“Background: Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid constituent of Cannabis sativa with pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties. With the emphasis on natural ingredients in cosmetics, CBD has become a new cosmetic ingredient due to its ability to alleviate inflammation. However, in-depth studies that directly compare the effective mechanism and the therapeutic potential of CBD are still needed.
Purpose: The aim of the present study was to investigate the anti-inflammatory effect of CBD in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages and compare it to dexamethasone (DEX).
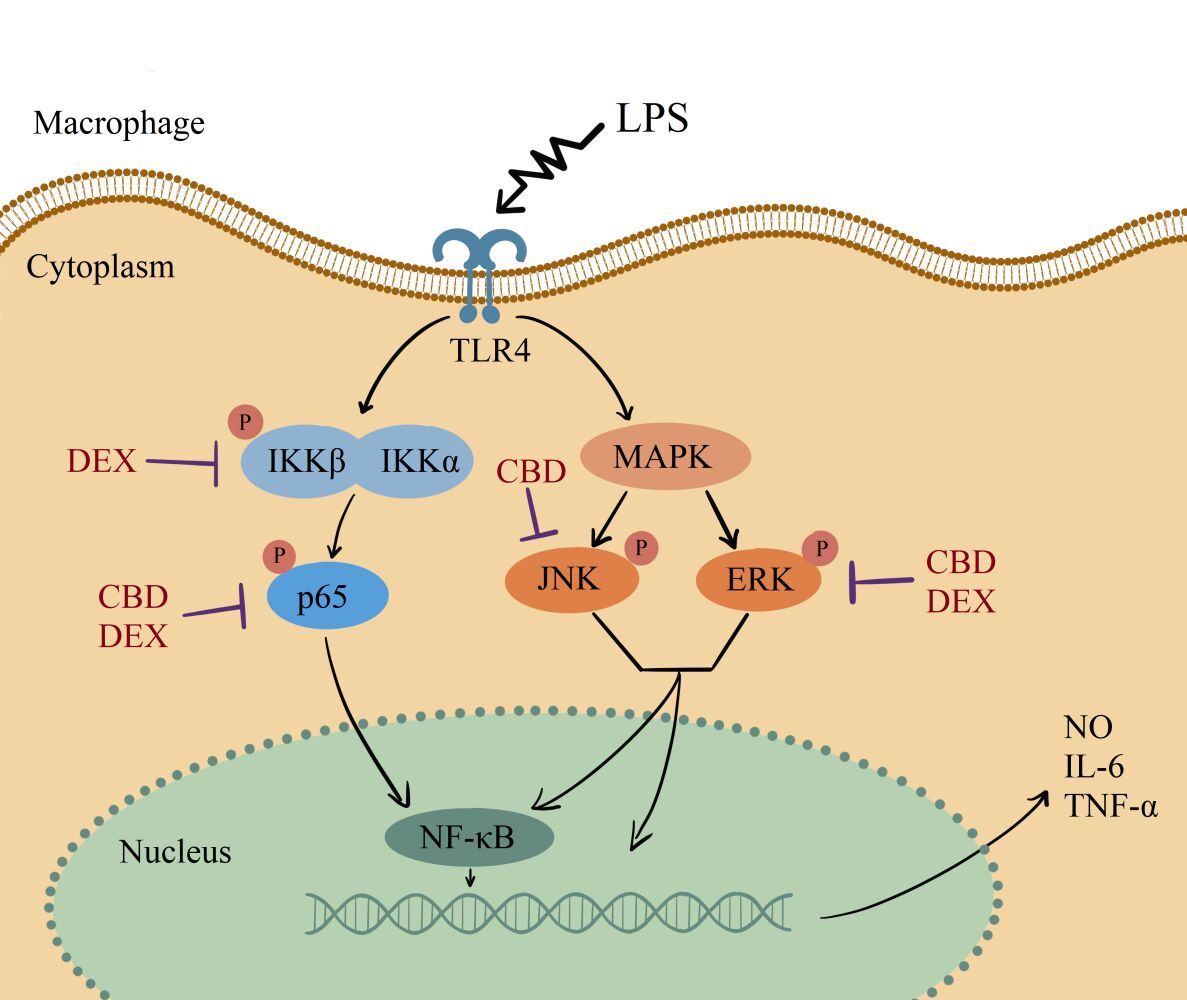
Methods: RAW264.7 macrophages in the logarithmic growth phase were incubated in the presence or absence of LPS. After that, the production of nitric oxide (NO), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were measured. A luciferase reporter assay for nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) was performed, and the phosphorylation levels of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and NF-κB signaling pathways were measured.
Results: The present study indicated that CBD had a similar anti-inflammatory effect to DEX by attenuating the LPS-induced production of NO, IL-6, and TNF-α. However, only CBD attenuated JNK phosphorylation levels, and only DEX attenuated IKK phosphorylation levels.
Conclusion: These results suggested that CBD and DEX exhibit similar anti-inflammatory effects on LPS-induced RAW264.7 macrophages mainly through suppressing the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways, but with different intracellular mechanisms. These findings suggested that CBD may be considered a natural anti-inflammatory agent for protecting skin from immune disorders.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36159203/
“As alternative and complementary therapies grow in dermatology, plant extracts such as CBD have garnered significant attention in dermatology. The present study provided new insight of CBD against LPS-induced inflammation. Our results suggested that CBD and DEX suppress the LPS-induced activation of the MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways in RAW264.7 cells through different intracellular components, indicating that the anti-inflammatory biological mechanism of CBD is different from other immuno-suppressants. Because macrophages exert various pro-inflammatory functions through multiple intracellular pathways, further in vivo and in vitro studies are necessary to enrich the theoretical knowledge of CBD and promote its future clinical application.”
