
Case presentation: Herein we present the case of a 21-year-old female Caucasian patient, with free history, diagnosed with HL stage IIB. The patient started first line chemotherapy and radiotherapy, with incomplete remission. She refused any other treatment. Five years later, the patient became pregnant and was offered chemotherapy in the 2nd trimester of pregnancy, that she refused, and delivered by C-section at 37 weeks. In the same year, the patient became pregnant again and was proposed termination of pregnancy, that she also refused. The MRI scan revealed progression of HL and she was admitted in the hospital several times for altered general condition, respiratory infections and increased need of painkillers including opioids.
At 26 weeks of pregnancy, the patient began on her own a treatment with pure cannabis. Her pain and general status got better and the tumor tissue decreased.
She delivered by C-section at 34 weeks a boy that presented in the first 24 h postpartum a withdrawal syndrome and intestinal invagination, requiring care in NICU and surgery with bowel resection.
Conclusion: Therefore, we can conclude that cannabis could be part of oncological treatment. No other case like this, as far as we know, has been previously reported.”

 “Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in women worldwide. In the last years, cannabinoids have gained attention in the clinical setting and clinical trials with cannabinoid-based preparations are underway. However, contradictory anti-tumour properties have also been reported. Thus, the elucidation of the molecular mechanisms behind their anti-tumour efficacy is crucial to better understand its therapeutic potential.
“Breast cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related death in women worldwide. In the last years, cannabinoids have gained attention in the clinical setting and clinical trials with cannabinoid-based preparations are underway. However, contradictory anti-tumour properties have also been reported. Thus, the elucidation of the molecular mechanisms behind their anti-tumour efficacy is crucial to better understand its therapeutic potential. “Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug. Advances in technology and scientific findings led to the discovery of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, that further led to the discovery of endogenous cannabinoids system consisting of G-protein-coupled receptors – cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 along with their ligands, mainly anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Endocannabinoid (EC) is shown to be a modulator not only for physiological functions but also for the immune system, endocrine network, and central nervous system. Medicinal research and meta-data analysis over the last few decades have shown a significant potential for both THC and cannabidiol (CBD) to exert palliative effects. People suffering from many forms of advanced stages of cancers undergo chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting followed by severe and chronic neuropathic pain and weight loss. THC and CBD exhibit effective analgesic, anxiolytic, and appetite-stimulating effect on patients suffering from cancer. Drugs currently available in the market to treat such chemotherapy-induced cancer-related ailments are Sativex (GW Pharmaceutical), Dronabinol (Unimed Pharmaceuticals), and Nabilone (Valeant Pharmaceuticals). Apart from exerting palliative effects, THC also shows promising role in the treatment of cancer growth, neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), and alcohol addiction and hence should be exploited for potential benefits. The current review discusses the nature and role of CB receptors, specific applications of cannabinoids, and major studies that have assessed the role of cannabinoids in cancer management.”
“Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug. Advances in technology and scientific findings led to the discovery of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, that further led to the discovery of endogenous cannabinoids system consisting of G-protein-coupled receptors – cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 along with their ligands, mainly anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Endocannabinoid (EC) is shown to be a modulator not only for physiological functions but also for the immune system, endocrine network, and central nervous system. Medicinal research and meta-data analysis over the last few decades have shown a significant potential for both THC and cannabidiol (CBD) to exert palliative effects. People suffering from many forms of advanced stages of cancers undergo chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting followed by severe and chronic neuropathic pain and weight loss. THC and CBD exhibit effective analgesic, anxiolytic, and appetite-stimulating effect on patients suffering from cancer. Drugs currently available in the market to treat such chemotherapy-induced cancer-related ailments are Sativex (GW Pharmaceutical), Dronabinol (Unimed Pharmaceuticals), and Nabilone (Valeant Pharmaceuticals). Apart from exerting palliative effects, THC also shows promising role in the treatment of cancer growth, neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), and alcohol addiction and hence should be exploited for potential benefits. The current review discusses the nature and role of CB receptors, specific applications of cannabinoids, and major studies that have assessed the role of cannabinoids in cancer management.” “Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown to slow cancer cell growth and is toxic to human glioblastoma cell lines. Thus, CBD could be an effective therapeutic for glioblastoma.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown to slow cancer cell growth and is toxic to human glioblastoma cell lines. Thus, CBD could be an effective therapeutic for glioblastoma.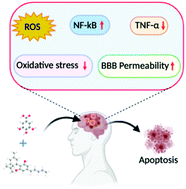
 “Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is an imbalance between the ER’s protein-folding load and capacity. It can be induced by various physiological conditions, activating the unfolded protein response to re-establish homeostasis, promoting cell survival. Under severe or chronic stress, apoptosis is induced. Normal cells generally do not experience continuous ER stress induction. The stressful conditions experienced in the tumour microenvironment facilitates chronic ER stress and UPR activation, which plays a pivotal role in tumour survival.
“Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is an imbalance between the ER’s protein-folding load and capacity. It can be induced by various physiological conditions, activating the unfolded protein response to re-establish homeostasis, promoting cell survival. Under severe or chronic stress, apoptosis is induced. Normal cells generally do not experience continuous ER stress induction. The stressful conditions experienced in the tumour microenvironment facilitates chronic ER stress and UPR activation, which plays a pivotal role in tumour survival. “Preclinical data suggest some cannabinoids may exert antitumour effects against glioblastoma (GBM). Safety and preliminary efficacy of nabiximols oromucosal cannabinoid spray plus dose-intense temozolomide (DIT) was evaluated in patients with first recurrence of GBM.
“Preclinical data suggest some cannabinoids may exert antitumour effects against glioblastoma (GBM). Safety and preliminary efficacy of nabiximols oromucosal cannabinoid spray plus dose-intense temozolomide (DIT) was evaluated in patients with first recurrence of GBM. “Glioblastomas (GBMs) are aggressive brain tumors with frequent genetic alterations in TP53 and PTEN tumor suppressor genes rendering resistance to standard chemotherapeutics. Cannabinoid type 1 and 2 (CB1/CB2) receptor expression in GBMs and antitumor activity of cannabinoids in glioma cells and animal models, raised promises for a targeted treatment of these tumors. The susceptibility of human glioma cells to CB2-agonists and their mechanism of action are not fully elucidated. We determined CB1 and CB2 expression in 14 low-grade and 21 high-grade tumor biopsies, GBM-derived primary cultures and established cell lines. The non-selective CB receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 (but not its inactive enantiomer) or the CB2-selective agonist JWH133 induced apoptosis in patient-derived glioma cultures and five established glioma cell lines despite p53 and/or PTEN deficiency. Growth inhibitory efficacy of cannabinoids correlated with CB1/CB2 expression (EC50 WIN55,212-2: 7.36-15.70 µM, JWH133: 12.15-143.20 µM). Treatment with WIN55,212-2 or JWH133 led to activation of the apoptotic mitochondrial pathway and DNA fragmentation. Synthetic cannabinoid action was associated with the induction of autophagy and knockdown of autophagy genes augmented cannabinoid-induced apoptotic cell death. The high susceptibility of human glioblastoma cells to synthetic cannabinoids, despite genetic defects contributing to apoptosis resistance, makes cannabinoids promising anti-glioma therapeutics.”
“Glioblastomas (GBMs) are aggressive brain tumors with frequent genetic alterations in TP53 and PTEN tumor suppressor genes rendering resistance to standard chemotherapeutics. Cannabinoid type 1 and 2 (CB1/CB2) receptor expression in GBMs and antitumor activity of cannabinoids in glioma cells and animal models, raised promises for a targeted treatment of these tumors. The susceptibility of human glioma cells to CB2-agonists and their mechanism of action are not fully elucidated. We determined CB1 and CB2 expression in 14 low-grade and 21 high-grade tumor biopsies, GBM-derived primary cultures and established cell lines. The non-selective CB receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 (but not its inactive enantiomer) or the CB2-selective agonist JWH133 induced apoptosis in patient-derived glioma cultures and five established glioma cell lines despite p53 and/or PTEN deficiency. Growth inhibitory efficacy of cannabinoids correlated with CB1/CB2 expression (EC50 WIN55,212-2: 7.36-15.70 µM, JWH133: 12.15-143.20 µM). Treatment with WIN55,212-2 or JWH133 led to activation of the apoptotic mitochondrial pathway and DNA fragmentation. Synthetic cannabinoid action was associated with the induction of autophagy and knockdown of autophagy genes augmented cannabinoid-induced apoptotic cell death. The high susceptibility of human glioblastoma cells to synthetic cannabinoids, despite genetic defects contributing to apoptosis resistance, makes cannabinoids promising anti-glioma therapeutics.”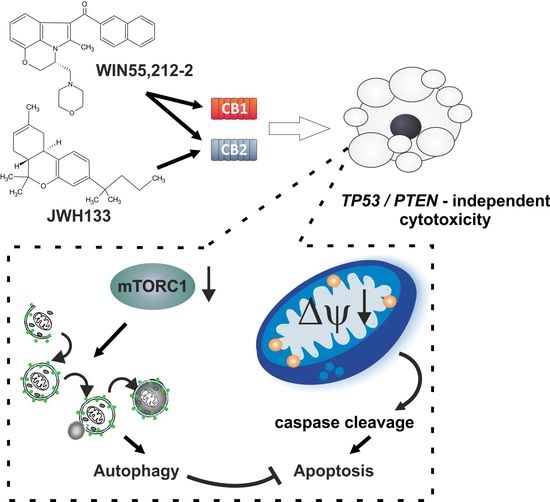
