 “The hematopoietic cytokine granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) is well known to stimulate proliferation of blood stem/progenitor cells of the leukocyte lineage, but is also recognized as a neurotrophic factor involved in brain self-repair processes. G-CSF administration has been shown to promote recovery from experimental models of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and to modulate components of the endocannabinoid system (eCS). Conversely, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9THC) treatment of normal mice has been shown to increase blood levels of G-CSF in the periphery.
“The hematopoietic cytokine granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF) is well known to stimulate proliferation of blood stem/progenitor cells of the leukocyte lineage, but is also recognized as a neurotrophic factor involved in brain self-repair processes. G-CSF administration has been shown to promote recovery from experimental models of traumatic brain injury (TBI) and to modulate components of the endocannabinoid system (eCS). Conversely, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9THC) treatment of normal mice has been shown to increase blood levels of G-CSF in the periphery.
Hypothesis: Administration of the phytocannabinoid Δ9THC will enhance brain repair following controlled cortical impact (CCI) by upregulating G-CSF and other neurotrophic factors (brain-derived neurotrophic factor [BDNF] and glial-derived neurotrophic factor [GDNF]) in brain regions.
Materials and Methods: C57BL/6J mice underwent CCI and were treated for 3 days with THC 3 mg/kg intraperitoneally. Motor function on a rotarod was recorded at baseline and 3, 7, and 14 days after CCI. Groups of mice were euthanized at 7 and 14 days. G-CSF, BDNF, and GDNF expression were measured at 7 and 14 days in cerebral cortex, striatum, and hippocampus on the side of the trauma.
Results: Δ9THC-treated mice ran on the rotarod longer than vehicle-treated mice and recovered to normal rotarod performance levels at 2 weeks. These mice, compared to vehicle-treated animals, exhibited significant upregulation of G-CSF as well as BDNF and GDNF in cerebral cortex, striatum, and hippocampus.
Conclusion: Administration of the phytocannabinoid Δ9THC promotes significant recovery from TBI and is associated with upregulation of brain G-CSF, BDNF, and GDNF, neurotrophic factors previously shown to mediate brain self-repair following TBI and stroke.”

 “Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most lethal subtype of glioma.
“Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most lethal subtype of glioma.  “A cannabinoid anticancer para-quinone, HU-331, which was synthesized by our group five decades ago, was shown to have very high efficacy against human cancer cell lines in-vitro and against in-vivo grafts of human tumors in nude mice. The main mechanism was topoisomerase IIα catalytic inhibition. Later, several groups synthesized related compounds. In the present presentation, we review the publications on compounds synthesized on the basis of HU-331, summarize their published activities and mechanisms of action and report the synthesis and action of novel quinones, thus expanding the structure-activity relationship in these series.”
“A cannabinoid anticancer para-quinone, HU-331, which was synthesized by our group five decades ago, was shown to have very high efficacy against human cancer cell lines in-vitro and against in-vivo grafts of human tumors in nude mice. The main mechanism was topoisomerase IIα catalytic inhibition. Later, several groups synthesized related compounds. In the present presentation, we review the publications on compounds synthesized on the basis of HU-331, summarize their published activities and mechanisms of action and report the synthesis and action of novel quinones, thus expanding the structure-activity relationship in these series.”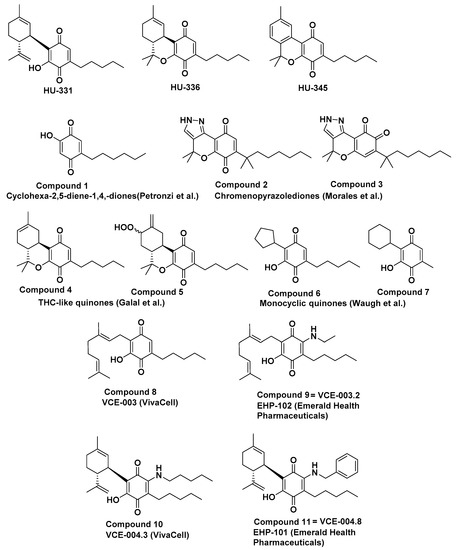

