
Tag Archives: antibacterial
Cannabinoids and Terpenes as an Antibacterial and Antibiofouling Promotor for PES Water Filtration Membranes.
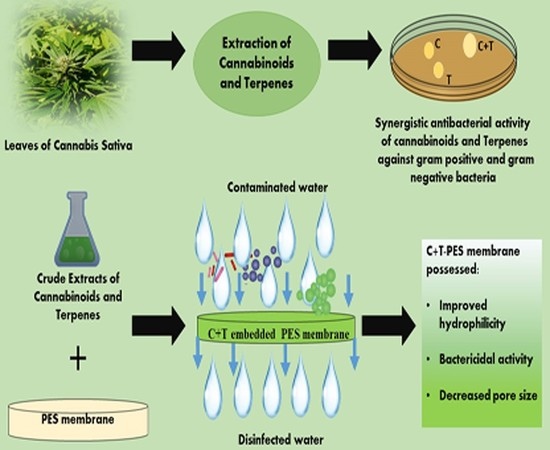
 “Plant phytochemicals have potential decontaminating properties, however, their role in the amelioration of hydrophobic water filtration membranes have not been elucidated yet.
“Plant phytochemicals have potential decontaminating properties, however, their role in the amelioration of hydrophobic water filtration membranes have not been elucidated yet.
In this work, phytochemicals (i.e., cannabinoids (C) and terpenes (T) from C. sativa) were revealed for their antibacterial activity against different Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria.
The results of this study established cannabinoids and terpenes as an inexpensive solution for polyethersulfone (PES) membrane surface modification.
These hybrid membranes can be easily deployed at an industrial scale for water filtration purposes.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32041149
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/25/3/691
Comparison of Efficacy of Cannabinoids versus Commercial Oral Care Products in Reducing Bacterial Content from Dental Plaque: A Preliminary Observation.

