
“Persistent deficits in social communication and interaction, and restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior, interests or activities, are the core items characterizing autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Strong inflammation states have been reported to be associated with ASD.
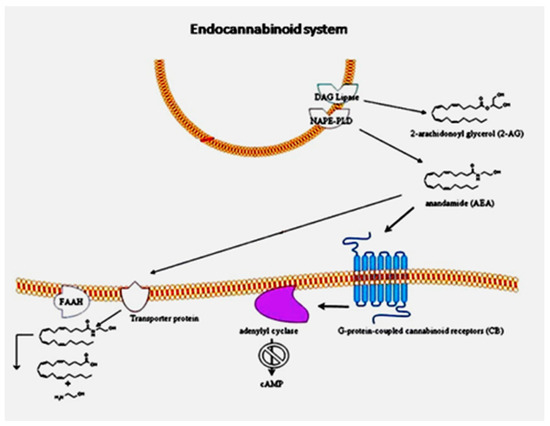
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) may be involved in ASD pathophysiology. This complex network of lipid signaling pathways comprises arachidonic acid and 2-arachidonoyl glycerol-derived compounds, their G-protein-coupled receptors (cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2) and the associated enzymes. Alterations of the ECS have been reported in both the brain and the immune system of ASD subjects.
ASD children show low EC tone as indicated by low blood levels of endocannabinoids. Acetaminophen use has been reported to be associated with an increased risk of ASD. This drug can act through the ECS to produce analgesia. It may be that acetaminophen use in children increases the risk for ASD by interfering with the ECS.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33805951/
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/26/7/1845
“Can autism be triggered by acetaminophen activation of the endocannabinoid system? Acetaminophen use in children has been associated with increased autism risk. Recent evidence suggests that acetaminophen’s analgesic actions result from activation of the endocannabinoid system, and activation of this system can have neuromodulatory consequences during development. This investigation was performed to determine if there is evidence to support the hypothesis that acetaminophen use can trigger autism by activation of the endocannabinoid system.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/20628445/
“Paracetamol (N-acetyl-p-aminophenol (APAP), otherwise known as acetaminophen) is the active ingredient in more than 600 medications used to relieve mild to moderate pain and reduce fever. APAP is widely used by pregnant women as governmental agencies, including the FDA and EMA, have long considered APAP appropriate for use during pregnancy when used as directed. However, increasing experimental and epidemiological research suggests that prenatal exposure to APAP might alter fetal development, which could increase the risks of some neurodevelopmental, reproductive and urogenital disorders.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34556849/
“Healing autism spectrum disorder with cannabinoids: a neuroinflammatory story” https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33358985/
