“Background: Little is known about cannabis use for insomnia in individuals with depression, anxiety, and comorbid depression and anxiety. To develop a better understanding of distinct profiles of cannabis use for insomnia management, a retrospective cohort study was conducted on a large naturalistic sample.
Methods: Data were collected using the medicinal cannabis tracking app, Strainprint®, which allows users to monitor and track cannabis use for therapeutic purposes. The current study examined users managing insomnia symptoms in depression (n = 100), anxiety (n = 463), and comorbid depression and anxiety (n = 114), for a total of 8476 recorded sessions. Inferential analyses used linear mixed effects modeling to examine self-perceived improvement across demographic variables and cannabis product variables.
Results: Overall, cannabis was perceived to be efficacious across all groups, regardless of age and gender. Dried flower and oral oil were reported as the most used and most efficacious product forms. In the depression group, all strains were perceived to be efficacious and comparisons between strains revealed indica-dominant (Mdiff = 1.81, 95% CI 1.26-2.36, Padj < .001), indica hybrid (Mdiff = 1.34, 95% CI 0.46-2.22, Padj = .045), and sativa-dominant (Mdiff = 1.83, 95% CI 0.68-2.99, Padj = .028) strains were significantly more efficacious than CBD-dominant strains. In anxiety and comorbid conditions, all strain categories were perceived to be efficacious with no significant differences between strains.
Conclusions: In terms of perceptions, individuals with depression, anxiety, and both conditions who use cannabis for insomnia report significant improvements in symptom severity after cannabis use. The current study highlights the need for placebo-controlled trials investigating symptom improvement and the safety of cannabinoids for sleep in individuals with mood and anxiety disorders.”

 “Anxiety and depressive disorders are highly prevalent. Patients are increasingly using medicinal cannabis products to treat these disorders, but little is known about the effects of medicinal cannabis use on symptoms of anxiety and depression.
“Anxiety and depressive disorders are highly prevalent. Patients are increasingly using medicinal cannabis products to treat these disorders, but little is known about the effects of medicinal cannabis use on symptoms of anxiety and depression. 
 “The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.
“The Endocannabinoid System (ECS) is primarily responsible for maintaining homeostasis, a balance in internal environment (temperature, mood, and immune system) and energy input and output in living, biological systems.  “Importance:
“Importance: 

 “The potential therapeutic use of some Cannabis sativa plant compounds has been attracting great interest, especially for managing neuropsychiatric disorders due to the relative lack of efficacy of the current treatments.
“The potential therapeutic use of some Cannabis sativa plant compounds has been attracting great interest, especially for managing neuropsychiatric disorders due to the relative lack of efficacy of the current treatments.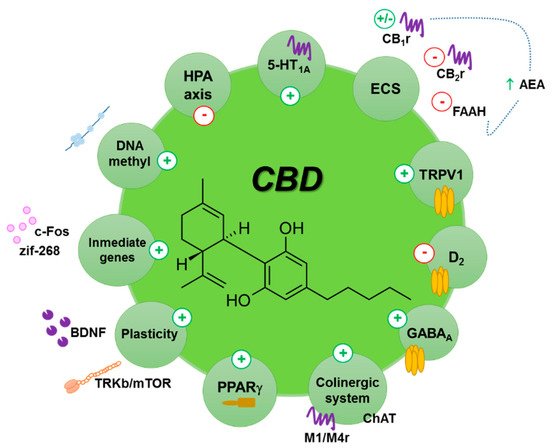
 “Anxiety disorders in young people are frequently comorbid with other mental disorders and respond unsatisfactorily to first-line treatment in many cases.
“Anxiety disorders in young people are frequently comorbid with other mental disorders and respond unsatisfactorily to first-line treatment in many cases.