 “”Medicinal cannabis” is defined as the use of cannabis-based products for the treatment of an illness. Investigations of cannabis compounds in psychiatric and neurological illnesses primarily focus on the major cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), which are hypothesised to benefit multiple illnesses manifesting cognitive impairment, neurodegeneration and neuro-inflammation, as well as chronic pain, epilepsy and post-traumatic stress disorder, respectively.
“”Medicinal cannabis” is defined as the use of cannabis-based products for the treatment of an illness. Investigations of cannabis compounds in psychiatric and neurological illnesses primarily focus on the major cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC), which are hypothesised to benefit multiple illnesses manifesting cognitive impairment, neurodegeneration and neuro-inflammation, as well as chronic pain, epilepsy and post-traumatic stress disorder, respectively.
The cannabis plant contains >500 compounds, including terpenes responsible for the flavour and fragrance profiles of plants. Recently, research has begun providing evidence on the potential use of certain plant-derived terpenes in modern medicine, demonstrating anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective effects of these compounds.
This review examined the effects of two key terpenes, pinene and linalool, on parameters relevant to neurological and psychiatric disorders, highlighting gaps in the literature and recommendations for future research into terpene therapeutics.
Overall, evidence is mostly limited to preclinical studies and well-designed clinical trials are lacking. Nevertheless, existing data suggests that pinene and linalool are relevant candidates for further investigation as novel medicines for illnesses, including stroke, ischemia, inflammatory and neuropathic pain (including migraine), cognitive impairment (relevant to Alzheimer’s disease and ageing), insomnia, anxiety, and depression.
Linalool and pinene influence multiple neurotransmitter, inflammatory and neurotrophic signals as well as behaviour, demonstrating psycho-activity (albeit non-intoxicating). Optimising the phytochemical profile of cannabis chemovars to yield therapeutic levels of beneficial terpenes and cannabinoids, such as linalool, pinene and CBD, could present a unique opportunity to discover novel medicines to treat psychiatric and neurological illnesses; however, further research is needed.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34512404/
“Overall, it appears that the importance of the terpene profile of plants to humans extends further than mere olfactory and gustatory delight. Rather, these compounds have the potential for use as treatments for serious chronic neurological and psychiatric illnesses.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.583211/full
 “This study consists of a brief psychological intervention, which uses Self-Regulation Therapy (SRT, procedure based on suggestion and classical conditioning), to improve coping with stress and emotionality by reproducing the positive effects of illegal drugs: cannabis, cocaine, ecstasy.
“This study consists of a brief psychological intervention, which uses Self-Regulation Therapy (SRT, procedure based on suggestion and classical conditioning), to improve coping with stress and emotionality by reproducing the positive effects of illegal drugs: cannabis, cocaine, ecstasy.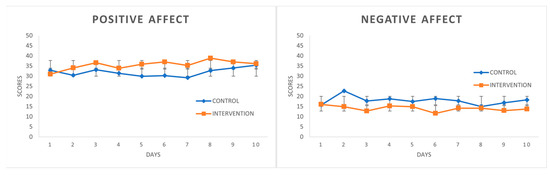

 “Decline in cognitive performance, an aspect of the normal aging process, is influenced by the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) signaling diminishes with advancing age in specific brain regions that regulate learning and memory and abolishing CB1 receptor signaling accelerates cognitive aging in mice.
“Decline in cognitive performance, an aspect of the normal aging process, is influenced by the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) signaling diminishes with advancing age in specific brain regions that regulate learning and memory and abolishing CB1 receptor signaling accelerates cognitive aging in mice.  “”Medicinal cannabis” is defined as the use of cannabis-based products for the treatment of an illness. Investigations of cannabis compounds in psychiatric and neurological illnesses primarily focus on the major cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ
“”Medicinal cannabis” is defined as the use of cannabis-based products for the treatment of an illness. Investigations of cannabis compounds in psychiatric and neurological illnesses primarily focus on the major cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ “The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
“The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.  “Introduction:
“Introduction:  “Background: Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is characterized by progressive deterioration in behaviors, executive function and/or language. The behavioral variant (Bv) is characterized by disinhibition and obsessive/compulsive behaviors. These symptoms are sometimes resistant to medications. This series examines patients suffering with treatment-resistant Bv-FTD who were prescribed cannabinoid and related compounds for other indications.
“Background: Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is characterized by progressive deterioration in behaviors, executive function and/or language. The behavioral variant (Bv) is characterized by disinhibition and obsessive/compulsive behaviors. These symptoms are sometimes resistant to medications. This series examines patients suffering with treatment-resistant Bv-FTD who were prescribed cannabinoid and related compounds for other indications. “The aberrant accumulation of disease-specific protein aggregates accompanying cognitive decline is a pathological hallmark of age-associated neurological disorders, also termed as proteinopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis.
“The aberrant accumulation of disease-specific protein aggregates accompanying cognitive decline is a pathological hallmark of age-associated neurological disorders, also termed as proteinopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis. “Background: Older adults (≥50 years) represent the fastest-growing population of people who use cannabis, potentially due to the increasing promotion of cannabis as medicine by dispensaries and cannabis websites. Given healthy aging and cannabis use are both associated with cognitive decline, it is important to establish the effects of cannabis on cognition in healthy aging.
“Background: Older adults (≥50 years) represent the fastest-growing population of people who use cannabis, potentially due to the increasing promotion of cannabis as medicine by dispensaries and cannabis websites. Given healthy aging and cannabis use are both associated with cognitive decline, it is important to establish the effects of cannabis on cognition in healthy aging. “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a central nervous system disease characterized by dementia, which has now become a major threat to global health.
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a central nervous system disease characterized by dementia, which has now become a major threat to global health. “Background/objectives: Use of cannabis is increasing in a variety of populations in the United States; however, few investigations about how and for what reasons cannabis is used in older populations exist.
“Background/objectives: Use of cannabis is increasing in a variety of populations in the United States; however, few investigations about how and for what reasons cannabis is used in older populations exist.