“In our previous study, we demonstrated the impact of overexpression of CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors and the inhibitory effect of endocannabinoids (2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) and Anandamide (AEA)) on canine (Canis lupus familiaris) and human (Homo sapiens) non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL) cell lines’ viability compared to cells treated with a vehicle.
The purpose of this study was to demonstrate the anti-cancer effects of the phytocannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and the synthetic cannabinoid WIN 55-212-22 (WIN) in canine and human lymphoma cell lines and to compare their inhibitory effect to that of endocannabinoids.
We used malignant canine B-cell lymphoma (BCL) (1771 and CLB-L1) and T-cell lymphoma (TCL) (CL-1) cell lines, and human BCL cell line (RAMOS). Our cell viability assay results demonstrated, compared to the controls, a biphasic effect (concentration range from 0.5 μM to 50 μM) with a significant reduction in cancer viability for both phytocannabinoids and the synthetic cannabinoid. However, the decrease in cell viability in the TCL CL-1 line was limited to CBD.
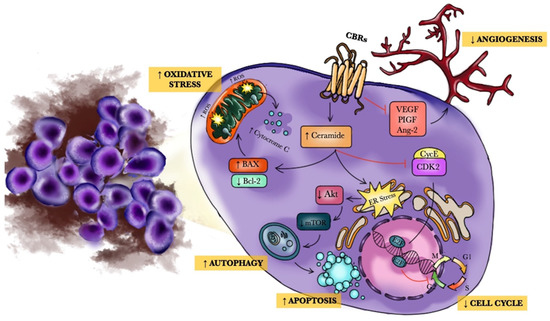
The results of the biochemical analysis using the 1771 BCL cell line revealed a significant increase in markers of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis, and a decrease in markers of mitochondrial function in cells treated with the exogenous cannabinoids compared to the control. Based on the IC50 values, CBD was the most potent phytocannabinoid in reducing lymphoma cell viability in 1771, Ramos, and CL-1. Previously, we demonstrated the endocannabinoid AEA to be more potent than 2-AG.
Our study suggests that future studies should use CBD and AEA for further cannabinoid testing as they might reduce tumor burden in malignant NHL of canines and humans.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/38672512/
“Our study demonstrated a significant moderate inhibitory effect of CBD, THC, and WIN on canine and human NHL cell viability. Our results also revealed that CBD, THC, and WIN decreased lymphoma cell viability because they increased oxidative stress, leading to downstream apoptosis.”



 “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a composite cell-signaling system that allows endogenous cannabinoid ligands to control cell functions through the interaction with cannabinoid receptors. Modifications of the ECS might contribute to the pathogenesis of different diseases, including cancers. However, the use of these compounds as antitumor agents remains debatable.
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is a composite cell-signaling system that allows endogenous cannabinoid ligands to control cell functions through the interaction with cannabinoid receptors. Modifications of the ECS might contribute to the pathogenesis of different diseases, including cancers. However, the use of these compounds as antitumor agents remains debatable.