 “Objective: Focal impaired awareness seizures (FIASs) are the most common seizure type in adults and are often refractory to medication. Management of FIASs is clinically challenging, and new interventions are needed for better seizure control. The amygdala-kindling model is a preclinical model of FIASs with secondary generalization.
“Objective: Focal impaired awareness seizures (FIASs) are the most common seizure type in adults and are often refractory to medication. Management of FIASs is clinically challenging, and new interventions are needed for better seizure control. The amygdala-kindling model is a preclinical model of FIASs with secondary generalization.
The present study assessed the efficacy of cannabidiol (CBD), ∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), and a combination of CBD and THC in a 15:1 ratio at suppressing focal and secondarily generalized seizures in the amygdala-kindled rat.
Results: CBD alone produced a partial suppression of both generalized seizures (median effective dose [ED50 ] = 283 mg/kg) and focal seizures (ED40 = 320 mg/kg) at doses that did not produce ataxia. THC alone also produced partial suppression of generalized (ED50 = 10 mg/kg) and focal (ED50 = 30 mg/kg) seizures, but doses of 10 mg/kg and above produced hypolocomotion, although not ataxia. The addition of a low dose of THC to CBD (15:1) left-shifted the CBD dose-response curve, producing much lower ED50 s for both generalized (ED50 = 26 + 1.73 mg/kg) and focal (ED50 = 40 + 2.66 mg/kg) seizures. No ataxia or hypolocomotion was seen at these doses of the CBD + THC combination.
Significance: CBD and THC both have antiseizure properties in the amygdala-kindling model, although THC produces suppression of the amygdala focus only at doses that produce hypolocomotion. The addition of small amounts of THC greatly improves the effectiveness of CBD. A combination of CBD and THC might be useful for the management of FIASs.”

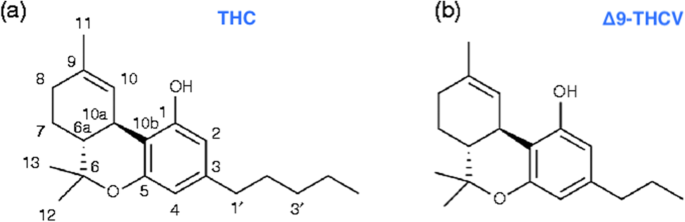 “Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is a cannabis-derived compound with unique properties that set it apart from the more common cannabinoids, such as Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The main advantage of THCV over THC is the lack of psychoactive effects.
“Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabivarin (THCV) is a cannabis-derived compound with unique properties that set it apart from the more common cannabinoids, such as Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC). The main advantage of THCV over THC is the lack of psychoactive effects.  “Background and purpose:
“Background and purpose:  “In recent decades, a lot of attention has been paid to Cannabis sativa L. due to its useful applications, including in fibers, oil, food for humans and animals, and therapeutics.
“In recent decades, a lot of attention has been paid to Cannabis sativa L. due to its useful applications, including in fibers, oil, food for humans and animals, and therapeutics.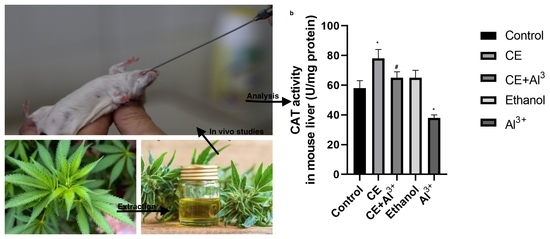
 “Evidence on the use and efficacy of medical cannabis for children is limited. We examined clinical and epidemiological characteristics of medical cannabis treatment and caregiver-reported effects in children and adolescents in Switzerland.
“Evidence on the use and efficacy of medical cannabis for children is limited. We examined clinical and epidemiological characteristics of medical cannabis treatment and caregiver-reported effects in children and adolescents in Switzerland. “Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (EDS) and related Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD) are debilitating connective tissue disorders that feature a prominent pain component for which there are limited therapeutic options for pain management.
“Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (EDS) and related Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD) are debilitating connective tissue disorders that feature a prominent pain component for which there are limited therapeutic options for pain management.  “We present the case of an 18-year-old woman who suffered from complications of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). Her pain was poorly controlled despite being on a myriad of analgesic medications at the time.
“We present the case of an 18-year-old woman who suffered from complications of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). Her pain was poorly controlled despite being on a myriad of analgesic medications at the time. “Central pain after stroke due to brainstem infarction is very rare. Treatment is difficult and specific guidelines are lacking. This is the report of a 61-year-old female patient who, after a posterolateral left medulla oblongata insult with incomplete Wallenberg syndrome, subsequently developed a burning and tingling pain in the contralateral leg and a burning and shooting pain in the ipsilateral face in trigeminal branches 1 and 2. More than 3 years of therapy with amitriptyline, gabapentin, pregabalin and various grade II and III opioids was ineffective or showed intolerable side effects. The administration of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol as an oromucosal spray in a 1:1 ratio improved the pain situation and quality of life quickly and permanently. The encouraging results in the present case may suggest that treatment with medical cannabis should be considered in similar cases when standard therapies are insufficient.”
“Central pain after stroke due to brainstem infarction is very rare. Treatment is difficult and specific guidelines are lacking. This is the report of a 61-year-old female patient who, after a posterolateral left medulla oblongata insult with incomplete Wallenberg syndrome, subsequently developed a burning and tingling pain in the contralateral leg and a burning and shooting pain in the ipsilateral face in trigeminal branches 1 and 2. More than 3 years of therapy with amitriptyline, gabapentin, pregabalin and various grade II and III opioids was ineffective or showed intolerable side effects. The administration of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol as an oromucosal spray in a 1:1 ratio improved the pain situation and quality of life quickly and permanently. The encouraging results in the present case may suggest that treatment with medical cannabis should be considered in similar cases when standard therapies are insufficient.” “
“