“Preclinical models provided ample evidence that cannabinoids are cytotoxic against cancer cells. Among the best studied phytocannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) is most promising for the treatment of cancer as it lacks the psychotomimetic properties of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). In vitro studies and animal experiments point to a concentration- (dose-)dependent anticancer effect. The effectiveness of pure compounds versus extracts is the subject of an ongoing debate. Actual results demonstrate that CBD-rich hemp extracts must be distinguished from THC-rich cannabis preparations. Whereas pure CBD was superior to CBD-rich extracts in most in vitro experiments, the opposite was observed for pure THC and THC-rich extracts, although exceptions were noted. The cytotoxic effects of CBD, THC and extracts seem to depend not only on the nature of cannabinoids and the presence of other phytochemicals but also largely on the nature of cell lines and test conditions. Neither CBD nor THC are universally efficacious in reducing cancer cell viability. The combination of pure cannabinoids may have advantages over single agents, although the optimal ratio seems to depend on the nature of cancer cells; the existence of a ‘one size fits all’ ratio is very unlikely. As cannabinoids interfere with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a better understanding of the circadian rhythmicity of the ECS, particularly endocannabinoids and receptors, as well as of the rhythmicity of biological processes related to the growth of cancer cells, could enhance the efficacy of a therapy with cannabinoids by optimization of the timing of the administration, as has already been reported for some of the canonical chemotherapeutics. Theoretically, a CBD dose administered at noon could increase the peak of anandamide and therefore the effects triggered by this agent. Despite the abundance of preclinical articles published over the last 2 decades, well-designed controlled clinical trials on CBD in cancer are still missing. The number of observations in cancer patients, paired with the anticancer activity repeatedly reported in preclinical in vitro and in vivo studies warrants serious scientific exploration moving forward.”
Category Archives: THC (Delta-9-Tetrahydrocannabinol)
Spinal astroglial cannabinoid receptors control pathological tremor

https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33737752/
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41593-021-00818-4
“Medical cannabis can reduce essential tremor: Turns on overlooked cells in central nervous system” https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/03/210319125519.htm
Cannabis, a Miracle Drug with Polyvalent Therapeutic Utility: Preclinical and Clinical-Based Evidence
“Cannabis sativa L. is an annual herbaceous dioecious plant which was first cultivated by agricultural human societies in Asia. Over the period of time, various parts of the plant like leaf, flower, and seed were used for recreational as well as therapeutic purposes. The main chemical components of Cannabis sativa are termed as cannabinoids, among them the key psychoactive constituent is Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol (CBD) as active nonpsychotic constituent. Upon doing extensive literature review, it was found that cannabis has been widely studied for a number of disorders. Very recently, a pure CBD formulation, named Epidiolex, got a green flag from both United States Food and Drug Administration and Drug Enforcement Administration for 2 rare types of epilepsies. This laid a milestone in medical cannabis research.
This review intends to give a basic and extensive assessment, from past till present, of the ethnological, plant, chemical, pharmacological, and legal aspects of C. sativa. Further, this review contemplates the evidence the studies obtained of cannabis components on Alzheimer’s, Parkinson’s, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, multiple sclerosis, emesis, epilepsy, chronic pain, and cancer as a cytotoxic agent as well as a palliative therapy. The assessment in this study was done by reviewing in extensive details from studies on historical importance, ethnopharmacological aspects, and legal grounds of C. sativa from extensive literature available on the scientific databases, with a vision for elevating further pharmaceutical research to investigate its total potential as a therapeutic agent.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34676349/
“This study has analyzed and reviewed the historical, botanical, chemical, ethnopharmacological, and legal aspects of C. sativa from the first human use to the present medical applications with an analysis of its multiple therapeutic applications for various diseased conditions in the contemporary scientific context. There is an abundance of support for its several medicative uses as well as a possible benefit in various diseased conditions. Extensive pharmacological examination is still needed to better understand the clinical significance and uses of active cannabinoids in the treatment and prevention of chronic diseases. Also, cannabis can be chemically standardized and under prescription can be used. With the majority of the United States currently legalizing medicinal cannabis and/or restricted CBD-only use, physicians need to be educated on the history and correct clinical use of cannabis, as a result of which patients can know more and more about possible treatment utilizing cannabis. Medical cannabis has shown to have clinical efficacy in our past, and in present, data show its therapeutic effects. Extensive research in the field of cannabis can be very fruitful for the medicine world.”
