




 “∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system.
“∆ 9 -Tetrahydrocannabinol (∆9 -THC), the active phytocannabinoid in cannabis, is virtually an adjunct to the endogenous endocannabinoid signaling system.
By interacting with G-protein-coupled receptors CB1 and CB2, ∆9 -THC affects peripheral and central circulation by lowering sympathetic activity, altering gene expression, cell proliferation, and differentiation, decreasing leukocyte migration, modulating neurotransmitter release thereby modulating cardiovascular functioning, tumorigenesis, immune responses, behavioral and locomotory activities respectively.
∆ 9 -THC is effective in suppressing chemotherapy-induced vomiting, retards malignant tumor growth, inhibits metastasis, and promotes apoptosis. Other mechanisms involved are targeting cell cycle at the G2-M phase in human breast cancer, downregulation of E2F transcription factor 1 (E2F1) in human glioblastoma multiforme, and stimulation of ER stress-induced autophagy.
∆ 9 -THC also plays a role in ameliorating neuroinflammation, excitotoxicity, neuroplasticity, trauma, and stroke and is associated with reliving childhood epilepsy, brain trauma, and neurodegenerative diseases.
∆9 -THC via CB1 receptors affects nociception, emotion, memory, and reduces neuronal excitability and excitotoxicity in epilepsy. It also increases renal blood flow, reduces intraocular pressure via a sympathetic pathway, and modulates hormonal release, thereby decreasing the reproductive function and increasing glucose metabolism.
Versatile medical marijuana has stimulated abundant research demonstrating substantial therapeutic promise, suggesting the possibilities of first-in-class drugs in diverse therapeutic segments. In this review, we represent the current pharmacological status of the phytocannabinoid, ∆ 9 -THC, and synthetic analogs in cancer, cardiovascular, and neurodegenerative disorders.”
 “Diabetes mellitus (DM), a metabolic disorder is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases worldwide across developed as well as developing nations. Hyperglycemia is the core feature of the type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), following insulin deficiency and impaired insulin secretion or sensitivity leads insulin resistance (IR), respectively. Genetic and environmental factors attributed to the pathogenesis of DM and various therapeutic strategies are available for the prevention and treatment of T2DM.
“Diabetes mellitus (DM), a metabolic disorder is one of the most prevalent chronic diseases worldwide across developed as well as developing nations. Hyperglycemia is the core feature of the type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), following insulin deficiency and impaired insulin secretion or sensitivity leads insulin resistance (IR), respectively. Genetic and environmental factors attributed to the pathogenesis of DM and various therapeutic strategies are available for the prevention and treatment of T2DM.
Among the numerous therapeutic approaches, the health effects of dietary/nutraceutical approach due to the presence of bioactive constituents, popularly termed phytochemicals are receiving special interest for pharmacological effects and therapeutic benefits. The phytochemicals classes, in particular sesquiterpenes received attention because of potent antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antihyperglycemic effects and health benefits mediating modulation of enzymes, receptors, and signaling pathways deranged in DM and its complications.
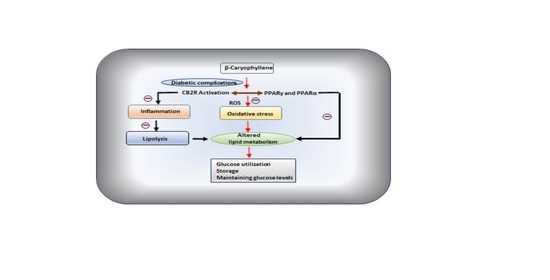
One of the terpene compounds, β-caryophyllene (BCP), received enormous attention because of its abundant occurrence, non-psychoactive nature, and dietary availability through consumption of edible plants including spices. BCP exhibit selective full agonism on cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2R), an important component of endocannabinoid system, and plays a role in glucose and lipid metabolism and represents the newest drug target for chronic inflammatory diseases.
Many studies demonstrated its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, organoprotective, and antihyperglycemic properties. In the present review, the plausible therapeutic potential of BCP in diabetes and associated complications has been comprehensively elaborated based on experimental and a few clinical studies available. Further, the pharmacological and molecular mechanisms of BCP in diabetes and its complications have been represented using synoptic tables and schemes.
Given the safe status, abundant natural occurrence, oral bioavailability, dietary use and pleiotropic properties modulating receptors and enzymes, BCP appears as a promising molecule for diabetes and its complications.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32998300/
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/12/10/2963
“β-caryophyllene (BCP) is a common constitute of the essential oils of numerous spice, food plants and major component in Cannabis.” http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23138934
 “Fish oil (FO) and phytocannabinoids have received considerable attention for their intestinal anti-inflammatory effects.
“Fish oil (FO) and phytocannabinoids have received considerable attention for their intestinal anti-inflammatory effects.
We investigated whether the combination of FO with cannabigerol (CBG) and cannabidiol (CBD) or a combination of all three treatments results in a more pronounced intestinal antiinflammatory action compared to the effects achieved separately.
