 “Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is evolving across the world and new treatments are urgently needed as with vaccines to prevent the illness and stem the contagion. The virus affects not only the lungs but also other tissues, thus lending support to the idea that COVID-19 is a systemic disease. The current vaccine and treatment development strategies ought to consider such systems medicine perspectives rather than a narrower focus on the lung infection only.
“Coronavirus disease-2019 (COVID-19) pandemic caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) is evolving across the world and new treatments are urgently needed as with vaccines to prevent the illness and stem the contagion. The virus affects not only the lungs but also other tissues, thus lending support to the idea that COVID-19 is a systemic disease. The current vaccine and treatment development strategies ought to consider such systems medicine perspectives rather than a narrower focus on the lung infection only.
COVID-19 is associated with elevated levels of the inflammatory cytokines such as interleukin-6 (IL-6), IL-10, and interferon-gamma (IFN-γ). Elevated levels of cytokines and the cytokine storm have been linked to fatal disease. This suggests new therapeutic strategies through blocking the cytokine storm. IL-6 is one of the major cytokines associated with the cytokine storm. IL-6 is also known to display pleiotropic/diverse pathophysiological effects. We suggest the blockage of IL-6 signaling and its downstream mediators such as Janus kinases (JAKs), and signal transducer and activators of transcription (STATs) offer potential hope for the treatment of severe cases of COVID-19. Thus, repurposing of already approved IL-6-JAK-STAT signaling inhibitors as well as other anti-inflammatory drugs, including dexamethasone, is under development for severe COVID-19 cases.
We conclude this expert review by highlighting the potential role of precision herbal medicines, for example, the Cannabis sativa, provided that omics technologies can be utilized to build a robust scientific evidence base on their clinical safety and efficacy. Precision herbal medicine buttressed by omics systems science would also help identify new molecular targets for drug discovery against COVID-19.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32857671/
“Cannabis sativa is a plant known to contain anti-inflammatory compounds such as cannabinoid cannabidiol. In addition to other compounds such as terpenes, these compounds have been suggested to have potential anticancer properties. Like other herbal plants, we suggest C. sativa warrants further mechanistic research in relationship to putative effects in COVID-19.”

 “Cannflavins are a group of prenylflavonoids derived from Cannabis sativa L.. Cannflavin A (CFL-A), B (CFL-B) and C (CFL-C) have been heralded for their anti-inflammatory properties in pre-clinical evaluations.
“Cannflavins are a group of prenylflavonoids derived from Cannabis sativa L.. Cannflavin A (CFL-A), B (CFL-B) and C (CFL-C) have been heralded for their anti-inflammatory properties in pre-clinical evaluations. “Keratinocytes, the major cell type of the epidermis, are particularly sensitive to environmental factors including exposure to sunlight and chemical agents. Since oxidative stress may arise as a result of these factors, compounds are actively sought that can act as protective agents.
“Keratinocytes, the major cell type of the epidermis, are particularly sensitive to environmental factors including exposure to sunlight and chemical agents. Since oxidative stress may arise as a result of these factors, compounds are actively sought that can act as protective agents. “Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading fast all around the world with more than fourteen millions of detected infected cases and more than 600.000 deaths by 20th July 2020. While scientist are working to find a vaccine, current epidemiological data shows that the most common comorbidities for patients with the worst prognosis, hypertension and diabetes, are often treated with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs).
“Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading fast all around the world with more than fourteen millions of detected infected cases and more than 600.000 deaths by 20th July 2020. While scientist are working to find a vaccine, current epidemiological data shows that the most common comorbidities for patients with the worst prognosis, hypertension and diabetes, are often treated with angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs). “Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disorder linked to various converging toxic mechanisms. Evidence suggests that hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation and excitotoxicity, all of which play important roles in the onset and progression of AD pathogenesis.
“Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is a multifactorial neurodegenerative disorder linked to various converging toxic mechanisms. Evidence suggests that hyperglycemia induces oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, inflammation and excitotoxicity, all of which play important roles in the onset and progression of AD pathogenesis. “Cannabis has been used for its medicinal purposes since ancient times. Its consumption leads to the activation of Cannabis receptors CB1 and CB2 that, through specific mechanisms can lead to modulation and progression of inflammation or repair. The novel findings are linked to the medical use of Cannabis in gastrointestinal (GI) system.
“Cannabis has been used for its medicinal purposes since ancient times. Its consumption leads to the activation of Cannabis receptors CB1 and CB2 that, through specific mechanisms can lead to modulation and progression of inflammation or repair. The novel findings are linked to the medical use of Cannabis in gastrointestinal (GI) system. “Purpose of review: To evaluate the impact of flavonoids and cannabinoids as anti-inflammatory and antiallergic treatments on the anterior surface of the eye.
“Purpose of review: To evaluate the impact of flavonoids and cannabinoids as anti-inflammatory and antiallergic treatments on the anterior surface of the eye. “Alcohol is a psychoactive substance highly used worldwide, whose harmful use might cause a broad range of mental and behavioural disorders. Underlying brain impact, the neuroinflammatory response induced by alcohol is recognised as a key contributing factor in the progression of other neuropathological processes, such as neurodegeneration. These sequels are determined by multiple factors, including age of exposure.
“Alcohol is a psychoactive substance highly used worldwide, whose harmful use might cause a broad range of mental and behavioural disorders. Underlying brain impact, the neuroinflammatory response induced by alcohol is recognised as a key contributing factor in the progression of other neuropathological processes, such as neurodegeneration. These sequels are determined by multiple factors, including age of exposure.
 “Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.
“Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.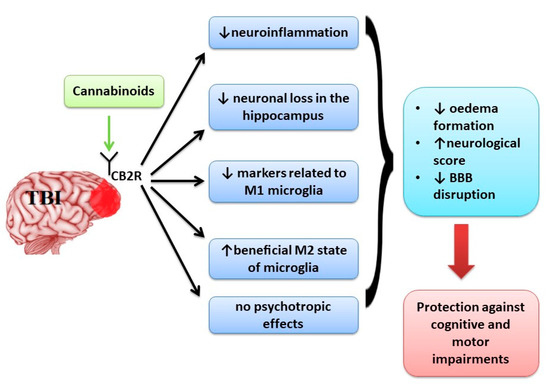
 “Diet and lifestyle-induced dysregulated lipid metabolism have been implicated in fatty liver disease. Chronic redox modulation and hepatic inflammation are key pathological mediators and hallmarks of fatty liver disease associated liver steatosis and steatohepatitis.
“Diet and lifestyle-induced dysregulated lipid metabolism have been implicated in fatty liver disease. Chronic redox modulation and hepatic inflammation are key pathological mediators and hallmarks of fatty liver disease associated liver steatosis and steatohepatitis.