 “Medical cannabis and individual cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), are receiving growing attention in both the media and the scientific literature. The Cannabis plant, however, produces over 100 different cannabinoids, and cannabigerol (CBG) serves as the precursor molecule for the most abundant phytocannabinoids.
“Medical cannabis and individual cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), are receiving growing attention in both the media and the scientific literature. The Cannabis plant, however, produces over 100 different cannabinoids, and cannabigerol (CBG) serves as the precursor molecule for the most abundant phytocannabinoids.
CBG exhibits affinity and activity characteristics between THC and CBD at the cannabinoid receptors, but appears to be unique in its interactions with alpha-2 adrenoceptors and 5-HT1A Studies indicate that CBG may have therapeutic potential in treating neurological disorders (e.g., Huntington’s Disease, Parkinson’s Disease, and multiple sclerosis), inflammatory bowel disease, as well as having antibacterial activity.
There is growing interest in the commercial use of this unregulated phytocannabinoid. This review focuses on the unique pharmacology of CBG, our current knowledge of its possible therapeutic utility, and its potential toxicological hazards.
Significance Statement Cannabigerol (CBG) is currently being marketed as a dietary supplement and, as with cannabidiol (CBD) before, many claims are being made about its benefits. Unlike CBD, however, little research has been performed on this unregulated molecule, and much of what is known warrants further investigation to identify potential areas of therapeutic uses and hazards.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33168643/
https://jpet.aspetjournals.org/content/early/2020/11/09/jpet.120.000340

 “The aberrant accumulation of disease-specific protein aggregates accompanying cognitive decline is a pathological hallmark of age-associated neurological disorders, also termed as proteinopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis.
“The aberrant accumulation of disease-specific protein aggregates accompanying cognitive decline is a pathological hallmark of age-associated neurological disorders, also termed as proteinopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown. “Current pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is symptomatic and palliative, with levodopa/carbidopa therapy remaining the prime treatment, and nevertheless, being unable to modulate the progression of the neurodegeneration. No available treatment for PD can enhance the patient’s life-quality by regressing this diseased state.
“Current pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is symptomatic and palliative, with levodopa/carbidopa therapy remaining the prime treatment, and nevertheless, being unable to modulate the progression of the neurodegeneration. No available treatment for PD can enhance the patient’s life-quality by regressing this diseased state.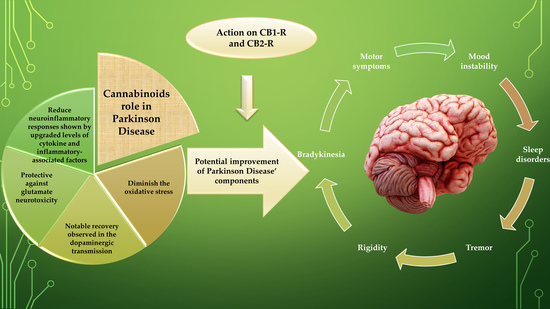
 “In the last few years research into Cannabis and its constituent phytocannabinoids has burgeoned, particularly in the potential application of novel cannabis phytochemicals for the treatment of diverse illnesses related to neurodegeneration and dementia, including Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and Huntington’s disease (HD). To date, these neurological diseases have mostly relied on symptomatological management. However, with an aging population globally, the search for more efficient and disease-modifying treatments that could delay or mitigate disease progression is imperative. In this context, this review aims to present a state of art in the research with cannabinoids and novel cannabinoid-based drug candidates that have been emerged as novel promising alternatives for drug development and innovation in the therapeutics of a number of diseases, especially those related to CNS-disturbance and impairment.”
“In the last few years research into Cannabis and its constituent phytocannabinoids has burgeoned, particularly in the potential application of novel cannabis phytochemicals for the treatment of diverse illnesses related to neurodegeneration and dementia, including Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and Huntington’s disease (HD). To date, these neurological diseases have mostly relied on symptomatological management. However, with an aging population globally, the search for more efficient and disease-modifying treatments that could delay or mitigate disease progression is imperative. In this context, this review aims to present a state of art in the research with cannabinoids and novel cannabinoid-based drug candidates that have been emerged as novel promising alternatives for drug development and innovation in the therapeutics of a number of diseases, especially those related to CNS-disturbance and impairment.” “Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is currently the most rapid growing neurodegenerative disease and over the past generation, its global burden has more than doubled. The onset of PD can arise due to environmental, sporadic or genetic factors. Nevertheless, most PD cases have an unknown etiology.
“Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is currently the most rapid growing neurodegenerative disease and over the past generation, its global burden has more than doubled. The onset of PD can arise due to environmental, sporadic or genetic factors. Nevertheless, most PD cases have an unknown etiology. “The antioxidant and CB2 receptor agonist properties of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (Δ9-THCV) afforded neuroprotection in experimental Parkinson’s disease (PD), whereas its CB1 receptor antagonist profile at doses lower than 5 mg/kg caused anti-hypokinetic effects.
“The antioxidant and CB2 receptor agonist properties of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (Δ9-THCV) afforded neuroprotection in experimental Parkinson’s disease (PD), whereas its CB1 receptor antagonist profile at doses lower than 5 mg/kg caused anti-hypokinetic effects. “Cannabis sativa, commonly known as marijuana, contains a pool of secondary plant metabolites with therapeutic effects.
“Cannabis sativa, commonly known as marijuana, contains a pool of secondary plant metabolites with therapeutic effects. “Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway with loss of substantia nigra pars compacta neurons and dopamine depletion. Various natural compounds showed protective actions against PD.
“Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopaminergic pathway with loss of substantia nigra pars compacta neurons and dopamine depletion. Various natural compounds showed protective actions against PD. “Generally, the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases are associated with advancing age, so they are usually diagnosed in late adulthood. A primary mechanism underlying the onset of neurodegenerative diseases is neuroinflammation. Based on this background, the concept of “neuroinflammaging” has emerged. In this deregulated neuroinflammatory process, a variety of immune cells participate, especially glial cells, proinflammatory cytokines, receptors, and subcellular organelles including mitochondria, which are mainly responsible for maintaining redox balance at the cellular level. Senescence and autophagic processes also play a crucial role in the neuroinflammatory disease associated with aging.
“Generally, the development and progression of neurodegenerative diseases are associated with advancing age, so they are usually diagnosed in late adulthood. A primary mechanism underlying the onset of neurodegenerative diseases is neuroinflammation. Based on this background, the concept of “neuroinflammaging” has emerged. In this deregulated neuroinflammatory process, a variety of immune cells participate, especially glial cells, proinflammatory cytokines, receptors, and subcellular organelles including mitochondria, which are mainly responsible for maintaining redox balance at the cellular level. Senescence and autophagic processes also play a crucial role in the neuroinflammatory disease associated with aging.