

“Cannabinoids are a group of terpenophenolic compounds derived from the Cannabis sativa L. plant. There is a growing body of evidence from cell culture and animal studies in support of cannabinoids possessing anticancer properties.
Method: A database search of peer reviewed articles published in English as full texts between January 1970 and April 2021 in Google Scholar, MEDLINE, PubMed and Web of Science was undertaken. References of relevant literature were searched to identify additional studies to construct a narrative literature review of oncological effects of cannabinoids in pre-clinical and clinical studies in various cancer types.
Results: Phyto-, endogenous and synthetic cannabinoids demonstrated antitumour effects both in vitro and in vivo. However, these effects are dependent on cancer type, the concentration and preparation of the cannabinoid and the abundance of receptor targets. The mechanism of action of synthetic cannabinoids, (-)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) has mainly been described via the traditional cannabinoid receptors; CB1 and CB2, but reports have also indicated evidence of activity through GPR55, TRPM8 and other ion channels including TRPA1, TRPV1 and TRPV2.
Conclusion: Cannabinoids have shown to be efficacious both as a single agent and in combination with antineoplastic drugs. These effects have occurred through various receptors and ligands and modulation of signalling pathways involved in hallmarks of cancer pathology. There is a need for further studies to characterise its mode of action at the molecular level and to delineate efficacious dosage and route of administration in addition to synergistic regimes.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34259916/
“Since time immemorial, the Cannabis plant has been used as a source of fibre, herbal remedy, medicinal and religious purposes. In the mid-nineteenth century, O’Shaughnessy and Moreau reported positive effects of cannabis on muscle spasms, vomiting, convulsions, rheumatism, tetanus, and rabies. However, during the twentieth century, its utilisation in Western medicine started to decline as a result of political prejudices and economic interests rather than scientific or medical reasons.
Plant-based, endogenous and synthetic cannabinoid compounds have shown merits in not only alleviating the unwanted side effects of antineoplastic drug regiments, but have also shown promising evidence in decreasing tumour burden, and one in vivo study so far concludes increasing survival rates in mice. Various extracted forms of cannabinoids from C. sativa have shown varying cytotoxic effects which should be explored in more detail in future studies as majority of the evidence originates from studies investigating mainly ∆9-THC and CBD’s actions.”
https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00432-021-03710-7

 “Recent cannabis exposure has been associated with lower rates of neurocognitive impairment in people with HIV (PWH). Cannabis’s anti-inflammatory properties may underlie this relationship by reducing chronic neuroinflammation in PWH.
“Recent cannabis exposure has been associated with lower rates of neurocognitive impairment in people with HIV (PWH). Cannabis’s anti-inflammatory properties may underlie this relationship by reducing chronic neuroinflammation in PWH.  “The therapeutic potential of
“The therapeutic potential of 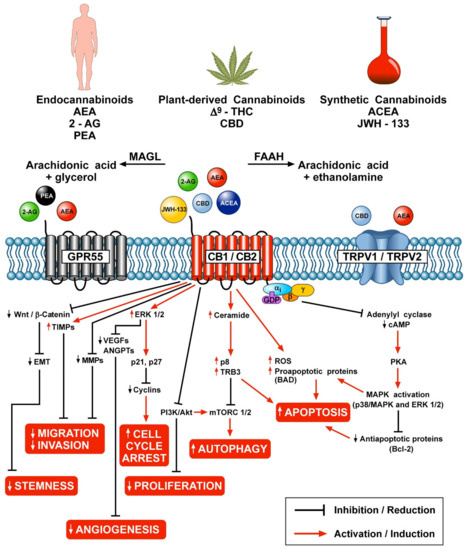
 “Cannabinoids, including delta-8- and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) have a palliative care impact and may therefore be beneficial against cancer.
