 “Pain prevalence among adults in the United States has increased 25% over the past two decades, resulting in high health-care costs and impacts to patient quality of life. In the last 30 years, our understanding of pain circuits and (intra)cellular mechanisms has grown exponentially, but this understanding has not yet resulted in improved therapies. Options for pain management are limited. Many analgesics have poor efficacy and are accompanied by severe side effects such as addiction, resulting in a devastating opioid abuse and overdose epidemic. These problems have encouraged scientists to identify novel molecular targets and develop alternative pain therapeutics.
“Pain prevalence among adults in the United States has increased 25% over the past two decades, resulting in high health-care costs and impacts to patient quality of life. In the last 30 years, our understanding of pain circuits and (intra)cellular mechanisms has grown exponentially, but this understanding has not yet resulted in improved therapies. Options for pain management are limited. Many analgesics have poor efficacy and are accompanied by severe side effects such as addiction, resulting in a devastating opioid abuse and overdose epidemic. These problems have encouraged scientists to identify novel molecular targets and develop alternative pain therapeutics.
Increasing preclinical and clinical evidence suggests that cannabis has several beneficial pharmacological activities, including pain relief.
Cannabis sativa contains more than 500 chemical compounds, with two principle phytocannabinoids, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). Beyond phytocannabinoids, more than 150 terpenes have been identified in different cannabis chemovars. Although the predominant cannabinoids, Δ9-THC and CBD, are thought to be the primary medicinal compounds, terpenes including the monoterpenes β-myrcene, α-pinene, limonene, and linalool, as well as the sesquiterpenes β-caryophyllene and α-humulene may contribute to many pharmacological properties of cannabis, including anti-inflammatory and antinociceptive effects.
The aim of this review is to summarize our current knowledge about terpene compounds in cannabis and to analyze the available scientific evidence for a role of cannabis-derived terpenes in modern pain management.
SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: Decades of research have improved our knowledge of cannabis polypharmacy and contributing phytochemicals, including terpenes. Reform of the legal status for cannabis possession and increased availability (medicinal and recreational) have resulted in cannabis use to combat the increasing prevalence of pain and may help to address the opioid crisis. Better understanding of the pharmacological effects of cannabis and its active components, including terpenes, may assist in identifying new therapeutic approaches and optimizing the use of cannabis and/or terpenes as analgesic agents.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34663685/
“Cannabis sativa has been used for medical, recreational, and spiritual purposes for thousands of years. Modern scientific studies have provided increasing amounts of preclinical and clinical evidence about its beneficial pharmacological effects, including pain relief. Recent changes in the legislation of cannabis usage and possession have resulted in cannabis-based products becoming widely used alternatives in fighting against many different illnesses. Medical marijuana has been applied to treat a host of indications, but the most frequent, and evidence-backed indication, is pain. Overall, cannabis terpenes have a high potential for pain management, alone or as adjunctive therapeutics, and are attractive compounds for the development of terpene-based analgesics given their generally-recognized-as-safe status with low side effect and toxicity profiles.”

 “While states are implementing policies to legalize cannabis for medical or recreational purposes, it remains a Schedule 1 controlled substance with no medical uses according to US federal law. The perception of cannabis depends on social and cultural norms that impact political institutions involved in implementing policy. Because of negative social constructions, such as the “gateway hypothesis,” legalization of cannabis has been slow and contentious.
“While states are implementing policies to legalize cannabis for medical or recreational purposes, it remains a Schedule 1 controlled substance with no medical uses according to US federal law. The perception of cannabis depends on social and cultural norms that impact political institutions involved in implementing policy. Because of negative social constructions, such as the “gateway hypothesis,” legalization of cannabis has been slow and contentious. 
 “The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
“The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.  “Objectives:
“Objectives:  “Introduction:
“Introduction: “Objectives: This article presents findings from a large prospective examination of Canadian medical cannabis patients, with a focus on the impacts of cannabis on prescription opioid use and quality of life over a 6-month period.
“Objectives: This article presents findings from a large prospective examination of Canadian medical cannabis patients, with a focus on the impacts of cannabis on prescription opioid use and quality of life over a 6-month period.
 “Although studied in a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the efficacy of medical cannabis (MC) for chronic pain remains controversial. Using an alternative approach, this multicenter, questionnaire-based prospective cohort was aimed to assess the long-term effects of MC on chronic pain of various etiologies and to identify predictors for MC treatment success.
“Although studied in a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the efficacy of medical cannabis (MC) for chronic pain remains controversial. Using an alternative approach, this multicenter, questionnaire-based prospective cohort was aimed to assess the long-term effects of MC on chronic pain of various etiologies and to identify predictors for MC treatment success.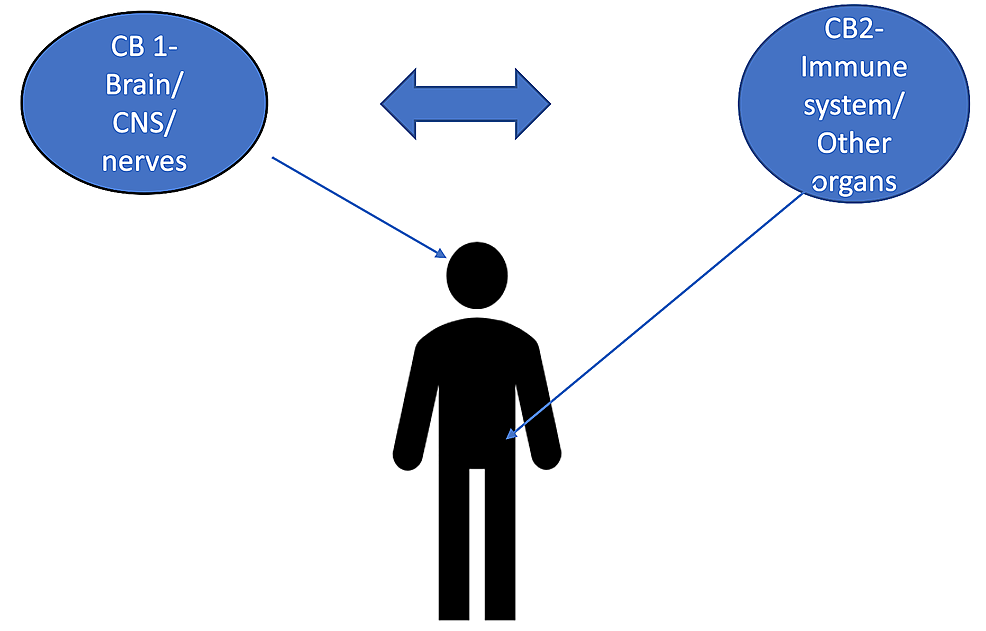 “The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches.
“The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches.