 “In this study cannabidiol (CBD) was administered orally to determine its effects and mechanisms in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of multiple sclerosis (MS). We hypothesized that 75 mg/kg of oral CBD given for 5 days after initiation of disease would reduce EAE severity through suppression of either the early peripheral immune or late neuroimmune response.
“In this study cannabidiol (CBD) was administered orally to determine its effects and mechanisms in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of multiple sclerosis (MS). We hypothesized that 75 mg/kg of oral CBD given for 5 days after initiation of disease would reduce EAE severity through suppression of either the early peripheral immune or late neuroimmune response.
EAE was induced in C57BL/6 mice at two different magnitudes, and peripheral inflammatory and neuroinflammatory responses were measured at days 3, 10, and 18. Th1, Th17, Tc1, Tc17, Tregs, and myeloid derived suppressor cells (MDSC) were identified from the lymph nodes and spleens of each mouse to determine if CBD altered the suppressor cell or inflammatory cell populations in secondary lymphoid tissues. Additionally, neuroinflammation was identified in brain and spinal cord tissues using various immunohistochemical techniques and flow cytometry.
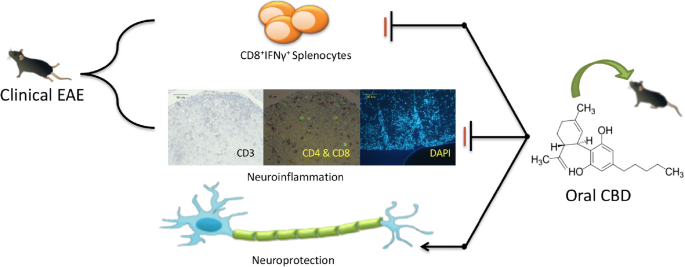
Early treatment of EAE with oral CBD reduced clinical disease at the day 18 timepoint which correlated with a significant decrease in the percentage of MOG35-55 specific IFN-γ producing CD8+ T cells in the spleen at day 10. Analysis of both T cell infiltration and lesion size within the spinal cord also showed a moderate reduction in neuroinflammation within the central nervous system (CNS).
These results provide evidence that oral CBD suppressed the peripheral immune response that precedes neuroinflammation; however, analysis of the neuroinflammatory endpoints also suggest that the modest reduction in neuroinflammation was only partially responsible for CBD’s neuroprotective capability. Graphical Abstract CBD was administered orally for the first 5 days following initiation of EAE. CBD attenuated clinical disease, and we found that CBD suppressed IFN-γ producing CD8+ T cells in the spleen at day 10. There was also modest suppression of neuroinflammation.
Together these data demonstrate that early, oral administration of CBD protected mice from disease, but the modest effects on neuroinflammation suggest other mechanisms participate in CBD’s neuroprotective effect in EAE.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32440886/
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11481-020-09917-8

 “The pathophysiological relevance of the endocannabinoid system has been widely demonstrated in a variety of diseases including cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic issues. Therefore, targeting the receptors and the endogenous machinery involved in this system can provide a successful therapeutic outcome.
“The pathophysiological relevance of the endocannabinoid system has been widely demonstrated in a variety of diseases including cancer, neurological disorders, and metabolic issues. Therefore, targeting the receptors and the endogenous machinery involved in this system can provide a successful therapeutic outcome. “The approval of 9-δ-tetrahydocannabinol (THC)+
“The approval of 9-δ-tetrahydocannabinol (THC)+ “The consistency, efficacy, and safety of cannabis-based medicines have been demonstrated in humans, leading to the approval of the first cannabis-based therapy to alleviate spasticity and pain associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). Indeed, the evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of
“The consistency, efficacy, and safety of cannabis-based medicines have been demonstrated in humans, leading to the approval of the first cannabis-based therapy to alleviate spasticity and pain associated with multiple sclerosis (MS). Indeed, the evidence supporting the therapeutic potential of  “Medicinal
“Medicinal 
 “To determine whether differences in disability status, spasticity severity, and spasticity duration at treatment start in patients with resistant multiple sclerosis (MS) spasticity might influence response to add-on tetrahydrocannabinol:
“To determine whether differences in disability status, spasticity severity, and spasticity duration at treatment start in patients with resistant multiple sclerosis (MS) spasticity might influence response to add-on tetrahydrocannabinol: “Cannabis sativa L. is an ancient medicinal plant wherefrom over 120 cannabinoids are extracted. In the past two decades, there has been increasing interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabis-based treatments for neurological disorders such as epilepsy, and there is now evidence for the medical use of cannabis and its effectiveness for a wide range of diseases.
“Cannabis sativa L. is an ancient medicinal plant wherefrom over 120 cannabinoids are extracted. In the past two decades, there has been increasing interest in the therapeutic potential of cannabis-based treatments for neurological disorders such as epilepsy, and there is now evidence for the medical use of cannabis and its effectiveness for a wide range of diseases.