 “Evidence on the use and efficacy of medical cannabis for children is limited. We examined clinical and epidemiological characteristics of medical cannabis treatment and caregiver-reported effects in children and adolescents in Switzerland.
“Evidence on the use and efficacy of medical cannabis for children is limited. We examined clinical and epidemiological characteristics of medical cannabis treatment and caregiver-reported effects in children and adolescents in Switzerland.
We collected clinical data from children and adolescents (< 18 years) who received Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD), or a combination of the two between 2008 and 2019 in Switzerland. Out of 205 contacted families, 90 agreed to participate. The median age at the first prescription was 11.5 years (interquartile range (IQR) 6-16), and 32 patients were female (36%). Fifty-one (57%) patients received CBD only and 39 (43%) THC. Patients were more likely to receive THC therapy if one of the following symptoms or signs were present: spasticity, pain, lack of weight gain, vomiting, or nausea, whereas seizures were the dominant indication for CBD therapy.
Improvements were reported in 59 (66%) study participants.
The largest treatment effects were reported for pain, spasticity, and frequency of seizures in participants treated with THC, and for those treated with pure CBD, the frequency of seizures. However, 43% of caregivers reported treatment interruptions, mainly because of lack of improvement (56%), side effects (46%), the need for a gastric tube (44%), and cost considerations (23%).
Conclusions: The effects of medical cannabis in children and adolescents with chronic conditions are unknown except for rare seizure disorders, but the caregiver-reported data analysed here may justify trials of medical cannabis with standardized concentrations of THC or CBD to assess its efficacy in the young.
What is Known: • The use of medical cannabis (THC and CBD) to treat a variety of diseases among children and adolescents is increasing. • In contrast to adults, there is no evidence to support the use of medical cannabis to treat chronic pain and spasticity in children, but substantial evidence to support the use of CBD in children with rare seizure disorders.
What is New: • This study provides important insights into prescription practices, dosages, and treatment outcomes in children and adolescents using medical cannabis data from a real-life setting.
• The effects of medical cannabis in children and adolescents with chronic conditions shown in our study support trials of medical cannabis for chronic conditions.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34309706/
“For two thirds of participants treated with standardized THC or CBD preparations, the caregiver reported an improvement in their condition and well-being. Medical cannabis could be a promising and useful therapy for children and adolescents with neurological conditions.”
 “In recent decades, a lot of attention has been paid to Cannabis sativa L. due to its useful applications, including in fibers, oil, food for humans and animals, and therapeutics.
“In recent decades, a lot of attention has been paid to Cannabis sativa L. due to its useful applications, including in fibers, oil, food for humans and animals, and therapeutics.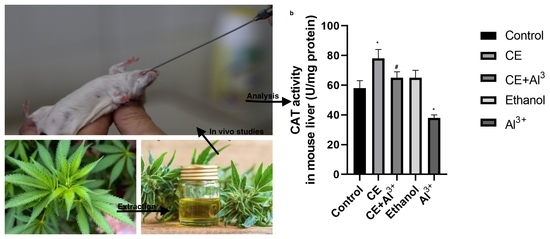

 “Background:
“Background:  “Introduction:
“Introduction: “Evidence on the use and efficacy of medical cannabis for children is limited. We examined clinical and epidemiological characteristics of medical cannabis treatment and caregiver-reported effects in children and adolescents in Switzerland.
“Evidence on the use and efficacy of medical cannabis for children is limited. We examined clinical and epidemiological characteristics of medical cannabis treatment and caregiver-reported effects in children and adolescents in Switzerland. “Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (EDS) and related Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD) are debilitating connective tissue disorders that feature a prominent pain component for which there are limited therapeutic options for pain management.
“Ehlers-Danlos Syndromes (EDS) and related Hypermobility Spectrum Disorders (HSD) are debilitating connective tissue disorders that feature a prominent pain component for which there are limited therapeutic options for pain management.  “We present the case of an 18-year-old woman who suffered from complications of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). Her pain was poorly controlled despite being on a myriad of analgesic medications at the time.
“We present the case of an 18-year-old woman who suffered from complications of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). Her pain was poorly controlled despite being on a myriad of analgesic medications at the time. “
“ “Coronavirus disease (COVID-19), caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is an ongoing pandemic and presents a public health emergency. It has affected millions of people and continues to affect more, despite tremendous social preventive measures. Identifying candidate drugs for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is crucial. The pathogenesis and the complications with advanced infection mainly involve an immune-inflammatory cascade. Therefore, therapeutic strategy relies on suppressing infectivity and inflammation, along with immune modulation.
“Coronavirus disease (COVID-19), caused by novel severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), is an ongoing pandemic and presents a public health emergency. It has affected millions of people and continues to affect more, despite tremendous social preventive measures. Identifying candidate drugs for the prevention and treatment of COVID-19 is crucial. The pathogenesis and the complications with advanced infection mainly involve an immune-inflammatory cascade. Therefore, therapeutic strategy relies on suppressing infectivity and inflammation, along with immune modulation.  “Venous Leg Ulcers are highly prevalent lower limb integumentary wounds that remain challenging to heal despite the use of evidence-based compression therapies. A multitude of adjuvant treatments have been studied but none have demonstrated enough efficacy to gain adoption into treatment guidelines.
“Venous Leg Ulcers are highly prevalent lower limb integumentary wounds that remain challenging to heal despite the use of evidence-based compression therapies. A multitude of adjuvant treatments have been studied but none have demonstrated enough efficacy to gain adoption into treatment guidelines.