 “The functions of the glycine receptor (GlyR) and γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor (GABAAR) are both impaired in hyperekplexia, a neurological disorder that is usually caused by GlyR mutations.
“The functions of the glycine receptor (GlyR) and γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor (GABAAR) are both impaired in hyperekplexia, a neurological disorder that is usually caused by GlyR mutations.
Although emerging evidence indicates that cannabinoids can directly restore normal GlyR function, whether they affect the GABAAR in hyperekplexia remains unknown.
Here, we show that dehydroxylcannabidiol (DH-CBD), a synthetic nonpsychoactive cannabinoid, restores both the GABA- and glycine-activated currents (IGABA and IGly ) in HEK-293 cells co-expressing a major GABAAR isoform (α1β2γ2) and GlyRα1 carrying a human hyperekplexia-associated mutation (GlyRα1 R271Q). Using co-immunoprecipitation and FRET assays, we found that DH-CBD disrupts the protein interaction between GABAAR and GlyRα1 R271Q
Furthermore, a point mutation of GlyRα1, changing Ser-296 to Ala-296, which is critical for cannabinoid binding on GlyR, significantly blocked the DH-CBD-induced restoration of IGABA and IGly currents. This S296A substitution also considerably attenuated the DH-CBD-induced disruption of the interaction between GlyRα1 R271Q and GABAAR.
These findings suggest that because it restores the functions of both GlyRα1 and GABAAR, DH-CBD may represent a potentially valuable candidate drug to manage hyperekplexia.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31757808
http://www.jbc.org/content/early/2019/11/22/jbc.RA119.011221

 “It is unclear whether
“It is unclear whether 
 “Delayed neurologic sequelae (DNS) are among the most serious complications of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning caused partly by elevated neuroinflammation.
“Delayed neurologic sequelae (DNS) are among the most serious complications of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning caused partly by elevated neuroinflammation. “The protective effect of
“The protective effect of  “Cannabis sativa L. is one of the most-studied species for its phytochemistry due to the abundance of secondary metabolites, including
“Cannabis sativa L. is one of the most-studied species for its phytochemistry due to the abundance of secondary metabolites, including 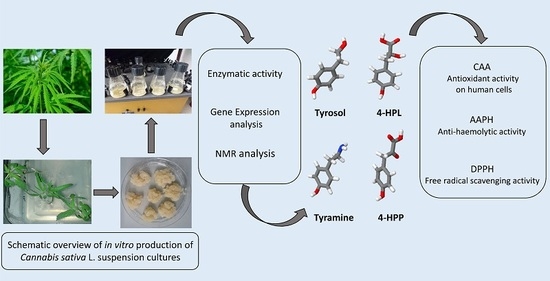
 “The hemp plant (
“The hemp plant ( “Endocannabinoids are produced within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and modulate energy homeostasis and food intake, at least in part, via vagally-dependent actions. The recent paper by Christie et al., [Christie, et al. J Physiol, 2019] demonstrate, for the first time, that
“Endocannabinoids are produced within the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and modulate energy homeostasis and food intake, at least in part, via vagally-dependent actions. The recent paper by Christie et al., [Christie, et al. J Physiol, 2019] demonstrate, for the first time, that  “Growing evidence suggests that medical marijuana laws have harm reduction effects across a variety of outcomes related to risky health behaviors. This study investigates the impact of medical marijuana laws on self-reported health using data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System from 1993 to 2013. In our analyses we separately identify the effect of a medical marijuana law and the impact of subsequent active and legally protected dispensaries. Our main results show surprisingly limited improvements in self-reported health after the legalization of medical marijuana and legally protected dispensaries. Subsample analyses reveal strong improvements in health among non-white individuals, those reporting chronic pain, and those with a high school degree, driven predominately by whether or not the state had active and legally protected dispensaries. We also complement the analysis by evaluating the impact on risky health behaviors and find that the aforementioned demographic groups experience large reductions in alcohol consumption after the implementation of a medical marijuana law.”
“Growing evidence suggests that medical marijuana laws have harm reduction effects across a variety of outcomes related to risky health behaviors. This study investigates the impact of medical marijuana laws on self-reported health using data from the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System from 1993 to 2013. In our analyses we separately identify the effect of a medical marijuana law and the impact of subsequent active and legally protected dispensaries. Our main results show surprisingly limited improvements in self-reported health after the legalization of medical marijuana and legally protected dispensaries. Subsample analyses reveal strong improvements in health among non-white individuals, those reporting chronic pain, and those with a high school degree, driven predominately by whether or not the state had active and legally protected dispensaries. We also complement the analysis by evaluating the impact on risky health behaviors and find that the aforementioned demographic groups experience large reductions in alcohol consumption after the implementation of a medical marijuana law.”