Colitis was induced in mice by 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (DNBS). CBD and CBG levels were detected and quantified by liquid chromatography coupled with time of flight mass spectrometry and ion trap mass spectrometry (LC-MS-IT-TOF). Endocannabinoids and related mediators were assessed by LC-MS. DNBS increased colon weight/colon length ratio, myeloperoxidase activity, interleukin-1β, and intestinal permeability.
CBG, but not CBD, given by oral gavage, ameliorated DNBS-induced colonic inflammation. FO pretreatment (at the inactive dose) increased the antiinflammatory action of CBG and rendered oral CBD effective while reducing endocannabinoid levels. Furthermore, the combination of FO, CBD, and a per se inactive dose of CBG resulted in intestinal anti-inflammatory effects. Finally, FO did not alter phytocannabinoid levels in the serum and in the colon.
By highlighting the apparent additivity between phytocannabinoids and FO, our preclinical data support a novel strategy of combining these substances for the potential development of a treatment of inflammatory bowel disease.”
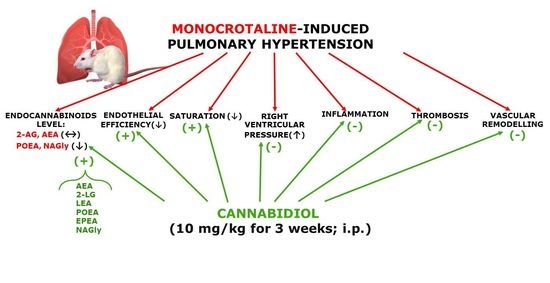
 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is known for its vasorelaxant (including in the human pulmonary artery), anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of our study was to examine the potential preventive effect of chronic CBD administration (10 mg/kg/day for three weeks) on monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) rats.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is known for its vasorelaxant (including in the human pulmonary artery), anti-proliferative and anti-inflammatory properties. The aim of our study was to examine the potential preventive effect of chronic CBD administration (10 mg/kg/day for three weeks) on monocrotaline (MCT)-induced pulmonary hypertension (PH) rats.
PH was connected with elevation of right ventricular systolic pressure; right ventricle hypertrophy; lung edema; pulmonary artery remodeling; enhancement of the vasoconstrictor and decreasing vasodilatory responses; increases in plasma concentrations of tissue plasminogen activator, plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 and leukocyte count; and a decrease in blood oxygen saturation.
CBD improved all abovementioned changes induced by PH except right ventricle hypertrophy and lung edema. In addition, CBD increased lung levels of some endocannabinoids (anandamide, N-arachidonoyl glycine, linolenoyl ethanolamide, palmitoleoyl ethanolamide and eicosapentaenoyl ethanolamide but not 2-arachidonoylglycerol). CBD did not affect the cardiopulmonary system of control rats or other parameters of blood morphology in PH.
Our data suggest that CBD ameliorates MCT-induced PH in rats by improving endothelial efficiency and function, normalization of hemostatic alterations and reduction of enhanced leukocyte count determined in PH. In conclusion, CBD may be a safe, promising therapeutic or adjuvant therapy agent for the treatment of human pulmonary artery hypertension.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32992900/
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/19/7077
 “Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.
“Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.
Oxygen-ozone (O2/O3) therapy is an emerging alternative tool for the treatment of several clinical disorders. O2/O3 therapy has been found to ameliorate mechanisms promoting chronic pain and inflammation, including hypoxia, inflammatory mediators, and infection.
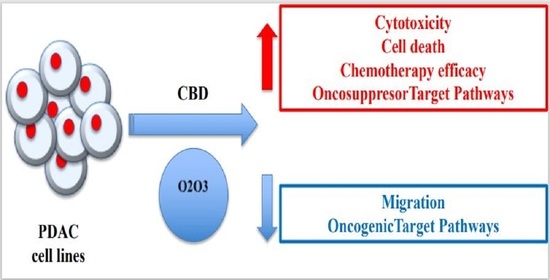
The advantages of using cannabinoids have been evaluated in vitro and in vivo models of several human cancers. Regarding PDAC, activation of cannabinoid receptors was found to induce pancreatic cancer cell apoptosis without affecting the normal pancreas cells.
In a murine model of PDAC, a combination of cannabidiol (CBD) and gemcitabine increased survival length by nearly three times. Herein, we evaluate the anticancer effect of CBD and O2/O3, alone or in combination, on two human PDAC cell lines, PANC-1 and MiaPaCa-2, examining expression profiles of 92 pancreatic adenocarcinoma associated genes, cytotoxicity, migration properties, and cell death. Finally, we assess the combination effects with gemcitabine and paclitaxel.
Summarizing, for the first time the antitumoral effect of combined therapy with CBD and oxygen-ozone therapy in PDAC is evidenced.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32992648/
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/12/10/2774
 “Cannabidiol (CBD), a natural occurring phytocannabinoid, is used extensively in consumer products ranging from foods to shampoos, topical oils and lotions.