 “Cannabis sativa
“Cannabis sativa

 “Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug. Advances in technology and scientific findings led to the discovery of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, that further led to the discovery of endogenous cannabinoids system consisting of G-protein-coupled receptors – cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 along with their ligands, mainly anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Endocannabinoid (EC) is shown to be a modulator not only for physiological functions but also for the immune system, endocrine network, and central nervous system. Medicinal research and meta-data analysis over the last few decades have shown a significant potential for both THC and cannabidiol (CBD) to exert palliative effects. People suffering from many forms of advanced stages of cancers undergo chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting followed by severe and chronic neuropathic pain and weight loss. THC and CBD exhibit effective analgesic, anxiolytic, and appetite-stimulating effect on patients suffering from cancer. Drugs currently available in the market to treat such chemotherapy-induced cancer-related ailments are Sativex (GW Pharmaceutical), Dronabinol (Unimed Pharmaceuticals), and Nabilone (Valeant Pharmaceuticals). Apart from exerting palliative effects, THC also shows promising role in the treatment of cancer growth, neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), and alcohol addiction and hence should be exploited for potential benefits. The current review discusses the nature and role of CB receptors, specific applications of cannabinoids, and major studies that have assessed the role of cannabinoids in cancer management.”
“Cannabis was extensively utilized for its medicinal properties till the 19th century. A steep decline in its medicinal usage was observed later due to its emergence as an illegal recreational drug. Advances in technology and scientific findings led to the discovery of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the primary psychoactive compound of cannabis, that further led to the discovery of endogenous cannabinoids system consisting of G-protein-coupled receptors – cannabinoid receptor 1 and cannabinoid receptor 2 along with their ligands, mainly anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol. Endocannabinoid (EC) is shown to be a modulator not only for physiological functions but also for the immune system, endocrine network, and central nervous system. Medicinal research and meta-data analysis over the last few decades have shown a significant potential for both THC and cannabidiol (CBD) to exert palliative effects. People suffering from many forms of advanced stages of cancers undergo chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting followed by severe and chronic neuropathic pain and weight loss. THC and CBD exhibit effective analgesic, anxiolytic, and appetite-stimulating effect on patients suffering from cancer. Drugs currently available in the market to treat such chemotherapy-induced cancer-related ailments are Sativex (GW Pharmaceutical), Dronabinol (Unimed Pharmaceuticals), and Nabilone (Valeant Pharmaceuticals). Apart from exerting palliative effects, THC also shows promising role in the treatment of cancer growth, neurodegenerative diseases (multiple sclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease), and alcohol addiction and hence should be exploited for potential benefits. The current review discusses the nature and role of CB receptors, specific applications of cannabinoids, and major studies that have assessed the role of cannabinoids in cancer management.” “The main aspects of severe COVID-19 disease pathogenesis include hyper-induction of proinflammatory cytokines, also known as ‘cytokine storm’, that precedes acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and often leads to death. COVID-19 patients often suffer from lung fibrosis, a serious and untreatable condition. There remains no effective treatment for these complications.
“The main aspects of severe COVID-19 disease pathogenesis include hyper-induction of proinflammatory cytokines, also known as ‘cytokine storm’, that precedes acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and often leads to death. COVID-19 patients often suffer from lung fibrosis, a serious and untreatable condition. There remains no effective treatment for these complications. “Inflammasomes are cytoplasmic inflammatory signaling protein complexes that detect microbial materials, sterile inflammatory insults, and certain host-derived elements. Inflammasomes, once activated, promote caspase-1-mediated maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18, leading to pyroptosis. Current advances in inflammasome research support their involvement in the development of chronic inflammatory disorders in contrast to their role in regulating innate immunity.
“Inflammasomes are cytoplasmic inflammatory signaling protein complexes that detect microbial materials, sterile inflammatory insults, and certain host-derived elements. Inflammasomes, once activated, promote caspase-1-mediated maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18, leading to pyroptosis. Current advances in inflammasome research support their involvement in the development of chronic inflammatory disorders in contrast to their role in regulating innate immunity.