 “It is well known that certain active ingredients of the plants of Cannabis genus, i.e., the “phytocannabinoids” [pCBs; e.g., (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), (−)-cannabidiol, etc.] can influence a wide array of biological processes, and the human body is able to produce endogenous analogs of these substances [“endocannabinoids” (eCB), e.g., arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide, AEA), 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), etc.]. These ligands, together with multiple receptors (e.g., CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, etc.), and a complex enzyme and transporter apparatus involved in the synthesis and degradation of the ligands constitute the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a recently emerging regulator of several physiological processes. The ECS is widely expressed in the human body, including several members of the innate and adaptive immune system, where eCBs, as well as several pCBs were shown to deeply influence immune functions thereby regulating inflammation, autoimmunity, antitumor, as well as antipathogen immune responses, etc. Based on this knowledge, many in vitro and in vivo studies aimed at exploiting the putative therapeutic potential of cannabinoid signaling in inflammation-accompanied diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis) or in organ transplantation, and to dissect the complex immunological effects of medical and “recreational” marijuana consumption. Thus, the objective of the current article is (i) to summarize the most recent findings of the field; (ii) to highlight the putative therapeutic potential of targeting cannabinoid signaling; (iii) to identify open questions and key challenges; and (iv) to suggest promising future directions for cannabinoid-based drug development.
“It is well known that certain active ingredients of the plants of Cannabis genus, i.e., the “phytocannabinoids” [pCBs; e.g., (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), (−)-cannabidiol, etc.] can influence a wide array of biological processes, and the human body is able to produce endogenous analogs of these substances [“endocannabinoids” (eCB), e.g., arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide, AEA), 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), etc.]. These ligands, together with multiple receptors (e.g., CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, etc.), and a complex enzyme and transporter apparatus involved in the synthesis and degradation of the ligands constitute the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a recently emerging regulator of several physiological processes. The ECS is widely expressed in the human body, including several members of the innate and adaptive immune system, where eCBs, as well as several pCBs were shown to deeply influence immune functions thereby regulating inflammation, autoimmunity, antitumor, as well as antipathogen immune responses, etc. Based on this knowledge, many in vitro and in vivo studies aimed at exploiting the putative therapeutic potential of cannabinoid signaling in inflammation-accompanied diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis) or in organ transplantation, and to dissect the complex immunological effects of medical and “recreational” marijuana consumption. Thus, the objective of the current article is (i) to summarize the most recent findings of the field; (ii) to highlight the putative therapeutic potential of targeting cannabinoid signaling; (iii) to identify open questions and key challenges; and (iv) to suggest promising future directions for cannabinoid-based drug development.
Active Components of Cannabis sativa (Hemp)—Phytocannabinoids (pCBs) and Beyond
It is known since ancient times that consumption of different parts of the plant Cannabis sativa can lead to psychotropic effects. Moreover, mostly, but not exclusively because of its potent analgesic actions, it was considered to be beneficial in the management of several diseases. Nowadays it is a common knowledge that these effects were mediated by the complex mixture of biologically active substances produced by the plant. So far, at least 545 active compounds have been identified in it, among which, the best-studied ones are the so-called pCBs. It is also noteworthy that besides these compounds, ca. 140 different terpenes [including the potent and selective CB2 agonist sesquiterpene β-caryophyllene (BCP)], multiple flavonoids, alkanes, sugars, non-cannabinoid phenols, phenylpropanoids, steroids, fatty acids, and various nitrogenous compounds can be found in the plant, individual biological actions of which are mostly still nebulous. Among the so far identified > 100 pCBs, the psychotropic (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and the non-psychotropic (−)-cannabidiol (CBD) are the best-studied ones, exerting a wide-variety of biological actions [including but not exclusively: anticonvulsive, analgesic, antiemetic, and anti inflammatory effects]. Of great importance, pCBs have been shown to modulate the activity of a plethora of cellular targets, extending their impact far beyond the “classical” (see above) cannabinoid signaling. Indeed, besides being agonists [or in some cases even antagonists of CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, some pCBs were shown to differentially modulate the activity of certain TRP channels, PPARs, serotonin, α adrenergic, adenosine or opioid receptors, and to inhibit COX and lipoxygenase enzymes, FAAH, EMT, etc.. Moreover, from a clinical point-of-view, it should also be noted that pCBs can indirectly modify pharmacokinetics of multiple drugs (e.g., cyclosporine A) by interacting with several cytochrome P 450 (CYP) enzymes. Taken together, pCBs can be considered as multitarget polypharmacons, each of them having unique “molecular fingerprints” created by the characteristic activation/inhibition pattern of its locally available cellular targets.