The present study compared the efficacy of oral care products and cannabinoids in reducing the bacterial content of dental plaques.
Sixty adults aged 18 to 45 years were categorized into six groups based on the Dutch periodontal screening index. Dental plaques of the adults were collected using paro-toothpick sticks and spread on two Petri dishes, each with four divisions. On Petri dish-A, cannabidiol (CBD), cannabichromene (CBC), cannabinol (CBN), and cannabigerol (CBG) were used, and on Petri dish-B, cannabigerolic acid (CBGA), Oral B, Colgate, and Cannabite F (a toothpaste formulation of pomegranate and algae) were used. The Petri dishes were sealed and incubated, followed by counting the number of colonies.
Results: By evaluating the colony count of the dental bacteria isolated from six groups, it was found that cannabinoids were more effective in reducing the bacterial colony count in dental plaques as compared to the well-established synthetic oral care products such as Oral B and Colgate.
Conclusion: Cannabinoids have the potential to be used as an effective antibacterial agent against dental plaque-associated bacteria. Moreover, it provides a safer alternative for synthetic antibiotics to reduce the development of drug resistance.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32038896
“To the best of our knowledge, no such study has been published that compares the efficiency of cannabinoids with that of oral care products against dental bacteria. Our study is the first of its kind conducted to compare the efficacy of well-established commercial oral care products and cannabinoids in reducing the bacterial content of the dental plaque. Reducing the bacterial content could significantly decrease and prevent gum diseases that have become a huge global burden owing to their direct relation with systemic diseases. Here we report a preliminary observatory study on effect of cannabinoids on reducing the bacterial content of dental plaque.”
Uncovering the hidden antibiotic potential of Cannabis.
 “The spread of antimicrobial resistance continues to be a priority health concern worldwide, necessitating exploration of alternative therapies.
“The spread of antimicrobial resistance continues to be a priority health concern worldwide, necessitating exploration of alternative therapies.
Cannabis sativa has long been known to contain antibacterial cannabinoids, but their potential to address antibiotic resistance has only been superficially investigated.
Here, we show that cannabinoids exhibit antibacterial activity against MRSA, inhibit its ability to form biofilms and eradicate pre-formed biofilms and stationary phase cells persistent to antibiotics.
We show that the mechanism of action of cannabigerol is through targeting the cytoplasmic membrane of Gram-positive bacteria and demonstrate in vivo efficacy of cannabigerol in a murine systemic infection model caused by MRSA.
We also show that cannabinoids are effective against Gram-negative organisms whose outer membrane is permeabilized, where cannabigerol acts on the inner membrane.
Finally, we demonstrate that cannabinoids work in combination with polymyxin B against multi-drug resistant Gram-negative pathogens, revealing the broad-spectrum therapeutic potential for cannabinoids.”
Antibacterial properties of hemp hurd powder against E. coli
 “Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) is an eco‐friendly and multifunctional plant. Hemp hurd is a by‐product of hemp plant during hemp fiber separation. Although hemp hurd is repeatedly announced owing antibacterial activity, it has never been systematically investigated and reported. In this study, the antibacterial activity of hemp hurd powder against Escherichia coli is investigated. This article reveals antibacterial activity of hemp hurd where hemp hurd powder inhibits the growth of E. coli. Meanwhile, the self‐contamination (forming during retting process) inside hemp hurd has dramatic impact on the antibacterial performance. To achieve better antibacterial activity, hemp hurd was heat treated to eliminate self‐contaminations. The impact of the particle sizes and heat treatment on the antibacterial effectiveness was evaluated.”
“Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) is an eco‐friendly and multifunctional plant. Hemp hurd is a by‐product of hemp plant during hemp fiber separation. Although hemp hurd is repeatedly announced owing antibacterial activity, it has never been systematically investigated and reported. In this study, the antibacterial activity of hemp hurd powder against Escherichia coli is investigated. This article reveals antibacterial activity of hemp hurd where hemp hurd powder inhibits the growth of E. coli. Meanwhile, the self‐contamination (forming during retting process) inside hemp hurd has dramatic impact on the antibacterial performance. To achieve better antibacterial activity, hemp hurd was heat treated to eliminate self‐contaminations. The impact of the particle sizes and heat treatment on the antibacterial effectiveness was evaluated.”
Cannabidiol Is a Novel Modulator of Bacterial Membrane Vesicles.
 “Membrane vesicles (MVs) released from bacteria participate in cell communication and host-pathogen interactions.
“Membrane vesicles (MVs) released from bacteria participate in cell communication and host-pathogen interactions.
Roles for MVs in antibiotic resistance are gaining increased attention and in this study we investigated if known anti-bacterial effects of cannabidiol (CBD), a phytocannabinoid from Cannabis sativa, could be in part attributed to effects on bacterial MV profile and MV release.
We found that CBD is a strong inhibitor of MV release from Gram-negative bacteria (E. coli VCS257), while inhibitory effect on MV release from Gram-positive bacteria (S. aureus subsp. aureus Rosenbach) was negligible. When used in combination with selected antibiotics, CBD significantly increased the bactericidal action of several antibiotics in the Gram-negative bacteria.
In addition, CBD increased antibiotic effects of kanamycin in the Gram-positive bacteria, without affecting MV release. CBD furthermore changed protein profiles of MVs released from E. coli after 1 h CBD treatment.
Our findings indicate that CBD may pose as a putative adjuvant agent for tailored co-application with selected antibiotics, depending on bacterial species, to increase antibiotic activity, including via MV inhibition, and help reduce antibiotic resistance.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31552202
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcimb.2019.00324/full
Chemical Characterization and Evaluation of the Antibacterial Activity of Essential Oils from Fibre-Type Cannabis sativa L. (Hemp).
 “Volatile terpenes represent the largest group of Cannabis sativa L. components and they are responsible for its aromatic properties. Even if many studies on C. sativa have been focused on cannabinoids, which are terpenophenolics, little research has been carried out on its volatile terpenic compounds.
“Volatile terpenes represent the largest group of Cannabis sativa L. components and they are responsible for its aromatic properties. Even if many studies on C. sativa have been focused on cannabinoids, which are terpenophenolics, little research has been carried out on its volatile terpenic compounds.
In the light of all the above, the present work was aimed at the chemical characterization of seventeen essential oils from different fibre-type varieties of C. sativa (industrial hemp or hemp) by means of GC-MS and GC-FID techniques.
In total, 71 compounds were identified, and the semi-quantitative analysis revealed that α- and β-pinene, β-myrcene and β-caryophyllene are the major components in all the essential oils analysed. In addition, a GC-MS method was developed here for the first time, and it was applied to quantify cannabinoids in the essential oils.
The antibacterial activity of hemp essential oils against some pathogenic and spoilage microorganisms isolated from food and food processing environment was also determined. The inhibitory effects of the essential oils were evaluated by both the agar well diffusion assay and the minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) evaluation. By using the agar diffusion method and considering the zone of inhibition, it was possible to preliminarily verify the inhibitory activity on most of the examined strains.
The results showed a good antibacterial activity of six hemp essential oils against the Gram-positive bacteria, thus suggesting that hemp essential oil can inhibit or reduce bacterial proliferation and it can be a valid support to reduce microorganism contamination, especially in the food processing field.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31234360
https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/24/12/2302

