Methods: Semistructured telephone interviews were conducted in a convenience sample of individuals (n = 24) with physician-confirmed oncologic diagnoses and state/district authorization to use MC (Arizona, California, Florida, Illinois, Massachusetts, Oregon, New York, and Washington, DC) from April 2017 to March 2019. Standard qualitative techniques were used to assess the degree of MC-related health care oversight, MC practices, and key information sources.
Results: Among 24 participants (median age, 57 years; range, 30-71 years; 16 women [67%]), MC certifications were typically issued by a professional new to a patient’s care after a brief, perfunctory consultation. Patients disclosed MCuse to their established medical teams but received little medical advice about whether and how to use MC. Patients with cancer used MC products as multipurpose symptom management and as cancer-directed therapy, sometimes in lieu of standard-of-care treatments. Personal experimentation, including methodical self-monitoring, was an important source of MC know-how. Absent formal advice from medical professionals, patients relied on nonmedical sources for MC information.
Conclusions: Patients with cancer used MC with minimal medical oversight. Most received MC certifications through brief meetings with unfamiliar professionals. Participants desired but were often unable to access high-quality clinical information about MC from their established medical teams. Because many patients are committed to using MC, a product sustained by a growing industry, medical providers should familiarize themselves with the existing data for MM and its limitations to address a poorly met clinical need.”
“Notably, oncology patients reported using medical cannabis (MC) for symptom management and as cancer‐directed therapy, sometimes instead of traditional treatments.”
 “Providers need to be better equipped to discuss medical cannabis with patients even if they are not willing to prescribe it. The oncology community would be well served to ensure that providers are aware of existing cannabis research and are able to incorporate it into their communications with patients instead of leaving patients to figure out medical cannabis on their own.”
“Providers need to be better equipped to discuss medical cannabis with patients even if they are not willing to prescribe it. The oncology community would be well served to ensure that providers are aware of existing cannabis research and are able to incorporate it into their communications with patients instead of leaving patients to figure out medical cannabis on their own.”
 “In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”
“In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”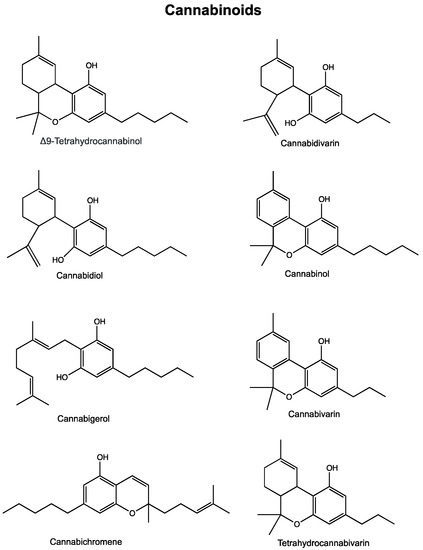
 “Astrocytomas, the most prevalent primary brain tumors, can be divided by histology and malignancy levels into four following types: pilocytic astrocytoma (grade I), diffuse fibrillary astrocytoma (grade II), anaplastic astrocytoma (grade III), and glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV). For high grade astrocytomas (grade III and grade IV), blood vessels formation is considered as the most important property.
“Astrocytomas, the most prevalent primary brain tumors, can be divided by histology and malignancy levels into four following types: pilocytic astrocytoma (grade I), diffuse fibrillary astrocytoma (grade II), anaplastic astrocytoma (grade III), and glioblastoma multiforme (grade IV). For high grade astrocytomas (grade III and grade IV), blood vessels formation is considered as the most important property. “The recent announcement of marijuana legalization in Canada spiked many discussions about potential health benefits of Cannabis sativa.
“The recent announcement of marijuana legalization in Canada spiked many discussions about potential health benefits of Cannabis sativa.  “Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequent and aggressive malignant brain tumour, with a poor prognosis despite available surgical and radio-chemotherapy, rising the necessity for searching alternative therapies. Several preclinical studies evaluating the efficacy of
“Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequent and aggressive malignant brain tumour, with a poor prognosis despite available surgical and radio-chemotherapy, rising the necessity for searching alternative therapies. Several preclinical studies evaluating the efficacy of  “The weak but noteworthy presence of (poly)phenols in hemp seeds has been long overshadowed by the essential polyunsaturated fatty acids and digestible proteins, considered responsible for their high nutritional benefits. Instead, lignanamides and their biosynthetic precursors, phenylamides, seem to display interesting and diverse biological activities only partially clarified in the last decades. Herein, negative mode HR-MS/MS techniques were applied to the chemical investigation of a (poly)phenol-rich fraction, obtained from hemp seeds after extraction/fractionation steps. This extract contained phenylpropanoid amides and their random oxidative coupling derivatives, lignanamides, which were the most abundant compounds and showed a high chemical diversity, deeply unraveled through high resolution tandem mass spectrometry (HR-MS/MS) tools.
“The weak but noteworthy presence of (poly)phenols in hemp seeds has been long overshadowed by the essential polyunsaturated fatty acids and digestible proteins, considered responsible for their high nutritional benefits. Instead, lignanamides and their biosynthetic precursors, phenylamides, seem to display interesting and diverse biological activities only partially clarified in the last decades. Herein, negative mode HR-MS/MS techniques were applied to the chemical investigation of a (poly)phenol-rich fraction, obtained from hemp seeds after extraction/fractionation steps. This extract contained phenylpropanoid amides and their random oxidative coupling derivatives, lignanamides, which were the most abundant compounds and showed a high chemical diversity, deeply unraveled through high resolution tandem mass spectrometry (HR-MS/MS) tools. “Radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy is the major treatment modality for human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). GBMs eventually relapse after treatment and the average survival of GBM patients is less than two years.
“Radiotherapy combined with chemotherapy is the major treatment modality for human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM). GBMs eventually relapse after treatment and the average survival of GBM patients is less than two years. “Cannabinoids are a group of structurally heterogeneous but pharmacologically related compounds, including plant-derived cannabinoids, synthetic substances and endogenous cannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol.
“Cannabinoids are a group of structurally heterogeneous but pharmacologically related compounds, including plant-derived cannabinoids, synthetic substances and endogenous cannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. “In recent years, the endocannabinoid system has received great interest as a potential therapeutic target in numerous pathological conditions.
“In recent years, the endocannabinoid system has received great interest as a potential therapeutic target in numerous pathological conditions.