“Cannabidiol (CBD), a natural occurring phytocannabinoid, is used extensively in consumer products ranging from foods to shampoos, topical oils and lotions.
Several studies demonstrated the anti-inflammatory and antioxidative properties of cannabidiol. Nevertheless, the role of cannabidiol use in sunscreens is largely unknown as no studies on its effect on keratinocytes or melanocytes exist. As such, we aimed to explore the effect of CBD on keratinocyte and melanocyte viability following ultraviolet B (UVB) irradiation.
CBD exhibited a dose-dependent protective effect on both keratinocytes and melanocyte viability. Further, since CBD does not demonstrate absorption in the UVB spectra, we speculate that the protective effect is due to reduction in reactive oxygen species.
To our knowledge, this is the first study demonstrating the protective effect of CBD on keratinocytes and melanocytes irradiated with UVB.”
 “The prevalence of mild traumatic brain injury is highest amongst the adolescent population and can lead to complications including neuroinflammation and excitotoxicity.
“The prevalence of mild traumatic brain injury is highest amongst the adolescent population and can lead to complications including neuroinflammation and excitotoxicity.
Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol, the main psychoactive component of cannabis, is known to have anti-inflammatory properties and serves as a neuroprotective agent against excitotoxicity.
Thus, we investigated the effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol on recovery when administered either prior to or following repeated mild brain injuries.
We hypothesized that, in both experiments, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol administration would provide neuroprotection against mild injury outcomes and confer therapeutic benefit.
Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol administration following repeated mild traumatic brain injury was beneficial to three of the six behavioural outcomes affected by injury (reducing anxiety and depressive-like behaviours while also mitigating injury-induced deficits in short-term working memory). Δ9-Tetrahydrocannabinol administration following injury also showed beneficial effects on the expression of Cnr1, Comt and Vegf-2R in the hippocampus, nucleus accumbens and prefrontal cortex.
There were no notable benefits of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol when administered prior to injury, suggesting that Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol may have potential therapeutic benefit on post-concussive symptomology when administered post-injury, but not pre-injury.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32954298/
“Overall, this study suggests that THC has potential therapeutic efficacy for the treatment of RmTBI-induced symptomology but requires additional examination.”
https://academic.oup.com/braincomms/article/2/1/fcaa042/5819138
 “Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with metabolic syndrome, which often includes obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Several studies in mice and humans have implicated the involvement of the gut microbiome in NAFLD.
“Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is associated with metabolic syndrome, which often includes obesity, diabetes, and dyslipidemia. Several studies in mice and humans have implicated the involvement of the gut microbiome in NAFLD.
While cannabis may potentially be beneficial for treating metabolic disorders such as NAFLD, the effects of cannabis on liver diseases and gut microbiota profile are yet to be addressed. In this study, we evaluated the therapeutic effects of cannabis strains with different cannabinoid profiles on NAFLD progression.
Conclusions: The results of this study indicate that the administration of cannabis containing elevated levels of THC may help ameliorate symptoms of NAFLD, whereas administration of CBD-rich cannabis extracts may cause a proinflammatory effect in the liver, linked with an unfavorable change in the microbiota profile. Our preliminary data suggest that these effects are mediated by mechanisms other than increased expression of the endocannabinoid receptors cannabinoid receptor 1 (CB1) and CB2.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32923658/
“The results of this study provide an indication that administration of certain strains of cannabis, preferably with a higher THC level, may be helpful in treating certain symptoms of metabolic syndrome, which include preventing the development and/or ameliorating the symptoms of NAFLD.”
 “Natural cannabinoids may have beneficial effects on various tissues and functions including a positive influence on the immune system and the inflammatory process.
“Natural cannabinoids may have beneficial effects on various tissues and functions including a positive influence on the immune system and the inflammatory process.
The purpose of this study was to investigate the effects of natural cannabinoids on the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-stimulated whole human blood cells.
Levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-6 (IL-6), and tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were measured before and after exposure of LPS-stimulated whole blood to different concentrations of Cannabidiol (CBD) or a combination of CBD and Tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) extract.
LPS stimulated the production of the pro-inflammatory cytokines. Exposure to both CBD and CBD/THC extracts significantly suppressed cytokine production in a dose-dependent manner. Exposure to cannabinoid concentrations of 50 μg/ml or 100 μg/ml resulted in a near-complete inhibition of cytokine production.
This study demonstrates that natural cannabinoids significantly suppress pro-inflammatory cytokine production in LPS-stimulated whole blood in a dose-dependent manner. The use of human whole blood, rather than isolated specific cells or tissues, may closely mimic an in vivo sepsis environment.
These findings highlight the role that natural cannabinoids may play in suppressing inflammation and call for additional studies of their use as possible novel therapeutic agents for acute and chronic inflammation.”