 “Glioblastoma is the most aggressive cancer among primary brain tumours. As with other cancers, the incidence of glioblastoma is increasing; despite modern therapies, the overall mean survival of patients post-diagnosis averages around 16 months, a figure that has not changed in many years. Cannabigerol (CBG) has only recently been reported to prevent the progression of certain carcinomas and has not yet been studied in glioblastoma. Here, we have compared the cytotoxic, apoptotic, and anti-invasive effects of the purified natural cannabinoid CBG together with CBD and THC on established differentiated glioblastoma tumour cells and glioblastoma stem cells. CBG and THC reduced the viability of both types of cells to a similar extent, whereas combining CBD with CBG was more efficient than with THC. CBD and CBG, both alone and in combination, induced caspase-dependent cell apoptosis, and there was no additive THC effect. Of note, CBG inhibited glioblastoma invasion in a similar manner to CBD and the chemotherapeutic temozolomide. We have demonstrated that THC has little added value in combined-cannabinoid glioblastoma treatment, suggesting that this psychotropic cannabinoid should be replaced with CBG in future clinical studies of glioblastoma therapy.”
“Glioblastoma is the most aggressive cancer among primary brain tumours. As with other cancers, the incidence of glioblastoma is increasing; despite modern therapies, the overall mean survival of patients post-diagnosis averages around 16 months, a figure that has not changed in many years. Cannabigerol (CBG) has only recently been reported to prevent the progression of certain carcinomas and has not yet been studied in glioblastoma. Here, we have compared the cytotoxic, apoptotic, and anti-invasive effects of the purified natural cannabinoid CBG together with CBD and THC on established differentiated glioblastoma tumour cells and glioblastoma stem cells. CBG and THC reduced the viability of both types of cells to a similar extent, whereas combining CBD with CBG was more efficient than with THC. CBD and CBG, both alone and in combination, induced caspase-dependent cell apoptosis, and there was no additive THC effect. Of note, CBG inhibited glioblastoma invasion in a similar manner to CBD and the chemotherapeutic temozolomide. We have demonstrated that THC has little added value in combined-cannabinoid glioblastoma treatment, suggesting that this psychotropic cannabinoid should be replaced with CBG in future clinical studies of glioblastoma therapy.” “Background: Breast Cancer (BC), a common death-causing disease and the deadliest cancer next to lung cancer, is characterized by an abnormal growth of cells in the tissues of the breast. BC chemotherapy is marked by targeting the activities of some receptors such as Estrogen Receptor alpha (ER-α). At present, one of the most commonly used and approved marketed therapeutic drug for BC is tamoxifen. Despite the short term success of tamoxifen usage, its long time treatment has been associated with significant side effects. Therefore, there is a pressing need for the development of novel anti-estrogens for the prevention and treatment of BC.
“Background: Breast Cancer (BC), a common death-causing disease and the deadliest cancer next to lung cancer, is characterized by an abnormal growth of cells in the tissues of the breast. BC chemotherapy is marked by targeting the activities of some receptors such as Estrogen Receptor alpha (ER-α). At present, one of the most commonly used and approved marketed therapeutic drug for BC is tamoxifen. Despite the short term success of tamoxifen usage, its long time treatment has been associated with significant side effects. Therefore, there is a pressing need for the development of novel anti-estrogens for the prevention and treatment of BC.