 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is the primary non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis (Cannabis sativa) and an increasingly popular dietary supplement as a result of widespread availability of CBD-containing products.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is the primary non-psychoactive compound found in cannabis (Cannabis sativa) and an increasingly popular dietary supplement as a result of widespread availability of CBD-containing products.
CBD is FDA-approved for the treatment of epilepsy and exhibits anxiolytic, antipsychotic, prosocial, and other behavioral effects in animal and human studies, however, the underlying mechanisms governing these phenotypes are still being elucidated. The epigenome, particularly DNA methylation, is responsive to environmental input and can govern persistent patterns of gene regulation affecting phenotype across the life course.
In order to understand the epigenomic activity of chronic cannabidiol exposure in the adult brain, 12-week-old male C57BL/6 mice were exposed to either 20 mg/kg CBD or vehicle daily by oral administration for fourteen days. Hippocampal tissue was collected and reduced-representation bisulfite sequencing (RRBS) was performed. Analyses revealed 3,323 differentially methylated loci (DMLs) in CBD-exposed animals with a small skew toward global hypomethylation.
Genes for cell adhesion and migration, dendritic spine development, and excitatory postsynaptic potential were found to be enriched in a gene ontology term analysis of DML-containing genes, and disease ontology enrichment revealed an overrepresentation of DMLs in gene sets associated with autism spectrum disorder, schizophrenia, and other phenotypes.
These results suggest that the epigenome may be a key substrate for CBD’s behavioral effects and provides a wealth of gene regulatory information for further study.”

 “Painful tonic spasm (PTS) is a common yet debilitating symptom in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), especially those with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Although carbamazepine is an effective treatment, it poses the risk of severe adverse reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS).
“Painful tonic spasm (PTS) is a common yet debilitating symptom in patients with neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorder (NMOSD), especially those with longitudinally extensive transverse myelitis. Although carbamazepine is an effective treatment, it poses the risk of severe adverse reactions, such as Steven-Johnson syndrome (SJS). “Cannabidiol (
“Cannabidiol ( “Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds with a high affinity for cannabinoid receptors affecting the central nervous system through the release of neurotransmitters. However, the current knowledge related to the role of such compounds in the regulation of cellular aging is limited. This study aimed to investigate the effect of cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol on the function of aged pancreatic islets.
“Cannabinoids are the chemical compounds with a high affinity for cannabinoid receptors affecting the central nervous system through the release of neurotransmitters. However, the current knowledge related to the role of such compounds in the regulation of cellular aging is limited. This study aimed to investigate the effect of cannabidiol and tetrahydrocannabinol on the function of aged pancreatic islets. “Despite widespread legalization, the impact of medicinal cannabis use on patient-level health and quality of life (QOL) has not been carefully evaluated.
“Despite widespread legalization, the impact of medicinal cannabis use on patient-level health and quality of life (QOL) has not been carefully evaluated. “The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.
“The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.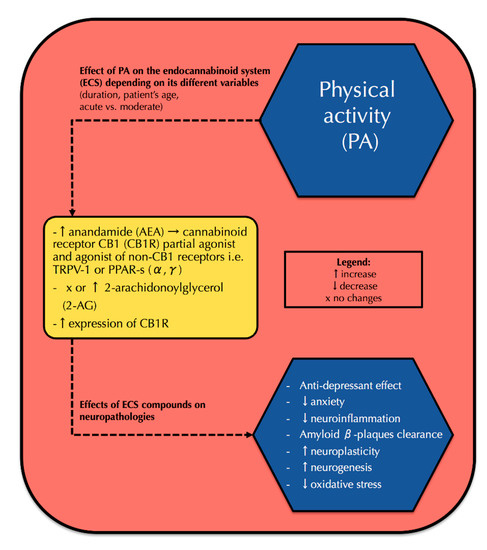
 “The emergence of multi-drug resistant bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) causes a major threat to public health due to its limited therapeutic options.
“The emergence of multi-drug resistant bacteria such as methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) causes a major threat to public health due to its limited therapeutic options.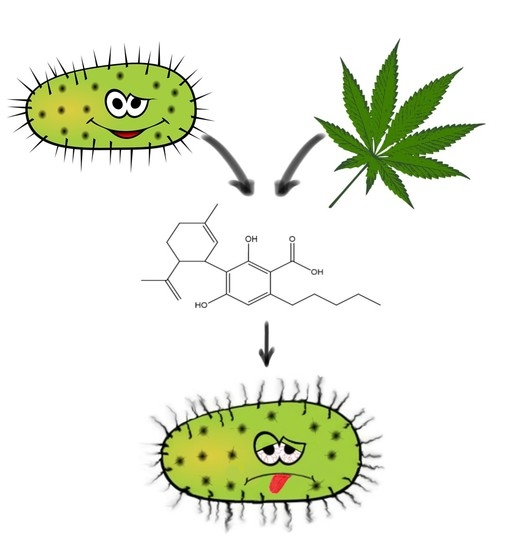
 “Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a frequent cause of abdominal pain and altered bowel habits, which is associated with significant healthcare utilization.
“Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a frequent cause of abdominal pain and altered bowel habits, which is associated with significant healthcare utilization. “Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) is the main phytocannabinoid in fiber and seed-oil hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) plants, but its potential health-related capabilities have been masked for years by a greater scientific interest towards its neutral derivative cannabidiol (CBD). This review aims to collect from the literature and critically discuss all the information about this molecule, starting from its biosynthesis, and focusing on its bioactivity, as an anti-inflammatory, anti-emetic, anti-convulsant, and anti-cancerogenic drug. Furthermore, in the awareness that, despite its multiple bioactive effects, currently poor efforts have been made to achieve its reliable purification, herein, we propose a relatively simple, fast, and inexpensive procedure for its recovery from pollen of industrial hemp cultivars. Spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques allowed us to unequivocally identify pure isolated CBDA and to distinguish it from the constitutional isomer tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA-A).”
“Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) is the main phytocannabinoid in fiber and seed-oil hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) plants, but its potential health-related capabilities have been masked for years by a greater scientific interest towards its neutral derivative cannabidiol (CBD). This review aims to collect from the literature and critically discuss all the information about this molecule, starting from its biosynthesis, and focusing on its bioactivity, as an anti-inflammatory, anti-emetic, anti-convulsant, and anti-cancerogenic drug. Furthermore, in the awareness that, despite its multiple bioactive effects, currently poor efforts have been made to achieve its reliable purification, herein, we propose a relatively simple, fast, and inexpensive procedure for its recovery from pollen of industrial hemp cultivars. Spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques allowed us to unequivocally identify pure isolated CBDA and to distinguish it from the constitutional isomer tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA-A).”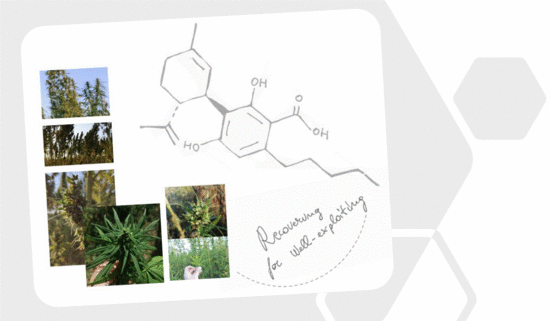
 “Identifying candidate drugs effective in the new coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is crucial,
“Identifying candidate drugs effective in the new coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is crucial,