“Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may stem from the formation of aberrant and enduring aversive memories. Some PTSD patients have recreationally used Cannabis, probably aiming at relieving their symptomatology.
“Posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) may stem from the formation of aberrant and enduring aversive memories. Some PTSD patients have recreationally used Cannabis, probably aiming at relieving their symptomatology.
Here, we seek to review and discuss the effects of THC on aversive memory extinction and anxiety in healthy humans and PTSD patients.
Results: At low doses, THC can enhance the extinction rate and reduce anxiety responses. Both effects involve the activation of cannabinoid type-1 receptors in discrete components of the corticolimbic circuitry, which could couterbalance the low “endocannabinoid tonus” reported in PTSD patients. The advantage of associating CBD with THC to attenuate anxiety while minimizing the potential psychotic or anxiogenic effect produced by high doses of THC has been reported. The effects of THC either alone or combined with CBD on aversive memory reconsolidation, however, are still unknown.
Conclusions: Current evidence from healthy humans and PTSD patients supports the THC value to suppress anxiety and aversive memory expression without producing significant adverse effects if used in low doses or when associated with CBD. Future studies are guaranteed to address open questions related to their dose ratios, administration routes, pharmacokinetic interactions, sex-dependent differences, and prolonged efficacy.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32842985/
“Altogether, the findings encourage future controlled studies evaluating the effects of low doses of THC to attenuate aversive/traumatic memory expression in PTSD patients.”
https://bmcpsychiatry.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12888-020-02813-8

 “Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.
“Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.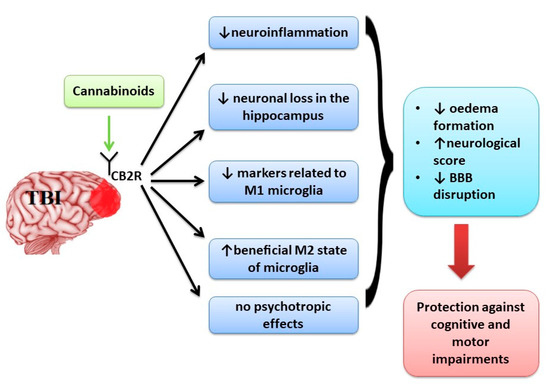
 “Few studies to date have measured the real-time effects of consumption of common and commercially available Cannabis products for the treatment of headache and migraine under naturalistic conditions. This study examines, for the first time, the effectiveness of using dried Cannabis flower, the most widely used type of Cannabis product in the United States, in actual time for treatment of headache- and migraine-related pain and the associations between different product characteristics and changes in symptom intensity following Cannabis use.
“Few studies to date have measured the real-time effects of consumption of common and commercially available Cannabis products for the treatment of headache and migraine under naturalistic conditions. This study examines, for the first time, the effectiveness of using dried Cannabis flower, the most widely used type of Cannabis product in the United States, in actual time for treatment of headache- and migraine-related pain and the associations between different product characteristics and changes in symptom intensity following Cannabis use. “Cannabinoid CB2 receptor (CB2) agonists are potential analgesics void of psychotropic effects.
“Cannabinoid CB2 receptor (CB2) agonists are potential analgesics void of psychotropic effects. “Chronic ethanol abuse can lead to harmful consequences for the heart, resulting in systolic dysfunction, variability in the heart rate, arrhythmia, and cardiac remodelling. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy is poorly understood. In this regard, the present study aimed to describe the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic cell death that may be involved in ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy and characterize CBR-mediated effects on the signalling pathway and myocardial injury.
“Chronic ethanol abuse can lead to harmful consequences for the heart, resulting in systolic dysfunction, variability in the heart rate, arrhythmia, and cardiac remodelling. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy is poorly understood. In this regard, the present study aimed to describe the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic cell death that may be involved in ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy and characterize CBR-mediated effects on the signalling pathway and myocardial injury. “Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.
“Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.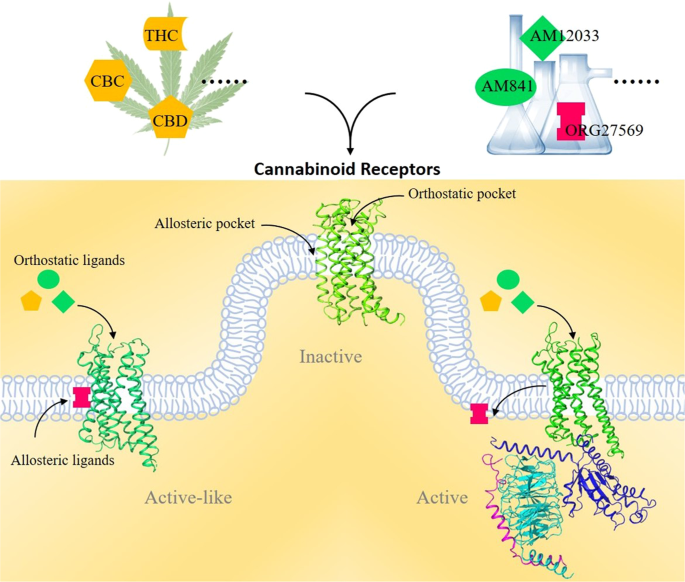
 “Thirty years ago, the discovery of a cannabinoid (CB) receptor that interacts with the psychoactive compound in Cannabis led to the identification of anandamide, an endogenous receptor ligand or endocannabinoid. Research on endocannabinoids has since exploded, and additional receptors along with their lipid mediators and signaling pathways continue to be revealed. Specifically, in humans, the release of endocannabinoids from membrane lipids occurs on demand and the signaling process is rapidly attenuated by the breakdown of the ligand suggesting a tight regulation of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Additionally, the varying distribution of CB receptors between the central nervous system and other tissues allows for the ECS to participate in a wide range of cognitive and physiological processes. Select plant-derived ‘phyto’cannabinoids such as Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) bind to the CB receptors and trigger the ECS, and in the case of Δ9-THC, while it has therapeutic value, can also produce detrimental effects. Current research is aimed at the identification of additional phytocannabinoids with minimal psychotropic effects with potential for therapeutic development. Although decades of research on the ECS and its components have expanded our understanding of the mechanisms and implications of endocannabinoid signaling in mammals, it continues to evolve. Here, we provide a brief overview of the ECS and its overlap with other related lipid-mediated signaling pathways.”
“Thirty years ago, the discovery of a cannabinoid (CB) receptor that interacts with the psychoactive compound in Cannabis led to the identification of anandamide, an endogenous receptor ligand or endocannabinoid. Research on endocannabinoids has since exploded, and additional receptors along with their lipid mediators and signaling pathways continue to be revealed. Specifically, in humans, the release of endocannabinoids from membrane lipids occurs on demand and the signaling process is rapidly attenuated by the breakdown of the ligand suggesting a tight regulation of the endocannabinoid system (ECS). Additionally, the varying distribution of CB receptors between the central nervous system and other tissues allows for the ECS to participate in a wide range of cognitive and physiological processes. Select plant-derived ‘phyto’cannabinoids such as Δ-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) bind to the CB receptors and trigger the ECS, and in the case of Δ9-THC, while it has therapeutic value, can also produce detrimental effects. Current research is aimed at the identification of additional phytocannabinoids with minimal psychotropic effects with potential for therapeutic development. Although decades of research on the ECS and its components have expanded our understanding of the mechanisms and implications of endocannabinoid signaling in mammals, it continues to evolve. Here, we provide a brief overview of the ECS and its overlap with other related lipid-mediated signaling pathways.”
 “In this study, we report the potential of cannabidiol, one of the major cannabis constituents, for enhancing osteoblastic differentiation in U2OS and MG-63 cells.
“In this study, we report the potential of cannabidiol, one of the major cannabis constituents, for enhancing osteoblastic differentiation in U2OS and MG-63 cells. “A post-antibiotic world is fast becoming a reality, given the rapid emergence of pathogens that are resistant to current drugs. Therefore, there is an urgent need to discover new classes of potent antimicrobial agents with novel modes of action.
“A post-antibiotic world is fast becoming a reality, given the rapid emergence of pathogens that are resistant to current drugs. Therefore, there is an urgent need to discover new classes of potent antimicrobial agents with novel modes of action.