major threat to global health.
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a central nervous system disease characterized by dementia, which has now become a major threat to global health.