 “Autism Spectrum Disorders comprise conditions that may affect cognitive development, motor skills, social interaction, communication, and behavior. This set of functional deficits often results in lack of independence for the diagnosed individuals, and severe distress for patients, families, and caregivers.
“Autism Spectrum Disorders comprise conditions that may affect cognitive development, motor skills, social interaction, communication, and behavior. This set of functional deficits often results in lack of independence for the diagnosed individuals, and severe distress for patients, families, and caregivers.
There is a mounting body of evidence indicating the effectiveness of pure cannabidiol (CBD) and CBD-enriched Cannabis sativa extract (CE) for the treatment of autistic symptoms in refractory epilepsy patients. There is also increasing data support for the hypothesis that non-epileptic autism shares underlying etiological mechanisms with epilepsy.
Here we report an observational study with a cohort of 18 autistic patients undergoing treatment with compassionate use of standardized CBD-enriched CE (with a CBD to THC ratio of 75/1).
Among the 15 patients who adhered to the treatment (10 non-epileptic and five epileptic) only one patient showed lack of improvement in autistic symptoms. Due to adverse effects, three patients discontinued CE use before 1 month.
After 6-9 months of treatment, most patients, including epileptic and non-epileptic, showed some level of improvement in more than one of the eight symptom categories evaluated: Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder; Behavioral Disorders; Motor Deficits; Autonomy Deficits; Communication and Social Interaction Deficits; Cognitive Deficits; Sleep Disorders and Seizures, with very infrequent and mild adverse effects.
The strongest improvements were reported for Seizures, Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder, Sleep Disorders, and Communication and Social Interaction Deficits. This was especially true for the 10 non-epileptic patients, nine of which presented improvement equal to or above 30% in at least one of the eight categories, six presented improvement of 30% or more in at least two categories and four presented improvement equal to or above 30% in at least four symptom categories.
Ten out of the 15 patients were using other medicines, and nine of these were able to keep the improvements even after reducing or withdrawing other medications.
The results reported here are very promising and indicate that CBD-enriched CE may ameliorate multiple ASD symptoms even in non-epileptic patients, with substantial increase in life quality for both ASD patients and caretakers.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31736860
“The findings presented here, taken together, support the notion that many autism symptoms are associated to neuronal hyperexcitability, and indicate that CBD-enriched CE yields positive effects in multiple autistic symptoms, without causing the typical side effects found in medicated ASD patients. Most patients in this study had improved symptoms even after supervised weaning of other neuropsychiatric drugs.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fneur.2019.01145/full


 “Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a multifactorial, pervasive neurodevelopmental disorder defined by the core symptoms of significant impairment in social interaction and communication as well as restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior. In addition to these core behaviors, persons with ASD frequently have associated noncore behavioral disturbance (ie, self-injury, aggression), as well as several medical comorbidities. Currently, no effective treatment exists for the core symptoms of ASD.
“Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a multifactorial, pervasive neurodevelopmental disorder defined by the core symptoms of significant impairment in social interaction and communication as well as restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior. In addition to these core behaviors, persons with ASD frequently have associated noncore behavioral disturbance (ie, self-injury, aggression), as well as several medical comorbidities. Currently, no effective treatment exists for the core symptoms of ASD. “The etiopathogenesis of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) remains largely unclear.
“The etiopathogenesis of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) remains largely unclear.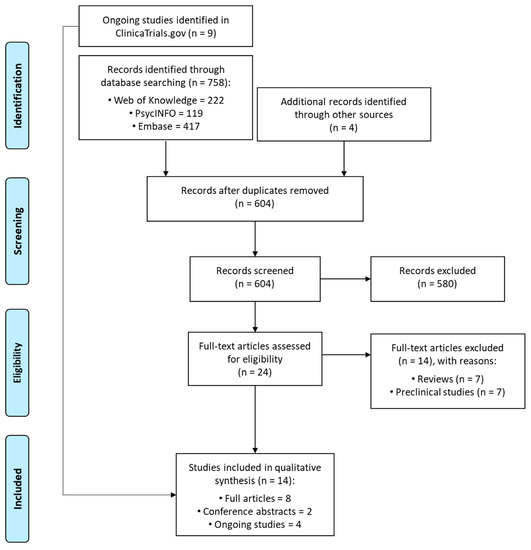

 “The use of medical cannabis in children is rapidly growing.
“The use of medical cannabis in children is rapidly growing. “Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a high cost neurodevelopmental condition; and there are currently no effective pharmacological treatments for its core symptoms. This has led some families and researchers to trial alternative remedies – including the non-intoxicating
“Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a high cost neurodevelopmental condition; and there are currently no effective pharmacological treatments for its core symptoms. This has led some families and researchers to trial alternative remedies – including the non-intoxicating  “Autism Spectrum Disorders comprise conditions that may affect cognitive development, motor skills, social interaction, communication, and behavior. This set of functional deficits often results in lack of independence for the diagnosed individuals, and severe distress for patients, families, and caregivers.
“Autism Spectrum Disorders comprise conditions that may affect cognitive development, motor skills, social interaction, communication, and behavior. This set of functional deficits often results in lack of independence for the diagnosed individuals, and severe distress for patients, families, and caregivers. “Microglia are the resident, innate immune cells of the central nervous system (CNS) and are critical in managing CNS injuries and infections. Microglia also maintain CNS homeostasis by influencing neuronal development, viability, and function. However, aberrant microglial activity and phenotypes are associated with CNS pathology, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Thus, improving our knowledge of microglial regulation could provide insights into the maintenance of CNS homeostasis as well as the prevention and treatment of ASD.
“Microglia are the resident, innate immune cells of the central nervous system (CNS) and are critical in managing CNS injuries and infections. Microglia also maintain CNS homeostasis by influencing neuronal development, viability, and function. However, aberrant microglial activity and phenotypes are associated with CNS pathology, including autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Thus, improving our knowledge of microglial regulation could provide insights into the maintenance of CNS homeostasis as well as the prevention and treatment of ASD.