 “Metastatic breast cancer is prevalent worldwide, and one of the most common sites of metastasis are long bones. Of patients with disease, the major symptom is pain, yet current medications fail to adequately result in analgesic efficacy and present major undesirable adverse effects.
“Metastatic breast cancer is prevalent worldwide, and one of the most common sites of metastasis are long bones. Of patients with disease, the major symptom is pain, yet current medications fail to adequately result in analgesic efficacy and present major undesirable adverse effects.
In our study we investigate the potential of a novel monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) inhibitor, MJN110, in a murine model of cancer induced bone pain (CIBP). Literature has previously demonstrated that MAGL inhibitors function to increase the endogenous concentrations of 2-arachydonylglycerol, which then activate CB1 and CB2 receptors inhibiting inflammation and pain.
Together, these data support the application for MJN110 as a novel therapeutic for cancer induced bone pain.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Current standard of care for metastatic breast cancer pain is opioid-based therapies with adjunctive chemotherapy, which have highly addictive and other deleterious side effects. The need for effective, non-opioid based therapies is essential and harnessing the endogenous cannabinoid system is proving to be a new target to treat various types of pain conditions. We present a novel drug targeting the endogenous cannabinoid system that is effective at reducing pain in a mouse model of metastatic breast cancer to bone.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32054717
http://jpet.aspetjournals.org/content/early/2020/02/13/jpet.119.262337

 “Radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy is the major treatment modality for human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). GBMs eventually relapse after treatment and the average survival of GBM patients is less than two years.
“Radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy is the major treatment modality for human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). GBMs eventually relapse after treatment and the average survival of GBM patients is less than two years. “Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g.,
“Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g.,  “Novel anticancer medicines, including targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, have greatly improved the management of cancers. However, both conventional and new anticancer treatments induce cardiac adverse effects, which remain a critical issue in clinic.
“Novel anticancer medicines, including targeted therapies and immune checkpoint inhibitors, have greatly improved the management of cancers. However, both conventional and new anticancer treatments induce cardiac adverse effects, which remain a critical issue in clinic. “Cannabinoids are a group of structurally heterogeneous but pharmacologically related compounds, including plant-derived cannabinoids, synthetic substances and endogenous cannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol.
“Cannabinoids are a group of structurally heterogeneous but pharmacologically related compounds, including plant-derived cannabinoids, synthetic substances and endogenous cannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. “In the last decade, we have observed an increased public and scientific interest in the clinical applications of medical cannabis.
“In the last decade, we have observed an increased public and scientific interest in the clinical applications of medical cannabis. “Endo-, phyto- and synthetic cannabinoids have been proposed as promising anti-cancer agents able to impair cancer cells’ behavior without affecting their non-transformed counterparts.
“Endo-, phyto- and synthetic cannabinoids have been proposed as promising anti-cancer agents able to impair cancer cells’ behavior without affecting their non-transformed counterparts.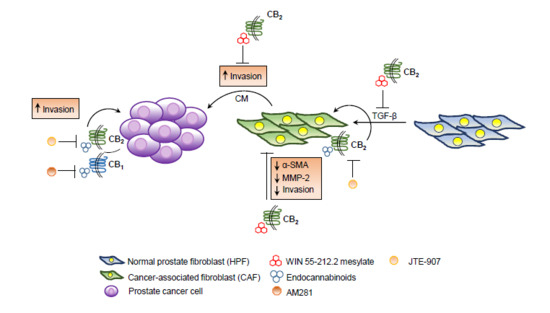
 “Recent changes to the legal status of marijuana in Canada warrant a review of the information that patients and families are accessing online regarding the role of
“Recent changes to the legal status of marijuana in Canada warrant a review of the information that patients and families are accessing online regarding the role of  “The aim of this review article is to summarize current knowledge about the role of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors in tumor disease modulation and to evaluate comprehensively the use of cannabinoids in cancer patients.
“The aim of this review article is to summarize current knowledge about the role of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors in tumor disease modulation and to evaluate comprehensively the use of cannabinoids in cancer patients.