Concluding Remarks—Lessons to Learn from Cannabis
Research efforts of the past few decades have unambiguously evidenced that ECS is one of the central orchestrators of both innate and adaptive immune systems, and that pure pCBs as well as complex cannabis-derivatives can also deeply influence immune responses. Although, many open questions await to be answered, pharmacological modulation of the (endo)cannabinoid signaling, and restoration of the homeostatic eCB tone of the tissues augur to be very promising future directions in the management of several pathological inflammation-accompanied diseases. Moreover, in depth analysis of the (quite complex) mechanism-of-action of the most promising pCBs is likely to shed light to previously unknown immune regulatory mechanisms and can therefore pave new “high”-ways toward developing completely novel classes of therapeutic agents to manage a wide-variety of diseases.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2017.01487/full
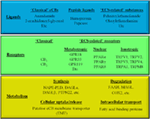
 “Ischemia and reperfusion of intestinal tissue (intestinal I/R) induces disruption of ileal contractility and chain responses of inflammatory.
“Ischemia and reperfusion of intestinal tissue (intestinal I/R) induces disruption of ileal contractility and chain responses of inflammatory.
 “The therapeutic effect of
“The therapeutic effect of  “Cannabichromene (CBC) is one of the most abundant phytocannabinoids in Cannabis spp. It has modest anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects and potentiates some effects of Δ9 – tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in vivo. How CBC exerts these effects is poorly defined and there is little information about its efficacy at cannabinoid receptors. We sought to determine the functional activity of CBC at CB1 and CB2 receptors.
“Cannabichromene (CBC) is one of the most abundant phytocannabinoids in Cannabis spp. It has modest anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects and potentiates some effects of Δ9 – tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) in vivo. How CBC exerts these effects is poorly defined and there is little information about its efficacy at cannabinoid receptors. We sought to determine the functional activity of CBC at CB1 and CB2 receptors. “Utilization and safety of
“Utilization and safety of  “Few studies have tested the hypothesis that adolescent
“Few studies have tested the hypothesis that adolescent  “Literature suggests the role of
“Literature suggests the role of  “It is well known that certain active ingredients of the plants of Cannabis genus, i.e., the “phytocannabinoids” [pCBs; e.g., (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), (−)-cannabidiol, etc.] can influence a wide array of biological processes, and the human body is able to produce endogenous analogs of these substances [“endocannabinoids” (eCB), e.g., arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide, AEA), 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), etc.]. These ligands, together with multiple receptors (e.g., CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, etc.), and a complex enzyme and transporter apparatus involved in the synthesis and degradation of the ligands constitute the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a recently emerging regulator of several physiological processes. The ECS is widely expressed in the human body, including several members of the innate and adaptive immune system, where eCBs, as well as several pCBs were shown to deeply influence immune functions thereby regulating inflammation, autoimmunity, antitumor, as well as antipathogen immune responses, etc. Based on this knowledge, many in vitro and in vivo studies aimed at exploiting the putative therapeutic potential of cannabinoid signaling in inflammation-accompanied diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis) or in organ transplantation, and to dissect the complex immunological effects of medical and “recreational” marijuana consumption. Thus, the objective of the current article is (i) to summarize the most recent findings of the field; (ii) to highlight the putative therapeutic potential of targeting cannabinoid signaling; (iii) to identify open questions and key challenges; and (iv) to suggest promising future directions for cannabinoid-based drug development.
“It is well known that certain active ingredients of the plants of Cannabis genus, i.e., the “phytocannabinoids” [pCBs; e.g., (−)-trans-Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), (−)-cannabidiol, etc.] can influence a wide array of biological processes, and the human body is able to produce endogenous analogs of these substances [“endocannabinoids” (eCB), e.g., arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide, AEA), 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), etc.]. These ligands, together with multiple receptors (e.g., CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, etc.), and a complex enzyme and transporter apparatus involved in the synthesis and degradation of the ligands constitute the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a recently emerging regulator of several physiological processes. The ECS is widely expressed in the human body, including several members of the innate and adaptive immune system, where eCBs, as well as several pCBs were shown to deeply influence immune functions thereby regulating inflammation, autoimmunity, antitumor, as well as antipathogen immune responses, etc. Based on this knowledge, many in vitro and in vivo studies aimed at exploiting the putative therapeutic potential of cannabinoid signaling in inflammation-accompanied diseases (e.g., multiple sclerosis) or in organ transplantation, and to dissect the complex immunological effects of medical and “recreational” marijuana consumption. Thus, the objective of the current article is (i) to summarize the most recent findings of the field; (ii) to highlight the putative therapeutic potential of targeting cannabinoid signaling; (iii) to identify open questions and key challenges; and (iv) to suggest promising future directions for cannabinoid-based drug development.
 “Our main aim was to investigate the short‐term therapeutic effects, safety/tolerability and potential side effects of the cannabis galenical preparation (Bedrocan) in patients with a range of chronic conditions unresponsive to other treatments.
“Our main aim was to investigate the short‐term therapeutic effects, safety/tolerability and potential side effects of the cannabis galenical preparation (Bedrocan) in patients with a range of chronic conditions unresponsive to other treatments.
 “Heavy metals pollution affects the nutritive value of fish.
“Heavy metals pollution affects the nutritive value of fish.