“So far, no vaccine has been successfully developed and there is no effective treatment of COVID-19.
“So far, no vaccine has been successfully developed and there is no effective treatment of COVID-19.
Since intensive inflammation leads to disease-induced morbidity and mortality, inhibition of the hyperinflammatory response is a definitive drug therapy objective.
Certainly, there is an urgent need for a substance that can potentially counter the effects of the virus and alleviate the symptoms and severity of the disease.
Could opioids/cannabinoids be an effective treatment for COVID-19?
Since opioids/cannabinoids receptors-based drugs can modulate immune cell migration and cytokine/chemokine secretion, they represent a promising pharmacological platform for developing anti-inflammatory therapeutics.
Therefore in the absence of effective treatments to decrease the damage associated with COVID-19 especially in those admitted to the ICU and suffer from exaggerated inflammatory response, opioids/cannabinoids receptor agonists might potentially open up an effective therapeutic approach in COVID-19 infection.
It is interesting to remember that physicians in the late 19th century used anodynes of opium tincture as a treatment of ‘bronchitis’ and other ailments in infants and children, as case reports and experience ‘demonstrated the efficacy’ of the concoction in controlling coughing and facilitating breathing.
Also, today some products of cannabinoids are used to modulate an inflammatory response. This permits us to rediscover the past and utilize the present, with hopes of finding the missing links in the pathophysiology of COVID-19, and raises the issue of opioids/cannabinoids utilization in the context of COVID-19.
It is suggested that clinical trials could be conducted on opioids/cannabinoids products with immunomodulatory activity. We hope that, with great efforts, scientific support, and sharing of information, the overcoming of COVID-19 will come soon.”
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/17476348.2020.1787836

 “HIV/SIV-associated oral mucosal disease/dysfunction (HAOMD) (gingivitis/periodontitis/salivary adenitis) represents a major comorbidity affecting HIV patients on anti-retroviral therapy.
“HIV/SIV-associated oral mucosal disease/dysfunction (HAOMD) (gingivitis/periodontitis/salivary adenitis) represents a major comorbidity affecting HIV patients on anti-retroviral therapy. “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid derived from Cannabis sativa. CBD initially drew scientific interest due to its anticonvulsant properties but increasing evidence of other therapeutic effects has attracted the attention of additional clinical and non-clinical populations, including athletes.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-intoxicating cannabinoid derived from Cannabis sativa. CBD initially drew scientific interest due to its anticonvulsant properties but increasing evidence of other therapeutic effects has attracted the attention of additional clinical and non-clinical populations, including athletes. “Hempseeds, the edible fruits of the Cannabis sativa L. plant, were initially considered a by-product of the hemp technical fibre industry. Nowadays, following the restorationing of the cultivation of C. sativa L. plants containing an amount of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) <0.3% or 0.2% (industrial hemp) there is a growing interest for the hempseeds production due to their high nutritional value and functional features.
