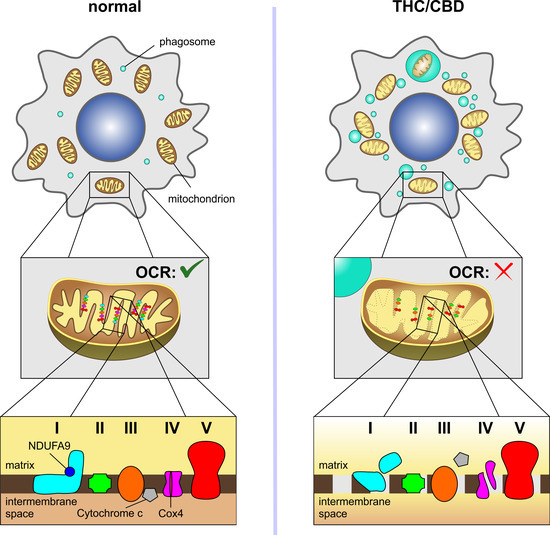
“Globally, it is evident that glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is an aggressive malignant cancer with a high mortality rate and no effective treatment options. Glioblastoma is classified as the stage-four progression of a glioma tumor, and its diagnosis results in a shortened life expectancy. Treatment options for GBM include chemotherapy, immunotherapy, surgical intervention, and conventional pharmacotherapy; however, at best, they extend the patient’s life by a maximum of 5 years. GBMs are considered incurable due to their high recurrence rate, despite various aggressive therapeutic approaches which can have many serious adverse effects.
Ceramides, classified as endocannabinoids, offer a promising novel therapeutic approach for GBM. Endocannabinoids may enhance the apoptosis of GBM cells but have no effect on normal healthy neural cells. Cannabinoids promote atypical protein kinase C, deactivate fatty acid amide hydrolase enzymes, and activate transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) and TRPV2 to induce pro-apoptotic signaling pathways without increasing endogenous cannabinoids. In previous in vivo studies, endocannabinoids, chemically classified as amide formations of oleic and palmitic acids, have been shown to increase the pro-apoptotic activity of human cancer cells and inhibit cell migration and angiogenesis.
This review focuses on the biological synthesis and pharmacology of endogenous cannabinoids for the enhancement of cancer cell apoptosis, which have potential as a novel therapy for GBM.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36805391/
“As discussed above, endocannabinoids could prove to be a viable alternative treatment for GBM.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S2095496423000055?via%3Dihub