 “Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia Nigra pars compacta, leading to classical PD motor symptoms. Current therapies are purely symptomatic and do not modify disease progression.
“Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia Nigra pars compacta, leading to classical PD motor symptoms. Current therapies are purely symptomatic and do not modify disease progression.
Cannabidiol (CBD), one of the main phytocannabinoids identified in Cannabis Sativa, which exhibits a large spectrum of therapeutic properties, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects, suggesting its potential as disease-modifying agent for PD.
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effects of chronic treatment with CBD (10 mg/kg, i.p.) on PD-associated neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory processes, and motor deficits in the 6-hydroxydopamine model. Moreover, we investigated the potential mechanisms by which CBD exerted its effects in this model.
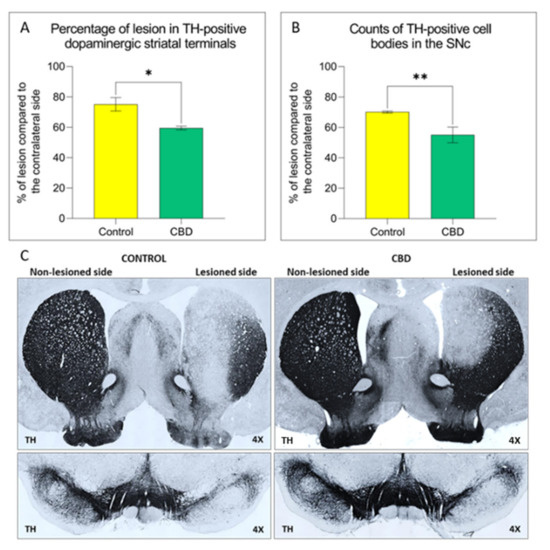
CBD-treated animals showed a reduction of nigrostriatal degeneration accompanied by a damping of the neuroinflammatory response and an improvement of motor performance. In particular, CBD exhibits a preferential action on astrocytes and activates the astrocytic transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1), thus, enhancing the endogenous neuroprotective response of ciliary neurotrophic factor (CNTF).
These results overall support the potential therapeutic utility of CBD in PD, as both neuroprotective and symptomatic agent.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34445626/
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/16/8920

 “Little is known about the patients’ view on treatment with medical cannabis (MC) for Parkinson’s disease (PD).
“Little is known about the patients’ view on treatment with medical cannabis (MC) for Parkinson’s disease (PD). “Medical cannabis and individual cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), are receiving growing attention in both the media and the scientific literature. The Cannabis plant, however, produces over 100 different cannabinoids, and cannabigerol (CBG) serves as the precursor molecule for the most abundant phytocannabinoids.
“Medical cannabis and individual cannabinoids, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), are receiving growing attention in both the media and the scientific literature. The Cannabis plant, however, produces over 100 different cannabinoids, and cannabigerol (CBG) serves as the precursor molecule for the most abundant phytocannabinoids. “The aberrant accumulation of disease-specific protein aggregates accompanying cognitive decline is a pathological hallmark of age-associated neurological disorders, also termed as proteinopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis.
“The aberrant accumulation of disease-specific protein aggregates accompanying cognitive decline is a pathological hallmark of age-associated neurological disorders, also termed as proteinopathies, including Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, Huntington’s disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and multiple sclerosis. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown.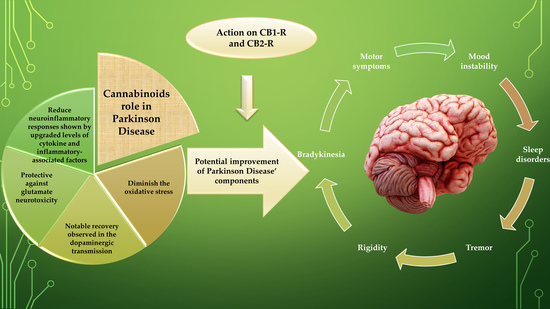
 “In the last few years research into Cannabis and its constituent phytocannabinoids has burgeoned, particularly in the potential application of novel cannabis phytochemicals for the treatment of diverse illnesses related to neurodegeneration and dementia, including Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and Huntington’s disease (HD). To date, these neurological diseases have mostly relied on symptomatological management. However, with an aging population globally, the search for more efficient and disease-modifying treatments that could delay or mitigate disease progression is imperative. In this context, this review aims to present a state of art in the research with cannabinoids and novel cannabinoid-based drug candidates that have been emerged as novel promising alternatives for drug development and innovation in the therapeutics of a number of diseases, especially those related to CNS-disturbance and impairment.”
“In the last few years research into Cannabis and its constituent phytocannabinoids has burgeoned, particularly in the potential application of novel cannabis phytochemicals for the treatment of diverse illnesses related to neurodegeneration and dementia, including Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and Huntington’s disease (HD). To date, these neurological diseases have mostly relied on symptomatological management. However, with an aging population globally, the search for more efficient and disease-modifying treatments that could delay or mitigate disease progression is imperative. In this context, this review aims to present a state of art in the research with cannabinoids and novel cannabinoid-based drug candidates that have been emerged as novel promising alternatives for drug development and innovation in the therapeutics of a number of diseases, especially those related to CNS-disturbance and impairment.” “Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is currently the most rapid growing neurodegenerative disease and over the past generation, its global burden has more than doubled. The onset of PD can arise due to environmental, sporadic or genetic factors. Nevertheless, most PD cases have an unknown etiology.
“Parkinson’s Disease (PD) is currently the most rapid growing neurodegenerative disease and over the past generation, its global burden has more than doubled. The onset of PD can arise due to environmental, sporadic or genetic factors. Nevertheless, most PD cases have an unknown etiology. “The antioxidant and CB2 receptor agonist properties of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (Δ9-THCV) afforded neuroprotection in experimental Parkinson’s disease (PD), whereas its CB1 receptor antagonist profile at doses lower than 5 mg/kg caused anti-hypokinetic effects.
“The antioxidant and CB2 receptor agonist properties of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabivarin (Δ9-THCV) afforded neuroprotection in experimental Parkinson’s disease (PD), whereas its CB1 receptor antagonist profile at doses lower than 5 mg/kg caused anti-hypokinetic effects.