“Phytocannabinoids represent a promising approach in glioblastoma therapy.
Previous work has shown that a combined treatment of glioblastoma cells with submaximal effective concentrations of psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) greatly increases cell death.
In the present work, the glioblastoma cell lines U251MG and U138MG were used to investigate whether the combination of THC and CBD in a 1:1 ratio is associated with a disruption of cellular energy metabolism, and whether this is caused by affecting mitochondrial respiration.
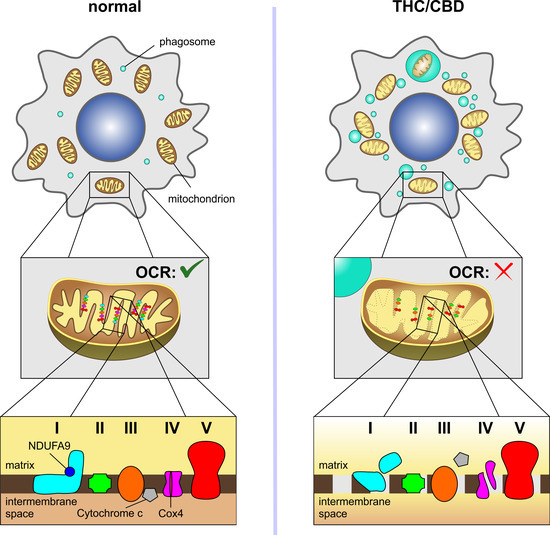
Here, the combined administration of THC and CBD (2.5 µM each) led to an inhibition of oxygen consumption rate and energy metabolism. These effects were accompanied by morphological changes to the mitochondria, a release of mitochondrial cytochrome c into the cytosol and a marked reduction in subunits of electron transport chain complexes I (NDUFA9, NDUFB8) and IV (COX2, COX4). Experiments with receptor antagonists and inhibitors showed that the degradation of NDUFA9 occurred independently of the activation of the cannabinoid receptors CB1, CB2 and TRPV1 and of usual degradation processes mediated via autophagy or the proteasomal system.
In summary, the results describe a previously unknown mitochondria-targeting mechanism behind the toxic effect of THC and CBD on glioblastoma cells that should be considered in future cancer therapy, especially in combination strategies with other chemotherapeutics.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35804909/
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a phytocannabinoid from Cannabis sativa L. that exhibits no psychoactivity and, like the psychoactive cannabinoid Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), shows anticancer effects in preclinical cell and animal models. Previous studies have indicated a stronger cancer-targeting effect when THC and CBD are combined. Here, we investigated how the combination of THC and CBD in a 1:1 ratio affects glioblastoma cell survival. The compounds were found to synergistically enhance cell death, which was attributed to mitochondrial damage and disruption of energy metabolism. A detailed look at the mitochondrial electron transfer chain showed that THC/CBD selectively decreased certain subunits of complexes I and IV. These data highlight the fundamental changes in cellular energy metabolism when cancer cells are exposed to a mixture of cannabinoids and underscore the potential of combining cannabinoids in cancer treatment.”
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/14/13/3129