“Cannabinoids, including delta-8- and delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) have a palliative care impact and may therefore be beneficial against cancer.  “Background:
“Background:  “Introduction:
“Introduction: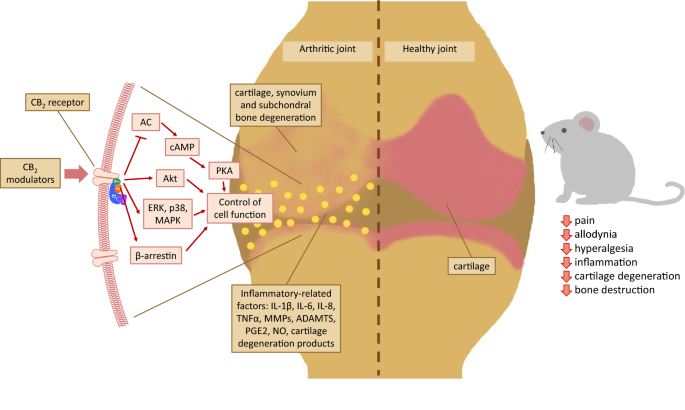 “Over the last several decades, the percentage of patients suffering from different forms of arthritis has increased due to the ageing population and the increasing risk of civilization diseases, e.g. obesity, which contributes to arthritis development. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are estimated to affect 50-60% of people over 65 years old and cause serious health and economic problems. Currently, therapeutic strategies are limited and focus mainly on pain attenuation and maintaining joint functionality. First-line therapies are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; in more advanced stages, stronger analgesics, such as opioids, are required, and in the most severe cases, joint arthroplasty is the only option to ensure joint mobility.
“Over the last several decades, the percentage of patients suffering from different forms of arthritis has increased due to the ageing population and the increasing risk of civilization diseases, e.g. obesity, which contributes to arthritis development. Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis are estimated to affect 50-60% of people over 65 years old and cause serious health and economic problems. Currently, therapeutic strategies are limited and focus mainly on pain attenuation and maintaining joint functionality. First-line therapies are nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs; in more advanced stages, stronger analgesics, such as opioids, are required, and in the most severe cases, joint arthroplasty is the only option to ensure joint mobility.  “Venous Leg Ulcers are highly prevalent lower limb integumentary wounds that remain challenging to heal despite the use of evidence-based compression therapies. A multitude of adjuvant treatments have been studied but none have demonstrated enough efficacy to gain adoption into treatment guidelines.
“Venous Leg Ulcers are highly prevalent lower limb integumentary wounds that remain challenging to heal despite the use of evidence-based compression therapies. A multitude of adjuvant treatments have been studied but none have demonstrated enough efficacy to gain adoption into treatment guidelines.  “Cannabinoids such as ▵-9-THC and CBD can downregulate the immune response by modulating the endocannabinoid system. This modulation is relevant for the treatment of prevalent autoimmune diseases (ADs), such as multiple sclerosis (MS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), diabetes mellitus type 1 (DMT1), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These conditions require new therapeutic options with fewer side effects for the control of the autoimmune response. Objective: to conduct a literature review of preclinical scientific evidence that supports further clinical investigations for the use of cannabinoids (natural or synthetic) as potential immunomodulators of the immune response in ADs.
“Cannabinoids such as ▵-9-THC and CBD can downregulate the immune response by modulating the endocannabinoid system. This modulation is relevant for the treatment of prevalent autoimmune diseases (ADs), such as multiple sclerosis (MS), systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), diabetes mellitus type 1 (DMT1), and rheumatoid arthritis (RA). These conditions require new therapeutic options with fewer side effects for the control of the autoimmune response. Objective: to conduct a literature review of preclinical scientific evidence that supports further clinical investigations for the use of cannabinoids (natural or synthetic) as potential immunomodulators of the immune response in ADs.  “An observational research design was used to evaluate which types of commonly labeled Cannabis flower product characteristics are associated with changes in momentary feelings of distress-related symptoms.
“An observational research design was used to evaluate which types of commonly labeled Cannabis flower product characteristics are associated with changes in momentary feelings of distress-related symptoms.