“Cannabis Found Effective in Fighting Drug-Resistant Bacteria”

1959: “[Hemp (Cannabis sativa)-an antibiotic drug. 3. Isolation and constitution of two acids from Cannabis sativa].” https://
1962: “Antibiotic activity of various types of cannabis resin.” https://
2008: “Antibacterial cannabinoids from Cannabis sativa: a structure-activity study.” https://
“Cannabis plant extracts can effectively fight drug-resistant bacteria.” http://abcnews.go.com/
“According to research, the five most common cannabinoid compounds in weed—tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol, cannabigerol, cannabinol and cannabichromene—can kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria.” https://
2014: “Better than antibiotics, cannabinoids kill antibiotic-resistant MRSA bacteria” http://
2019: “Cannabis Found Effective in Fighting Drug-Resistant Bacteria” https://
“Cannabis oil kills bacteria better than established antibiotics… providing a possible new weapon in the war on superbugs, according to new research. It offers hope of curing killer infections – including MRSA and pneumonia, say scientists.” https://

Chromatographic Analyses, In Vitro Biological Activities, and Cytotoxicity of Cannabis sativa L. Essential Oil: A Multidisciplinary Study.

“Due to renewed interest in the cultivation and production of Italian Cannabis sativa L., we proposed a multi-methodological approach to explore chemically and biologically both the essential oil and the aromatic water of this plant. We reported the chemical composition in terms of cannabinoid content, volatile component, phenolic and flavonoid pattern, and color characteristics. Then, we demonstrated the ethnopharmacological relevance of this plant cultivated in Italy as a source of antioxidant compounds toward a large panel of enzymes (pancreatic lipase, α-amylase, α-glucosidase, and cholinesterases) and selected clinically relevant, multidrug-sensible, and multidrug-resistant microbial strains (Staphylococcus aureus, Helicobacter pylori, Candida, and Malassezia spp.), evaluating the cytotoxic effects against normal and malignant cell lines. Preliminary in vivo cytotoxicity was also performed on Galleria mellonella larvae. The results corroborate the use of this natural product as a rich source of important biologically active molecules with particular emphasis on the role exerted by naringenin, one of the most important secondary metabolites.”
Attenuation of Listeria monocytogenes Virulence by Cannabis sativa L. Essential Oil.

“Anti-virulence strategies are being explored as a novel approach to combat pathogens. Such strategies include inhibition of surface adhesion, tissue invasion, toxin production, and/or interference with the gene regulation of other virulence traits.
Listeria monocytogenes, the causative agent of listeriosis, is a facultative intracellular food pathogen characterized by a wide distribution in the environment. Its ability to persist within biofilms and to develop resistance to sanitizers is the cause of significant problems in food processing plants and of steep costs for the food industry.
In humans, the treatment of listeriosis is hampered by the intracellular location of listeriae and the poor intracellular penetration of some antibiotics. Eleven L. monocytogenes isolates from patients who were diagnosed with invasive listeriosis in Italy in 2014-2016 were studied.
This in vitro and in vivo study explored the antibacterial and anti-virulence properties of a steam-distilled essential oil of Cannabis sativa L., which is being intensively investigated for its high content in powerful bioactive phytochemicals.
Susceptibility experiments demonstrated a moderate bactericidal activity of the essential oil (Minimum Bactericidal Concentration > 2048 μg/mL).
Food contamination with L. monocytogenes is a major concern for the food industry, particularly for plants making ready-to-eat and processed food.
The present work provides a baseline in the study of the anti-virulence properties of the C. sativa essential oil against L. monocytogenes. Further studies are needed to understand if it could be used as an alternative agent for the control of L. monocytogenes in food processing plants.”
