“Cannabinoid-based medications possess unique multimodal analgesic mechanisms of action, modulating diverse pain targets.
Cannabinoids are classified based on their origin into three categories: endocannabinoids (present endogenously in human tissues), phytocannabinoids (plant derived) and synthetic cannabinoids (pharmaceutical). Cannabinoids exert an analgesic effect, peculiarly in hyperalgesia, neuropathic pain and inflammatory states.
Endocannabinoids are released on demand from postsynaptic terminals and travels retrograde to stimulate cannabinoids receptors on presynaptic terminals, inhibiting the release of excitatory neurotransmitters. Cannabinoids (endogenous and phytocannabinoids) produce analgesia by interacting with cannabinoids receptors type 1 and 2 (CB1 and CB2), as well as putative non-CB1/CB2 receptors; G protein-coupled receptor 55, and transient receptor potential vanilloid type-1. Moreover, they modulate multiple peripheral, spinal and supraspinal nociception pathways.
Cannabinoids-opioids cross-modulation and synergy contribute significantly to tolerance and antinociceptive effects of cannabinoids. This narrative review evaluates cannabinoids’ diverse mechanisms of action as it pertains to nociception modulation relevant to the practice of anesthesiologists and pain medicine physicians.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33239391/
https://rapm.bmj.com/content/early/2020/11/24/rapm-2020-102114

 “Chronic pelvic pain affects women across all demographics. Its management is complex and requires a multimodal approach.
“Chronic pelvic pain affects women across all demographics. Its management is complex and requires a multimodal approach. “Although studied in a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the efficacy of medical cannabis (MC) for chronic pain remains controversial. Using an alternative approach, this multicenter, questionnaire-based prospective cohort was aimed to assess the long-term effects of MC on chronic pain of various etiologies and to identify predictors for MC treatment success.
“Although studied in a few randomized controlled trials (RCTs), the efficacy of medical cannabis (MC) for chronic pain remains controversial. Using an alternative approach, this multicenter, questionnaire-based prospective cohort was aimed to assess the long-term effects of MC on chronic pain of various etiologies and to identify predictors for MC treatment success.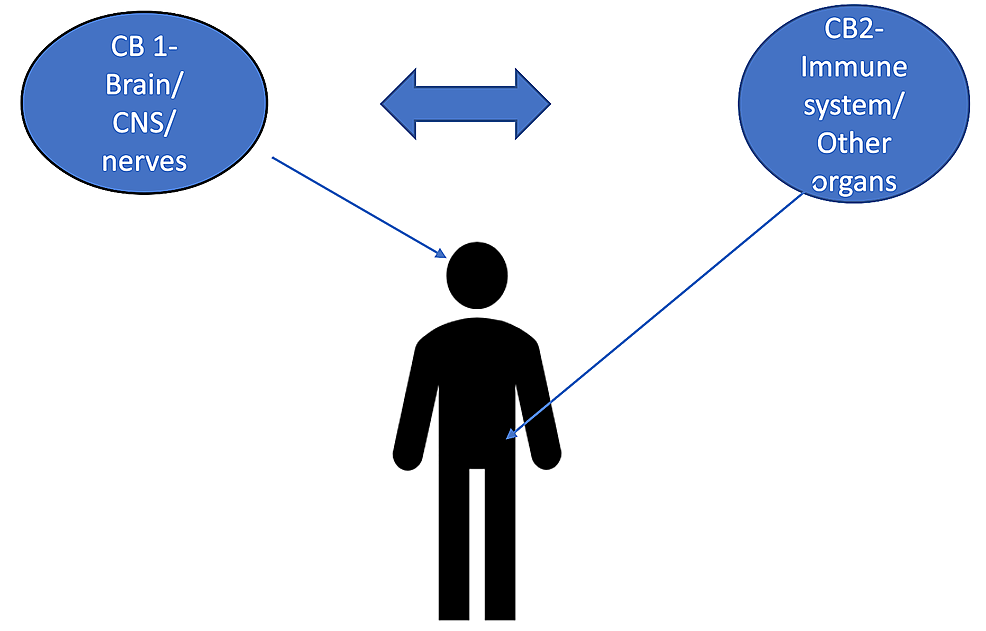 “The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches.
“The burden of chronic pain has affected many individuals leading to distress and discomfort, alongside numerous side effects with conventional therapeutic approaches. “Cannabinoids help in pain treatment through their action on CB1 and CB2 receptors.
“Cannabinoids help in pain treatment through their action on CB1 and CB2 receptors. “Chronic pain can be recurrent or constant pain that lasts for longer than 3 months and can result in disability, suffering, and a physical disturbance. Related to the complex nature of chronic pain, treatments have a pharmacological and non-pharmacological approach.
“Chronic pain can be recurrent or constant pain that lasts for longer than 3 months and can result in disability, suffering, and a physical disturbance. Related to the complex nature of chronic pain, treatments have a pharmacological and non-pharmacological approach. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is reported to produce pain relief, but the clinically relevant cellular and molecular mechanisms remain uncertain.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is reported to produce pain relief, but the clinically relevant cellular and molecular mechanisms remain uncertain. “Cannabis exposure is becoming more common in older age but little is known about how it is associated with brain health in this population.
“Cannabis exposure is becoming more common in older age but little is known about how it is associated with brain health in this population. “To determine if cannabis may be used as an alternative or adjunct treatment for intermittent and chronic prescription opioid users.
“To determine if cannabis may be used as an alternative or adjunct treatment for intermittent and chronic prescription opioid users. “Recent years have seen an increase in the adoption of cannabinoid medicines, which have demonstrated effectiveness for the treatment of chronic pain.
“Recent years have seen an increase in the adoption of cannabinoid medicines, which have demonstrated effectiveness for the treatment of chronic pain.