 “Healthy aging includes freedom from disease, ability to engage in physical activity, and maintenance of cognitive skills for which diet is a major lifestyle factor. Aging, diet, and health are at the forefront of well-being for the growing population of older adults with the caveat of reducing and controlling pain. Obesity and diabetes risk increase in frequency in adults, and exercise is encouraged to control weight, reduce risk of type II diabetes, and maintain muscle mass and mobility.
“Healthy aging includes freedom from disease, ability to engage in physical activity, and maintenance of cognitive skills for which diet is a major lifestyle factor. Aging, diet, and health are at the forefront of well-being for the growing population of older adults with the caveat of reducing and controlling pain. Obesity and diabetes risk increase in frequency in adults, and exercise is encouraged to control weight, reduce risk of type II diabetes, and maintain muscle mass and mobility.
One area of research that appears to integrate many aspects of healthy aging is focused on understanding the endocannabinoid system (ECS) because of its role in systemic energy metabolism, inflammation, pain, and brain biology. Physical activity is important for maintaining health throughout the life cycle. The benefits of exercise facilitate macronutrient use, promote organ health, and augment the maintenance of metabolic activity and physiological functions. One outcome of routine exercise is a generalized well-being, and perhaps, this is linked to the ECS.
The purpose of this review is to briefly present the current knowledge of key components of the ECS that contribute to appetite and influence systemic energy metabolism, and dietary factors that alter the responses of ligand binding and activation of cannabinoidreceptors and its role in the brain. Herein, the objectives are to (1) explain the role of the ECS in the body, (2) describe the relationship between dietary polyunsaturated fatty acids and macronutrient intake and systemic metabolism, and (3) present areas of promising research where exercise induces endocannabinoid production in the brain to benefit well-being. There are many gaps in the knowledge of how the ECS participates in controlling pain through exercise; however, emerging research will reveal key relationships to understand this system in the brain and body.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31280882
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S027153171930572X?via%3Dihub
 “Confident relationships between diabetes and liver damage have previously been established.
“Confident relationships between diabetes and liver damage have previously been established.
 “Endocannabinoid system consists of
“Endocannabinoid system consists of 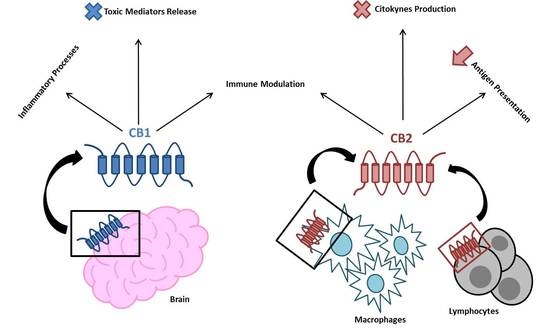
 “The endocannabinoid (eCB) system, i.e. the receptors that respond to the psychoactive component of
“The endocannabinoid (eCB) system, i.e. the receptors that respond to the psychoactive component of 
 “The biological effects of endocannabinoid system are mediated by two types of receptors,
“The biological effects of endocannabinoid system are mediated by two types of receptors,  “Obese individuals are more likely to show insulin resistance (IR). However, limited population studies on
“Obese individuals are more likely to show insulin resistance (IR). However, limited population studies on 
 “The
“The  “Healthy aging includes freedom from disease, ability to engage in physical activity, and maintenance of cognitive skills for which diet is a major lifestyle factor. Aging, diet, and health are at the forefront of well-being for the growing population of older adults with the caveat of reducing and controlling pain. Obesity and diabetes risk increase in frequency in adults, and exercise is encouraged to control weight, reduce risk of type II diabetes, and maintain muscle mass and mobility.
“Healthy aging includes freedom from disease, ability to engage in physical activity, and maintenance of cognitive skills for which diet is a major lifestyle factor. Aging, diet, and health are at the forefront of well-being for the growing population of older adults with the caveat of reducing and controlling pain. Obesity and diabetes risk increase in frequency in adults, and exercise is encouraged to control weight, reduce risk of type II diabetes, and maintain muscle mass and mobility.