
The effects of the active compound of cannabis, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), on gut motility and tone have been studied in several experimental models. It is unknown whether these effects correlate with improved healthcare utilization among cannabis users.
The purpose of this study is to evaluate the impact of cannabis use on inpatient length of stay and resource utilization for patients with a primary discharge diagnosis of IBS.
Cannabis users were less likely to have the following: upper gastrointestinal endoscopy (17.9% vs. 26.1%; adjusted odds ratio [aOR]: 0.51 [0.36 to 0.73]; p<0.001) and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy (21.1% vs. 28.7%; aOR: 0.54 [0.39 to 0.75]; p<0.001). Additionally, cannabis users had shorter length of stay (2.8 days vs. 3.6 days; p=0.004) and less total charges (US$20,388 vs. US$23,624). There was no difference in the frequency of CT abdomen performed.
Cannabis use may decrease inpatient healthcare utilization in IBS patients. These effects could possibly be through the effect of cannabis on the endocannabinoid system.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32528750/
“Our study provides evidence to suggest that cannabis use may decrease healthcare utilization and costs among hospitalized patients with IBS. These findings are likely attributable to the effects of cannabis’ active compound, THC, on gastrointestinal motility and colonic compliance. The role of cannabis in the treatment for IBS has potential for significant impact at the individual and population level given the burden of IBS on individual quality of life and healthcare expenditures.”

 “Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) is the main phytocannabinoid in fiber and seed-oil hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) plants, but its potential health-related capabilities have been masked for years by a greater scientific interest towards its neutral derivative cannabidiol (CBD). This review aims to collect from the literature and critically discuss all the information about this molecule, starting from its biosynthesis, and focusing on its bioactivity, as an anti-inflammatory, anti-emetic, anti-convulsant, and anti-cancerogenic drug. Furthermore, in the awareness that, despite its multiple bioactive effects, currently poor efforts have been made to achieve its reliable purification, herein, we propose a relatively simple, fast, and inexpensive procedure for its recovery from pollen of industrial hemp cultivars. Spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques allowed us to unequivocally identify pure isolated CBDA and to distinguish it from the constitutional isomer tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA-A).”
“Cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) is the main phytocannabinoid in fiber and seed-oil hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) plants, but its potential health-related capabilities have been masked for years by a greater scientific interest towards its neutral derivative cannabidiol (CBD). This review aims to collect from the literature and critically discuss all the information about this molecule, starting from its biosynthesis, and focusing on its bioactivity, as an anti-inflammatory, anti-emetic, anti-convulsant, and anti-cancerogenic drug. Furthermore, in the awareness that, despite its multiple bioactive effects, currently poor efforts have been made to achieve its reliable purification, herein, we propose a relatively simple, fast, and inexpensive procedure for its recovery from pollen of industrial hemp cultivars. Spectroscopic and spectrometric techniques allowed us to unequivocally identify pure isolated CBDA and to distinguish it from the constitutional isomer tetrahydrocannabinolic acid (THCA-A).”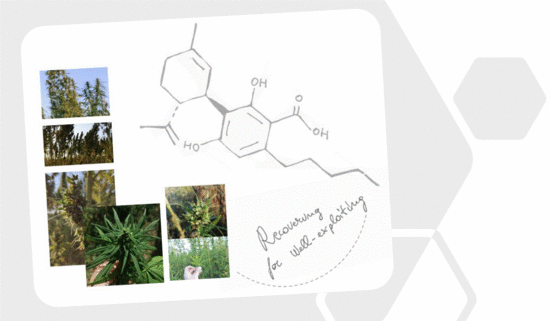
 “Identifying candidate drugs effective in the new coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is crucial,
“Identifying candidate drugs effective in the new coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) is crucial, 
