 “In the absence of effective antivirals and vaccination, the pandemic of COVID-19 remains the most significant challenge to our health care system in decades. There is an urgent need for definitive therapeutic intervention.
“In the absence of effective antivirals and vaccination, the pandemic of COVID-19 remains the most significant challenge to our health care system in decades. There is an urgent need for definitive therapeutic intervention.
Clinical reports indicate that the cytokine storm associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) is the leading cause of mortality in severe cases of some respiratory viral infections, including COVID-19.
In recent years, cannabinoids have been investigated extensively due to their potential effects on the human body. Among all cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) has demonstrated potent anti-inflammatory effects in a variety of pathological conditions. Therefore, it is logical to explore whether CBD can reduce the cytokine storm and treat ARDS.
Materials and Methods: In this study, we show that intranasal application of Poly(I:C), a synthetic analogue of viral double-stranded RNA, simulated symptoms of severe viral infections inducing signs of ARDS and cytokine storm.
Discussion: The administration of CBD downregulated the level of proinflammatory cytokines and ameliorated the clinical symptoms of Poly I:C-induced ARDS.
Conclusion: Our results suggest a potential protective role for CBD during ARDS that may extend CBD as part of the treatment of COVID-19 by reducing the cytokine storm, protecting pulmonary tissues, and re-establishing inflammatory homeostasis.”

 “In the present study, the antimicrobial effect of Cannabis sativa Futura 75 was evaluated both in vitro against foodborne bacterial pathogens, and on food against naturally occurring microbial groups of minced meat stored for 8 days at 4°C.
“In the present study, the antimicrobial effect of Cannabis sativa Futura 75 was evaluated both in vitro against foodborne bacterial pathogens, and on food against naturally occurring microbial groups of minced meat stored for 8 days at 4°C. “Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed contains high contents of various nutrients, including fatty acids and proteins.
“Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed contains high contents of various nutrients, including fatty acids and proteins.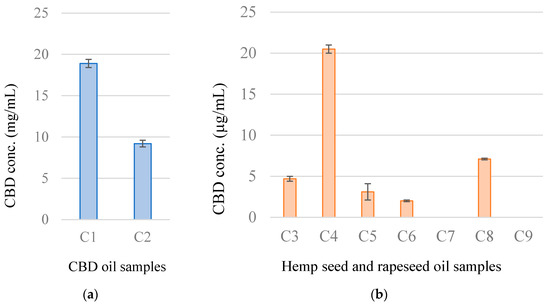
 “Cannabis products have been used for centuries by humans for recreational and medical purposes. Resent research, proposed the promising therapeutic potential of cannabis and related cannabinoids for a wide range of medical conditions, including psychiatric and neurological diseases.
“Cannabis products have been used for centuries by humans for recreational and medical purposes. Resent research, proposed the promising therapeutic potential of cannabis and related cannabinoids for a wide range of medical conditions, including psychiatric and neurological diseases. “Cannabis and cannabinoid-based extracts have long been utilized for their perceived therapeutic value, and support for the legalization of cannabis for medicinal purposes continues to increase worldwide.
“Cannabis and cannabinoid-based extracts have long been utilized for their perceived therapeutic value, and support for the legalization of cannabis for medicinal purposes continues to increase worldwide. “Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Cannabaceae) is an ancient cultivated plant originating from Central Asia and historically has been a multi-use crop valued for its fiber, food, and medicinal uses. Various oriental and Asian cultures kept records of its production and numerous uses.
“Industrial hemp (Cannabis sativa L., Cannabaceae) is an ancient cultivated plant originating from Central Asia and historically has been a multi-use crop valued for its fiber, food, and medicinal uses. Various oriental and Asian cultures kept records of its production and numerous uses.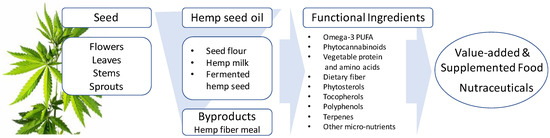
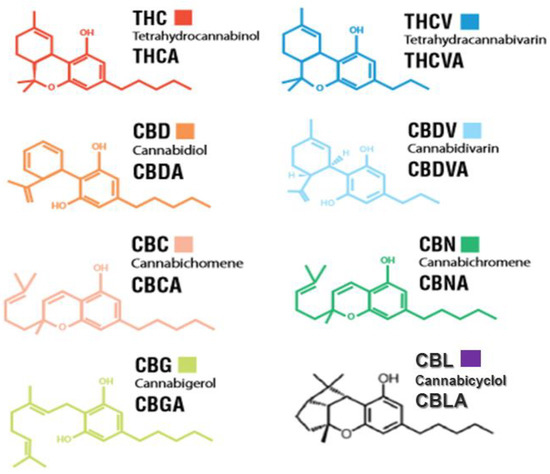
 “The immune-suppressive effects of cannabidiol (CBD) are attributed to the modulation of essential immunological signaling pathways and receptors. Mechanistic understanding of the pharmacological effects of CBD emphasizes the therapeutic potential of CBD as a novel immune modulator.
“The immune-suppressive effects of cannabidiol (CBD) are attributed to the modulation of essential immunological signaling pathways and receptors. Mechanistic understanding of the pharmacological effects of CBD emphasizes the therapeutic potential of CBD as a novel immune modulator. “Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
“Non-Uremic Calciphylaxis (NUC) is a rare condition that often manifests as intractable and painful integumentary wounds, afflicting patients with a high burden of co-morbidity.
 “Previous preclinical studies have demonstrated that cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG), two non-psychotomimetic phytocannabinoids from Cannabis sativa, induce neuroprotective effects on toxic and neurodegenerative processes.
“Previous preclinical studies have demonstrated that cannabidiol (CBD) and cannabigerol (CBG), two non-psychotomimetic phytocannabinoids from Cannabis sativa, induce neuroprotective effects on toxic and neurodegenerative processes.