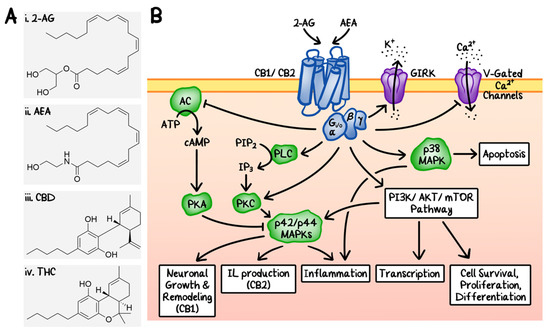
“Recently, there has been a growing interest in the medical applications of Cannabis plants. They owe their unique properties to a group of secondary metabolites known as phytocannabinoids, which are specific for this genus. Phytocannabinoids, and cannabinoids generally, can interact with cannabinoid receptors being part of the endocannabinoid system present in animals. Over the years a growing body of scientific evidence has been gathered, suggesting that these compounds have therapeutic potential.
“Recently, there has been a growing interest in the medical applications of Cannabis plants. They owe their unique properties to a group of secondary metabolites known as phytocannabinoids, which are specific for this genus. Phytocannabinoids, and cannabinoids generally, can interact with cannabinoid receptors being part of the endocannabinoid system present in animals. Over the years a growing body of scientific evidence has been gathered, suggesting that these compounds have therapeutic potential.
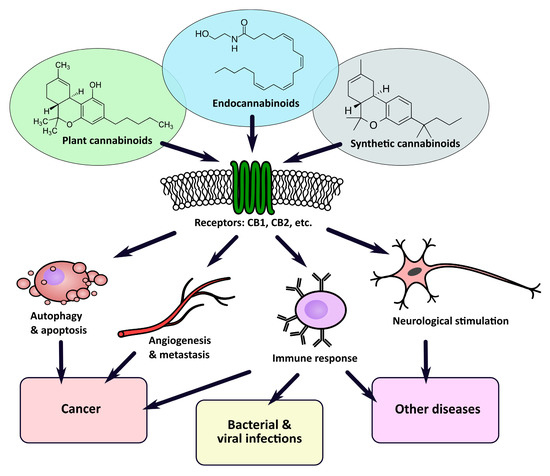
In this article, we review the classification of cannabinoids, the molecular mechanisms of their interaction with animal cells as well as their potential application in the treatment of human diseases. Specifically, we focus on the research concerning the anticancer potential of cannabinoids in preclinical studies, their possible use in cancer treatment and palliative medicine, as well as their influence on the immune system. We also discuss their potential as therapeutic agents in infectious, autoimmune, and gastrointestinal inflammatory diseases.
We postulate that the currently ongoing and future clinical trials should be accompanied by research focused on the cellular and molecular response to cannabinoids and Cannabis extracts, which will ultimately allow us to fully understand the mechanism, potency, and safety profile of cannabinoids as single agents and as complementary drugs.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33383838/
“Additionally, much evidence from pre-clinical and clinical studies has been gathered over the last decade, suggesting that multiple substances produced by Cannabis plants have a therapeutic potential, including anticancer properties.”
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/1/263/htm

 “Melanoma causes the highest number of skin cancer-related deaths worldwide. New treatment methods are essential for the management of this life-threatening disease.
“Melanoma causes the highest number of skin cancer-related deaths worldwide. New treatment methods are essential for the management of this life-threatening disease.
 “Low tetrahydrocannabinol Cannabis sativa products, also known as hemp products, have become widely available and their use in veterinary patients has become increasingly popular. Despite prevalence of use, the veterinary literature is lacking and evidence-based resource for cannabinoid efficacy.
“Low tetrahydrocannabinol Cannabis sativa products, also known as hemp products, have become widely available and their use in veterinary patients has become increasingly popular. Despite prevalence of use, the veterinary literature is lacking and evidence-based resource for cannabinoid efficacy. “Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant.
“Cannabis has long been used for healing and recreation in several regions of the world. Over 400 bioactive constituents, including more than 100 phytocannabinoids, have been isolated from this plant. The non-psychoactive cannabidiol (CBD) and the psychoactive Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (Δ9-THC) are the major and widely studied constituents from this plant. “Cannabidiol (CBD) has anti-tumorigenic activity. However, the anti-cancer effect of CBD on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remains unclear. The cytotoxicity of CBD on HNSCC was analyzed using cell survival and colony-forming assays in vitro.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) has anti-tumorigenic activity. However, the anti-cancer effect of CBD on head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) remains unclear. The cytotoxicity of CBD on HNSCC was analyzed using cell survival and colony-forming assays in vitro. “Research within a gynecologic oncology population has lagged behind the uptake in use of medical cannabis for symptom control. This study seeks to evaluate patient experience with prescribed medical cannabis obtained through licensed dispensaries in women with gynecologic malignancies.
“Research within a gynecologic oncology population has lagged behind the uptake in use of medical cannabis for symptom control. This study seeks to evaluate patient experience with prescribed medical cannabis obtained through licensed dispensaries in women with gynecologic malignancies. “With the current COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), there is an urgent need for new therapies and prevention strategies that can help curtail disease spread and reduce mortality.
“With the current COVID-19 pandemic, caused by the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), there is an urgent need for new therapies and prevention strategies that can help curtail disease spread and reduce mortality. “Recently, cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), have been the subject of intensive research and heavy scrutiny. Cannabinoids encompass a wide array of organic molecules, including those that are physiologically produced in humans, synthesized in laboratories, and extracted primarily from the Cannabis sativa plant. These organic molecules share similarities in their chemical structures as well as in their protein binding profiles. However, pronounced differences do exist in their mechanisms of action and clinical applications, which will be briefly compared and contrasted in this review. The mechanism of action of CBD and its potential applications in cancer therapy will be the major focus of this review article.”
“Recently, cannabinoids, such as cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ9 -tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), have been the subject of intensive research and heavy scrutiny. Cannabinoids encompass a wide array of organic molecules, including those that are physiologically produced in humans, synthesized in laboratories, and extracted primarily from the Cannabis sativa plant. These organic molecules share similarities in their chemical structures as well as in their protein binding profiles. However, pronounced differences do exist in their mechanisms of action and clinical applications, which will be briefly compared and contrasted in this review. The mechanism of action of CBD and its potential applications in cancer therapy will be the major focus of this review article.”