 “In late December 2019, a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2 or CoV-19) appeared in Wuhan, China, causing a global pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 causes mild to severe respiratory tract inflammation, often developing into lung fibrosis with thrombosis in pulmonary small vessels and causing even death. COronaVIrus Disease (COVID-19) patients manifest exacerbated inflammatory and immune responses, cytokine storm, prevalence of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages and increased levels of resident and circulating immune cells. Men show higher susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection than women, likely due to estrogens production. The protective role of estrogens, as well as an immune-suppressive activity that limits the excessive inflammation, can be mediated by cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2). The role of this receptor in modulating inflammation and immune response is well documented in fact in several settings. The stimulation of CB2 receptors is known to limit the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, shift the macrophage phenotype towards the anti-inflammatory M2 type and enhance the immune-modulating properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. For these reasons, we hypothesize that CB2 receptor can be a therapeutic
“In late December 2019, a novel coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2 or CoV-19) appeared in Wuhan, China, causing a global pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 causes mild to severe respiratory tract inflammation, often developing into lung fibrosis with thrombosis in pulmonary small vessels and causing even death. COronaVIrus Disease (COVID-19) patients manifest exacerbated inflammatory and immune responses, cytokine storm, prevalence of pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages and increased levels of resident and circulating immune cells. Men show higher susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection than women, likely due to estrogens production. The protective role of estrogens, as well as an immune-suppressive activity that limits the excessive inflammation, can be mediated by cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2). The role of this receptor in modulating inflammation and immune response is well documented in fact in several settings. The stimulation of CB2 receptors is known to limit the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines, shift the macrophage phenotype towards the anti-inflammatory M2 type and enhance the immune-modulating properties of mesenchymal stromal cells. For these reasons, we hypothesize that CB2 receptor can be a therapeutic 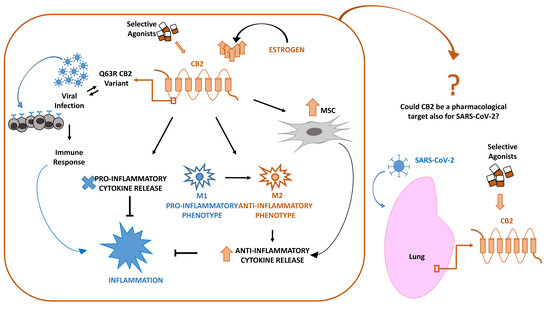

 “In this study cannabidiol (CBD) was administered orally to determine its effects and mechanisms in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of multiple sclerosis (MS). We hypothesized that 75 mg/kg of oral CBD given for 5 days after initiation of disease would reduce EAE severity through suppression of either the early peripheral immune or late neuroimmune response.
“In this study cannabidiol (CBD) was administered orally to determine its effects and mechanisms in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) model of multiple sclerosis (MS). We hypothesized that 75 mg/kg of oral CBD given for 5 days after initiation of disease would reduce EAE severity through suppression of either the early peripheral immune or late neuroimmune response.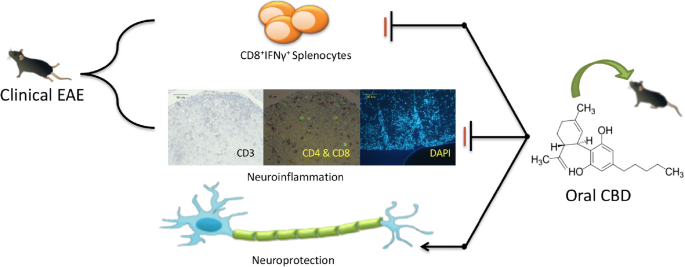
 “Two patient case reports are presented describing the use of cannabidiol (CBD) for the symptomatic relief of a lumbar compression fracture and in the mitigation of thoracic discomfort and dysesthesia secondary to a surgically resected meningioma.
“Two patient case reports are presented describing the use of cannabidiol (CBD) for the symptomatic relief of a lumbar compression fracture and in the mitigation of thoracic discomfort and dysesthesia secondary to a surgically resected meningioma.