Cannabinoids and Neurogenesis: The Promised Solution for Neurodegeneration?
 “The concept of neurons as irreplaceable cells does not hold true today. Experiments and evidence of neurogenesis, also, in the adult brain give hope that some compounds or drugs can enhance this process, helping to reverse the outcomes of diseases or traumas that once were thought to be everlasting.
“The concept of neurons as irreplaceable cells does not hold true today. Experiments and evidence of neurogenesis, also, in the adult brain give hope that some compounds or drugs can enhance this process, helping to reverse the outcomes of diseases or traumas that once were thought to be everlasting.
Cannabinoids, both from natural and artificial origins, already proved to have several beneficial effects (e.g., anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidants and analgesic action), but also capacity to increase neuronal population, by replacing the cells that were lost and/or regenerate a damaged nerve cell.
Neurogenesis is a process which is not highly represented in literature as neuroprotection, though it is as important as prevention of nervous system damage, because it can represent a possible solution when neuronal death is already present, such as in neurodegenerative diseases.
The aim of this review is to resume the experimental evidence of phyto- and synthetic cannabinoids effects on neurogenesis, both in vitro and in vivo, in order to elucidate if they possess also neurogenetic and neurorepairing properties.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34684894/
“The current results of cannabinoids effects on neurogenesis are encouraging, and it is expectable that the amount of evidence continues to increase in the future with other experiments.”
Health Outcomes among Adults Initiating Medical Cannabis for Chronic Pain: A 3-month Prospective Study Incorporating Ecological Momentary Assessment (EMA)
 “In response to the need of more rigorous data on medical cannabis and chronic pain, we conducted a 3-month prospective study incorporating ecological momentary assessment (EMA) to examine the effects of medical cannabis on pain, anxiety/depression, sleep, and quality of life.
“In response to the need of more rigorous data on medical cannabis and chronic pain, we conducted a 3-month prospective study incorporating ecological momentary assessment (EMA) to examine the effects of medical cannabis on pain, anxiety/depression, sleep, and quality of life.
Data were collected from 46 adults (Mean age=55.7±11.9, 52.2% male) newly initiating medical cannabis treatment for chronic pain. Participants completed a baseline survey, EMA for approximately 1 week pre- and up to 3 weeks post- medical cannabis treatment, and a 3-month follow-up survey.
The self-reported EMA data (2535 random and 705 daily assessments) indicated significant reductions in momentary pain intensity (b = -16.5, p < .001, 16.5 points reduction on 0-100 visual analog) and anxiety (b = -0.89, p < .05), and significant increase in daily sleep duration (b = 0.34, p < .01) and sleep quality (b = 0.32, p <.001) after participants initiated medical cannabis for a few weeks.
At 3 months, self-reported survey data showed significantly lower levels of worst pain (t = -2.38, p < .05), pain interference (t = -3.82, p < .05), and depression (t = -3.43, p < .01), as well as increased sleep duration (t = 3.95, p < .001), sleep quality (t = -3.04, p < .01), and quality of life (t = 4.48, p < .001) compared to baseline.
