 “Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant.
“Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant.
Cannabinoids exert their effects through the endocannabinoid system (ECS) that comprises cannabinoid receptors (CB1, CB2), endogenous ligands, and metabolizing enzymes. Several preclinical studies have demonstrated the potential of cannabinoids against leukemia, lymphoma, glioblastoma, and cancers of the breast, colorectum, pancreas, cervix and prostate.
Cannabis and its constituents can modulate multiple cancer related pathways such as PKB, AMPK, CAMKK-β, mTOR, PDHK, HIF-1α, and PPAR-γ. Cannabinoids can block cell growth, progression of cell cycle and induce apoptosis selectively in tumour cells. Cannabinoids can also enhance the efficacy of cancer therapeutics. These compounds have been used for the management of anorexia, queasiness, and pain in cancer patients.
Cannabinoid based products such as dronabinol, nabilone, nabiximols, and epidyolex are now approved for medical use in cancer patients. Cannabinoids are reported to produce a favourable safety profile. However, psychoactive properties and poor bioavailability limit the use of some cannabinoids. The Academic Institutions across the globe are offering training courses on cannabis. How cannabis and its constituents exert anticancer activities is discussed in this article. We also discuss areas that require attention and more extensive research.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33246167/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1043661820316108?via%3Dihub

 “Cannabidiol (CBD) has anti-tumorigenic activity. However, the anti-cancer effect of CBD on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remains unclear. The cytotoxicity of CBD on HNSCC was analyzed using cell survival and colony-forming assays in vitro.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) has anti-tumorigenic activity. However, the anti-cancer effect of CBD on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remains unclear. The cytotoxicity of CBD on HNSCC was analyzed using cell survival and colony-forming assays in vitro. “Research within a gynecologic oncology population has lagged behind the uptake in use of medical cannabis for symptom control. This study seeks to evaluate patient experience with prescribed medical cannabis obtained through licensed dispensaries in women with gynecologic malignancies.
“Research within a gynecologic oncology population has lagged behind the uptake in use of medical cannabis for symptom control. This study seeks to evaluate patient experience with prescribed medical cannabis obtained through licensed dispensaries in women with gynecologic malignancies. “Objectives: To assess the motivation of cancer survivors to consume medical cannabis and to assess the patterns of use, perceived efficacy, as well as side and adverse effects.
“Objectives: To assess the motivation of cancer survivors to consume medical cannabis and to assess the patterns of use, perceived efficacy, as well as side and adverse effects. “Recently, cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), have been the subject of intensive research and heavy scrutiny. Cannabinoids encompass a wide array of organic molecules, including those that are physiologically produced in humans, synthesized in laboratories, and extracted primarily from the Cannabis sativa plant. These organic molecules share similarities in their chemical structures as well as in their protein binding profiles. However, pronounced differences do exist in their mechanisms of action and clinical applications, which will be briefly compared and contrasted in this review. The mechanism of action of CBD and its potential applications in cancer therapy will be the major focus of this review article.”
“Recently, cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), have been the subject of intensive research and heavy scrutiny. Cannabinoids encompass a wide array of organic molecules, including those that are physiologically produced in humans, synthesized in laboratories, and extracted primarily from the Cannabis sativa plant. These organic molecules share similarities in their chemical structures as well as in their protein binding profiles. However, pronounced differences do exist in their mechanisms of action and clinical applications, which will be briefly compared and contrasted in this review. The mechanism of action of CBD and its potential applications in cancer therapy will be the major focus of this review article.”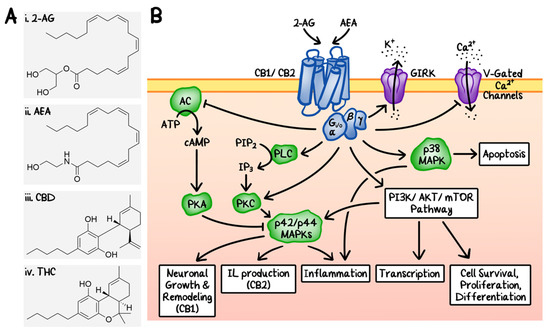
 “The anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids including CBD (Cannabidiol) and THC ((-)-trans-∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol) have been reported in the case of pancreatic cancer (PC).
“The anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids including CBD (Cannabidiol) and THC ((-)-trans-∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol) have been reported in the case of pancreatic cancer (PC). “The prevalence of cancer pain will continue to rise as pain is common among the survivorship and general cancer population. As interest in cannabis and cannabinoids for medicinal use including pain management continues to rise, there is growing need to update and review the current state of evidence for their use. The literature was searched for articles in English with key words cannabis, cannabinoids, and cancer pain. The sources of articles were PubMed, Embase, and open Google search.
“The prevalence of cancer pain will continue to rise as pain is common among the survivorship and general cancer population. As interest in cannabis and cannabinoids for medicinal use including pain management continues to rise, there is growing need to update and review the current state of evidence for their use. The literature was searched for articles in English with key words cannabis, cannabinoids, and cancer pain. The sources of articles were PubMed, Embase, and open Google search. “The cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2R) represents an interesting and new therapeutic target for its involvement in the first steps of neurodegeneration as well as in cancer onset and progression.
“The cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2R) represents an interesting and new therapeutic target for its involvement in the first steps of neurodegeneration as well as in cancer onset and progression.
 “This study evaluated the synergistic anti-cancer potential of cannabinoid combinations across the MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines. Cannabinoids were combined and their synergistic interactions were evaluated using median effect analysis.
“This study evaluated the synergistic anti-cancer potential of cannabinoid combinations across the MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines. Cannabinoids were combined and their synergistic interactions were evaluated using median effect analysis. “Providers need to be better equipped to discuss medical cannabis with patients even if they are not willing to prescribe it. The oncology community would be well served to ensure that providers are aware of existing cannabis research and are able to incorporate it into their communications with patients instead of leaving patients to figure out medical cannabis on their own.”
“Providers need to be better equipped to discuss medical cannabis with patients even if they are not willing to prescribe it. The oncology community would be well served to ensure that providers are aware of existing cannabis research and are able to incorporate it into their communications with patients instead of leaving patients to figure out medical cannabis on their own.”