“Hempseeds, the edible fruits of the Cannabis sativa L. plant, were initially considered a by-product of the hemp technical fibre industry. Nowadays, following the restorationing of the cultivation of C. sativa L. plants containing an amount of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) <0.3% or 0.2% (industrial hemp) there is a growing interest for the hempseeds production due to their high nutritional value and functional features.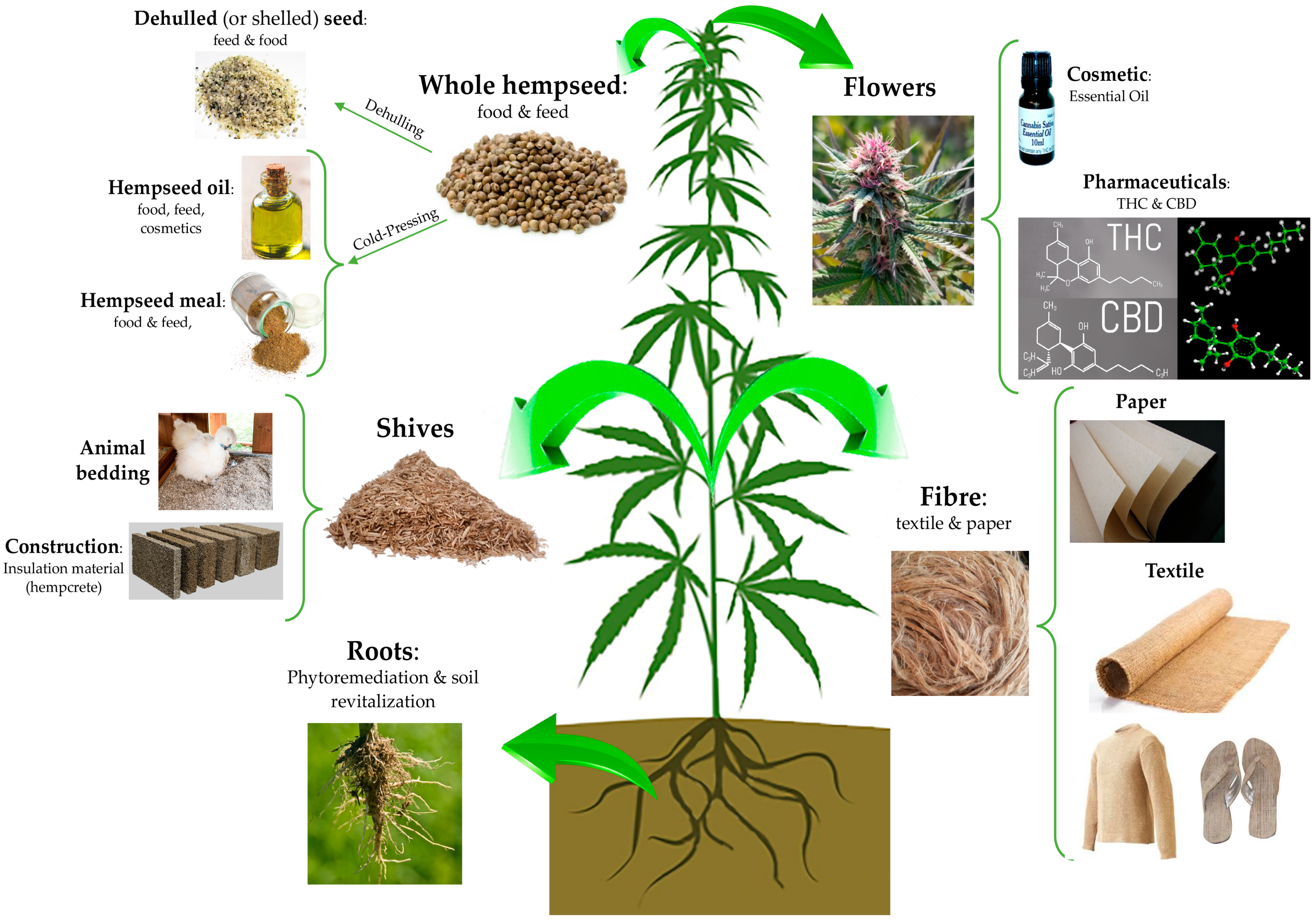
 “Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening complication that can ensue following Staphylococcus aureus infection. The enterotoxin produced by these bacteria (SEB) acts as a superantigen thereby activating a large proportion of T cells leading to cytokine storm and severe lung injury.
“Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS) is a life-threatening complication that can ensue following Staphylococcus aureus infection. The enterotoxin produced by these bacteria (SEB) acts as a superantigen thereby activating a large proportion of T cells leading to cytokine storm and severe lung injury. “Studies have reported changes in the endocannabinoid system in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), playing a role in the pathophysiology of AD. Cannabinoids have been shown to have neuroprotective properties, reduce neuroinflammation, and enhance neurogenesis. Evidence suggests that the utilization of marijuana products containing both tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) or CBD alone have been effective and safe for use in older people with agitation associated with dementia.
“Studies have reported changes in the endocannabinoid system in the brain of patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD), playing a role in the pathophysiology of AD. Cannabinoids have been shown to have neuroprotective properties, reduce neuroinflammation, and enhance neurogenesis. Evidence suggests that the utilization of marijuana products containing both tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD) or CBD alone have been effective and safe for use in older people with agitation associated with dementia. “Objective: To determine whether cannabis may reduce HIV-related persistent inflammation, we evaluated the relationship of cannabis use in people with HIV (PWH) to inflammatory cytokines in CSF and blood plasma.
“Objective: To determine whether cannabis may reduce HIV-related persistent inflammation, we evaluated the relationship of cannabis use in people with HIV (PWH) to inflammatory cytokines in CSF and blood plasma. “The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.
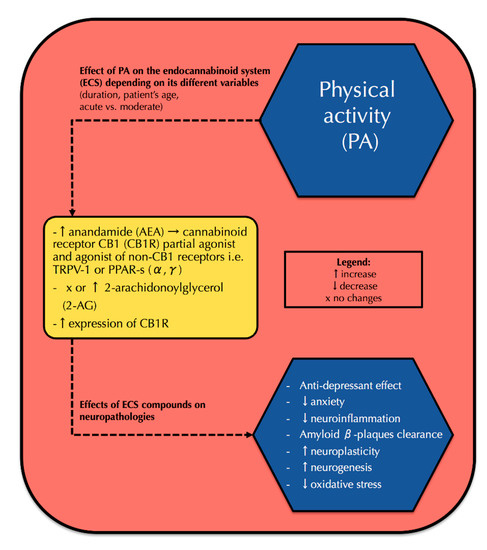
“The worldwide prevalence of neurological and neurodegenerative disorders, such as depression or Alzheimer’s disease, has spread extensively throughout the last decades, becoming an enormous health issue.