In our sample of primarily middle-aged and older adults with chronic pain, medical cannabis was associated with reduced pain intensity/inference, lower anxiety/depression, and improved sleep and quality of life.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34671723/
https://publications.sciences.ucf.edu/cannabis/index.php/Cannabis/article/view/97
Inflammaging and Cannabinoids
 “Aging is a complex phenomenon associated with a wide spectrum of physical and physiological changes affecting every part of all metazoans, if they escape death prior to reaching maturity. Critical to survival, the immune system evolved as the principal component of response to injury and defense against pathogen invasions. Because how significantly immune system affects and is affected by aging, several neologisms now appear to encapsulate these reciprocal relationships, such as Immunosenescence. The central part of Immunosenescence is Inflammaging -a sustained, low-grade, sterile inflammation occurring after reaching reproductive prime. Once initiated, the impact of Inflammaging and its adverse effects determine the direction and magnitudes of further Inflammaging. In this article, we review the nature of this vicious cycle, we will propose that phytocannabinoids as immune regulators may possess the potential as effective adjunctive therapies to slow and, in certain cases, reverse the pathologic senescence to permit a more healthy aging.”
“Aging is a complex phenomenon associated with a wide spectrum of physical and physiological changes affecting every part of all metazoans, if they escape death prior to reaching maturity. Critical to survival, the immune system evolved as the principal component of response to injury and defense against pathogen invasions. Because how significantly immune system affects and is affected by aging, several neologisms now appear to encapsulate these reciprocal relationships, such as Immunosenescence. The central part of Immunosenescence is Inflammaging -a sustained, low-grade, sterile inflammation occurring after reaching reproductive prime. Once initiated, the impact of Inflammaging and its adverse effects determine the direction and magnitudes of further Inflammaging. In this article, we review the nature of this vicious cycle, we will propose that phytocannabinoids as immune regulators may possess the potential as effective adjunctive therapies to slow and, in certain cases, reverse the pathologic senescence to permit a more healthy aging.”
“The beneficial effects of cannabinoids may be considered as alternative therapy in treating age-related diseases.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1568163721002348?via%3Dihub
The potential of cannabinoids and inhibitors of endocannabinoid degradation in respiratory diseases
 “The global incidence of respiratory diseases and complications is increasing. Therefore, new methods of treatment, as well as prevention, need to be investigated.
“The global incidence of respiratory diseases and complications is increasing. Therefore, new methods of treatment, as well as prevention, need to be investigated.
A group of compounds that should be considered for use in respiratory diseases is cannabinoids. There are three groups of cannabinoids – plant-derived phytocannabinoids, synthetic cannabinoids, and endogenous endocannabinoids including the enzymes responsible for their synthesis and degradation.
All cannabinoids exert their biological effects through either type 1 cannabinoid receptors (CB1) and/or type 2 cannabinoid receptors (CB2). In numerous studies (in vitro and in vivo), cannabinoids and inhibitors of endocannabinoid degradation have shown beneficial anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anti-cancer, and anti-fibrotic properties.
Although in the respiratory system, most of the studies have focused on the positive properties of cannabinoids and inhibitors of endocannabinoid degradation. There are few research reports discussing the negative impact of these compounds. This review summarizes the properties and mechanisms of action of cannabinoids and inhibitors of endocannabinoid degradation in various models of respiratory diseases.
A short description of the effects selected cannabinoids have on the human respiratory system and their possible use in the fight against COVID-19 is also presented. Additionally, a brief summary is provided of cannabinoid receptors properties and their expression in the respiratory system and cells of the immune system.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34648805/
“Phytocannabinoids are terpenophenolic compounds produced by specialized parts of the Cannabis sativa plant and are found in high concentrations in marijuana and hashish. In most of models, these compounds have shown positive biological properties. Anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-cancer and anti-fibrotic actions are especially emphasized.”
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0014299921007160?via%3Dihub
Activity of THC, CBD, and CBN on Human ACE2 and SARS-CoV1/2 Main Protease to Understand Antiviral Defense Mechanism
 “THC, CBD, and CBN were reported as promising candidates against SARS-CoV2 infection, but the mechanism of action of these three cannabinoids is not understood.
“THC, CBD, and CBN were reported as promising candidates against SARS-CoV2 infection, but the mechanism of action of these three cannabinoids is not understood.
This study aims to determine the mechanism of action of THC, CBD, and CBN by selecting two essential targets that directly affect the coronavirus infections as viral main proteases and human angiotensin-converting enzyme2.
Tested THC and CBD presented a dual-action action against both selected targets. Only CBD acted as a potent viral main protease inhibitor at the IC50 value of 1.86 ± 0.04 µM and exhibited only moderate activity against human angiotensin-converting enzyme2 at the IC50 value of 14.65 ± 0.47 µM.
THC acted as a moderate inhibitor against both viral main protease and human angiotensin-converting enzymes2 at the IC50 value of 16.23 ± 1.71 µM and 11.47 ± 3.60 µM, respectively.
Here, we discuss cannabinoid-associated antiviral activity mechanisms based on in silico docking studies and in vitro receptor binding studies.”
https://www.thieme-connect.de/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/a-1581-3707
Inducing Effects of Illegal Drugs to Improve Mental Health by Self-Regulation Therapy: A Pilot Study
 “This study consists of a brief psychological intervention, which uses Self-Regulation Therapy (SRT, procedure based on suggestion and classical conditioning), to improve coping with stress and emotionality by reproducing the positive effects of illegal drugs: cannabis, cocaine, ecstasy.
“This study consists of a brief psychological intervention, which uses Self-Regulation Therapy (SRT, procedure based on suggestion and classical conditioning), to improve coping with stress and emotionality by reproducing the positive effects of illegal drugs: cannabis, cocaine, ecstasy.
Results: SRT was superior to non-intervention for the 4 coping strategies (η2 = 0.829, 0.453, 0.411 and 0.606) and for positive (η2 = 0.371) and negative emotionality (η2 = 0.419). An improvement in scores was evidenced in the follow-up scores compared to the pre-intervention measures.
Conclusions: This study shows for the first time that it is possible to use illegal drugs, considered harmful to public health, to improve young people’s coping capacity and emotionality by reproducing their positive effects with SRT.”
https://www.mdpi.com/1660-4601/18/19/10387
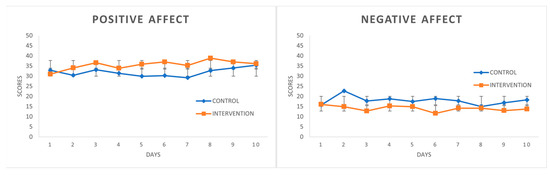
Antidepressant and Anxiolytic Effects of Medicinal Cannabis Use in an Observational Trial
 “Anxiety and depressive disorders are highly prevalent. Patients are increasingly using medicinal cannabis products to treat these disorders, but little is known about the effects of medicinal cannabis use on symptoms of anxiety and depression.
“Anxiety and depressive disorders are highly prevalent. Patients are increasingly using medicinal cannabis products to treat these disorders, but little is known about the effects of medicinal cannabis use on symptoms of anxiety and depression.
The aim of the present observational study was to assess general health in medicinal cannabis users and non-using controls with anxiety and/or depression.
Results: Medicinal cannabis use was associated with lower self-reported depression, but not anxiety, at baseline. Medicinal cannabis users also reported superior sleep, quality of life, and less pain on average. Initiation of medicinal cannabis during the follow-up period was associated with significantly decreased anxiety and depressive symptoms, an effect that was not observed in Controls that never initiated cannabis use.
Conclusions: Medicinal cannabis use may reduce anxiety and depressive symptoms in clinically anxious and depressed populations. Future placebo-controlled studies are necessary to replicate these findings and to determine the route of administration, dose, and product formulation characteristics to optimize clinical outcomes.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.729800/full
“Johns Hopkins: New Study Backs Claims That Cannabis Can Reduce Anxiety And Depression” https://finance.yahoo.com/news/johns-hopkins-study-backs-claims-145005658.html
“Report Shows Cannabis is Effective in Treating Anxiety, Depression” https://www.legalreader.com/report-shows-cannabis-is-effective-in-treating-anxiety-depression/
