 “Cannabidiol (CBD), a phytochemical derived from Cannabis sativa L., has been demonstrated to exhibit promising anti-tumor properties in multiple cancer types. However, the effects of CBD on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells remain unknown. We have shown that CBD effectively suppresses HCC cell growth in vivo and in vitro, and induced HCC cell pyroptosis in a caspase-3/GSDME-dependent manner. We further demonstrated that accumulation of integrative stress response (ISR) and mitochondrial stress may contribute to the initiation of pyroptotic signaling by CBD. Simultaneously, CBD can repress aerobic glycolysis through modulation of the ATF4-IGFBP1-Akt axis, due to the depletion of ATP and crucial intermediate metabolites. Collectively, these observations indicate that CBD could be considered as a potential compound for HCC therapy.”
“Cannabidiol (CBD), a phytochemical derived from Cannabis sativa L., has been demonstrated to exhibit promising anti-tumor properties in multiple cancer types. However, the effects of CBD on hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cells remain unknown. We have shown that CBD effectively suppresses HCC cell growth in vivo and in vitro, and induced HCC cell pyroptosis in a caspase-3/GSDME-dependent manner. We further demonstrated that accumulation of integrative stress response (ISR) and mitochondrial stress may contribute to the initiation of pyroptotic signaling by CBD. Simultaneously, CBD can repress aerobic glycolysis through modulation of the ATF4-IGFBP1-Akt axis, due to the depletion of ATP and crucial intermediate metabolites. Collectively, these observations indicate that CBD could be considered as a potential compound for HCC therapy.”
“Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is an extremely malignant cancer, accounting for almost 95% of primary liver cancer cases. Cannabidiol (CBD), a phytochemical derived from Cannabis sativa L., has been shown to have anti-tumor activity and to be a potential compound for tumor therapy. Previous studies have demonstrated that CBD treatment could effectively induce cell apoptosis in tumor cells. In this study, we have shown that CBD can effectively suppress HCC cell growth both in vitro and in vivo, which was similar to the anti-tumor activity of CBD observed in other cancer types. In summary, a mechanistic model of CBD anti-tumor activity in HCC cell pyroptosis and growth was demonstrated. All the observations described herein reveal a novel mechanism of the anti-tumor activity of CBD in HCC cells, suggesting that CBD could be considered as a promising compound for HCC therapy.”
https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2021.697832/full

 “Background:
“Background:  “Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) were isolated from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMSCs) and were further encapsulated with cannabidiol (CBD) through sonication method (CBD EVs). CBD EVs displayed an average particle size of 114.1±1.02 nm, zeta potential of -30.26±0.12 mV, entrapment efficiency of 92.3±2.21% and stability for several months at 4 °C. CBD release from the EVs was observed as 50.74±2.44% and 53.99±1.4% at pH 6.8 and pH 7.4, respectively after 48 h. Ourin-vitrostudies demonstrated that CBD either alone or in EVs form significantly sensitized MDA-MB-231 cells to doxorubicin (DOX) (*P<0.05). Flow cytometry and migration studies revealed that CBD EVs either alone or in combination with DOX induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest and decreased migration of MDA-MB-231 cells, respectively. CBD EVs and DOX combination significantly reduced tumor burden (***P<0.001) in MDA-MB-231 xenograft tumor model. Western blotting and immunocytochemical analysis demonstrated that CBD EVs and DOX combination decreased the expression of proteins involved in inflammation, metastasis and increased the expression of proteins involved in apoptosis. CBD EVs and DOX combination will have profound clinical significance in not only decreasing the side effects but also increasing the therapeutic efficacy of DOX in TNBC.”
“Extracellular Vesicles (EVs) were isolated from human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells (hUCMSCs) and were further encapsulated with cannabidiol (CBD) through sonication method (CBD EVs). CBD EVs displayed an average particle size of 114.1±1.02 nm, zeta potential of -30.26±0.12 mV, entrapment efficiency of 92.3±2.21% and stability for several months at 4 °C. CBD release from the EVs was observed as 50.74±2.44% and 53.99±1.4% at pH 6.8 and pH 7.4, respectively after 48 h. Ourin-vitrostudies demonstrated that CBD either alone or in EVs form significantly sensitized MDA-MB-231 cells to doxorubicin (DOX) (*P<0.05). Flow cytometry and migration studies revealed that CBD EVs either alone or in combination with DOX induced G1 phase cell cycle arrest and decreased migration of MDA-MB-231 cells, respectively. CBD EVs and DOX combination significantly reduced tumor burden (***P<0.001) in MDA-MB-231 xenograft tumor model. Western blotting and immunocytochemical analysis demonstrated that CBD EVs and DOX combination decreased the expression of proteins involved in inflammation, metastasis and increased the expression of proteins involved in apoptosis. CBD EVs and DOX combination will have profound clinical significance in not only decreasing the side effects but also increasing the therapeutic efficacy of DOX in TNBC.” “Our laboratory is interested in searching for a new plant-based therapeutics to treat ovarian cancer.
“Our laboratory is interested in searching for a new plant-based therapeutics to treat ovarian cancer. “Melanoma is one of the most aggressive malignances in human. Recently developed therapies improved overall survival rate, however, the treatment of melanoma still remains a challenging issue.
“Melanoma is one of the most aggressive malignances in human. Recently developed therapies improved overall survival rate, however, the treatment of melanoma still remains a challenging issue. 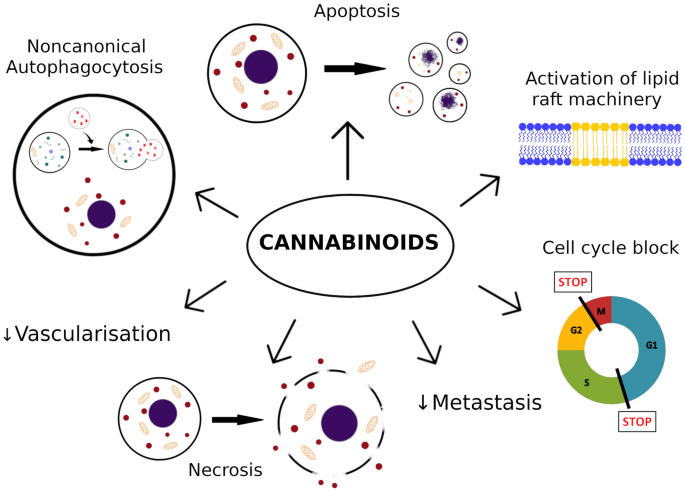
 “This study aimed to obtain and characterize extracted hemp oil enriched in cannabidiol (CBD) by decarboxylation of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) and to give new insights into its antioxidant and anticancer effects.
“This study aimed to obtain and characterize extracted hemp oil enriched in cannabidiol (CBD) by decarboxylation of cannabidiolic acid (CBDA) and to give new insights into its antioxidant and anticancer effects.  “Background:
“Background: