 “The anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids including CBD (Cannabidiol) and THC ((-)-trans-∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol) have been reported in the case of pancreatic cancer (PC).
“The anti-cancer effects of cannabinoids including CBD (Cannabidiol) and THC ((-)-trans-∆9-tetrahydrocannabinol) have been reported in the case of pancreatic cancer (PC).
The connection of these cannabinoids to KRas oncogenes that mutate in more than 90% of PC, and their effects on PD-L1, a key target of immune checkpoint blockade, have not been thoroughly investigated. Using cell lines and mouse models of PC, the effects of CBD and THC on cancer growth, the interaction between PC cells and a stromal cell, namely pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs), and the mechanism(s) involved were determined by cell-based assays and mouse study in vivo.
CBD and THC inhibited the proliferation of PC, PSC, and PSC-stimulated PC cells. They also suppressed pancreatic tumour growth in mice. Furthermore, CBD and/or THC reduced the expression of PD-L1 by either PC or PSC cells. Knockout of p-21 activated kinase 1 (PAK1, activated by KRas) in PC and PSC cells and, in mice, dramatically decreased or blocked these inhibitory effects of CBD and/or THC.
These results indicated that CBD and THC exerted their inhibitions on PC and PSC via a p-21 activated kinase 1 (PAK1)-dependent pathway, suggesting that CBD and THC suppress Kras activated pathway by targeting PAK1. The inhibition by CBD and THC of PD-L1 expression will enhance the immune checkpoint blockade of PC.”

 “The cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2R) represents an interesting and new therapeutic target for its involvement in the first steps of neurodegeneration as well as in cancer onset and progression.
“The cannabinoid receptor subtype 2 (CB2R) represents an interesting and new therapeutic target for its involvement in the first steps of neurodegeneration as well as in cancer onset and progression.
 “This study evaluated the synergistic anti-cancer potential of cannabinoid combinations across the MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines. Cannabinoids were combined and their synergistic interactions were evaluated using median effect analysis.
“This study evaluated the synergistic anti-cancer potential of cannabinoid combinations across the MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 human breast cancer cell lines. Cannabinoids were combined and their synergistic interactions were evaluated using median effect analysis. “Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.
“Pancreatic cancer (PC) is related to lifestyle risks, chronic inflammation, and germline mutations in BRCA1/2, ATM, MLH1, TP53, or CDKN2A. Surgical resection and adjuvant chemotherapy are the main therapeutic strategies but are less effective in patients with high-grade tumors.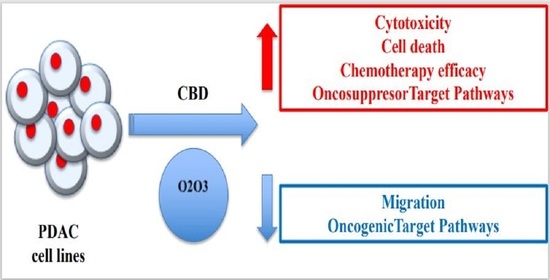
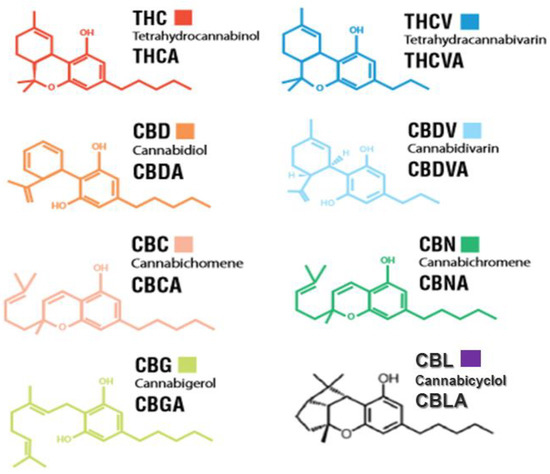
 “Multidrug resistance (MDR) to known chemotherapeutic agents is increasing while the development of new drugs is lacking behind. Combination therapies might increase the development of effective treatment.
“Multidrug resistance (MDR) to known chemotherapeutic agents is increasing while the development of new drugs is lacking behind. Combination therapies might increase the development of effective treatment.

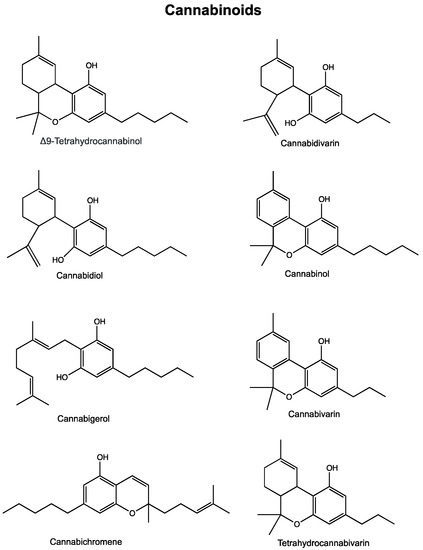
 “In this work, we evaluated, for the first time, the antitumor effect of cannabidiol (CBD) as monotherapy and in combination with conventional chemotherapeutics in ovarian cancer and developed PLGA-microparticles as CBD carriers to optimize its anticancer activity.
“In this work, we evaluated, for the first time, the antitumor effect of cannabidiol (CBD) as monotherapy and in combination with conventional chemotherapeutics in ovarian cancer and developed PLGA-microparticles as CBD carriers to optimize its anticancer activity.