“Despite the long history of cannabinoid use for medicinal and ritual purposes, an endogenous system of cannabinoid-controlled receptors, as well as their ligands and the enzymes that synthesise and degrade them, was only discovered in the 1990s. Since then, the endocannabinoid system has attracted widespread scientific interest regarding new pharmacological targets in cancer treatment among other reasons.
Meanwhile, extensive preclinical studies have shown that cannabinoids have an inhibitory effect on tumour cell proliferation, tumour invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, chemoresistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and induce tumour cell apoptosis and autophagy as well as immune response. Appropriate cannabinoid compounds could moreover be useful for cancer patients as potential combination partners with other chemotherapeutic agents to increase their efficacy while reducing unwanted side effects.
In addition to the direct activation of cannabinoid receptors through the exogenous application of corresponding agonists, another strategy is to activate these receptors by increasing the endocannabinoid levels at the corresponding pathological hotspots. Indeed, a number of studies accordingly showed an inhibitory effect of blockers of the endocannabinoid-degrading enzymes fatty acid amide hydrolase (FAAH) and monoacylglycerol lipase (MAGL) on tumour development and spread.
This review summarises the relevant preclinical studies with FAAH and MAGL inhibitors compared to studies with cannabinoids and provides an overview of the regulation of the endocannabinoid system in cancer.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34830856/
“Cannabinoids have been shown to suppress tumour cell proliferation, tumour invasion, metastasis, angiogenesis, chemoresistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition and to induce tumour cell apoptosis, autophagy and immune response. This review focuses on the current status of investigations on the impact of inhibitors of endocannabinoid-degrading enzymes on tumour growth and spread in preclinical oncology research.”
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/13/22/5701

 “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a composite cell-signaling system that allows endogenous cannabinoid ligands to control cell functions through the interaction with cannabinoid receptors. Modifications of the ECS might contribute to the pathogenesis of different diseases, including cancers. However, the use of these compounds as antitumor agents remains debatable.
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a composite cell-signaling system that allows endogenous cannabinoid ligands to control cell functions through the interaction with cannabinoid receptors. Modifications of the ECS might contribute to the pathogenesis of different diseases, including cancers. However, the use of these compounds as antitumor agents remains debatable. 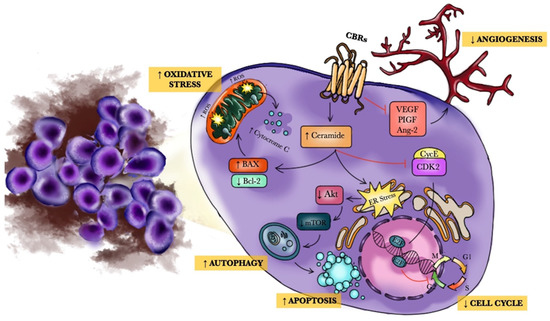
 “Anticancer activity of different phenols is documented, but underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Recently, we have shown that cannabidiol kills the cells of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) by a direct interaction with mitochondria, with their consequent dysfunction.
“Anticancer activity of different phenols is documented, but underlying mechanisms remain elusive. Recently, we have shown that cannabidiol kills the cells of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) by a direct interaction with mitochondria, with their consequent dysfunction.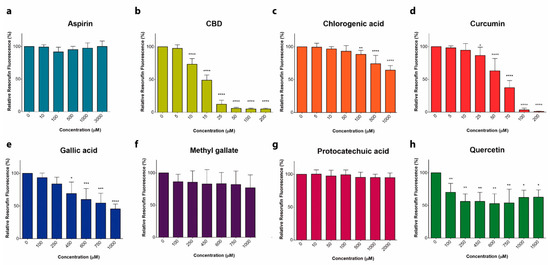
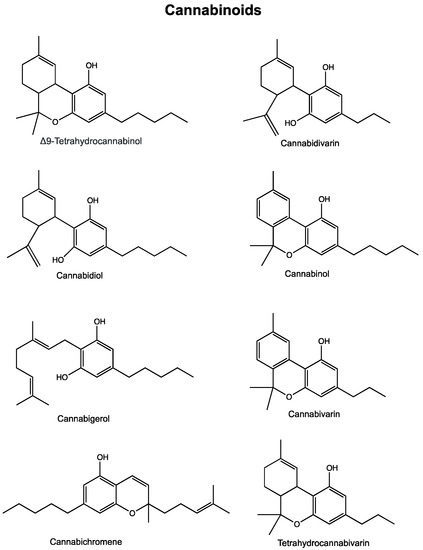
 “Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant.
“Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant. “In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”
“In recent years, and even more since its legalization in several jurisdictions, cannabis and the endocannabinoid system have received an increasing amount of interest related to their potential exploitation in clinical settings. Cannabinoids have been suggested and shown to be effective in the treatment of various conditions. In cancer, the endocannabinoid system is altered in numerous types of tumours and can relate to cancer prognosis and disease outcome. Additionally, cannabinoids display anticancer effects in several models by suppressing the proliferation, migration and/or invasion of cancer cells, as well as tumour angiogenesis. However, the therapeutic use of cannabinoids is currently limited to the treatment of symptoms and pain associated with chemotherapy, while their potential use as cytotoxic drugs in chemotherapy still requires validation in patients. Along with cannabinoids, cannabis contains several other compounds that have also been shown to exert anti-tumorigenic actions. The potential anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids, present in cannabis, are explored in this literature review.”