
“The oil extracted from hemp seeds has significant nutritional and biological properties due to the unique composition of polyunsaturated fatty acids and various antioxidant compounds. The potential of this oil for the prevention of oxidative stress and for the treatment of oxidative-stress-induced ailments is of increasing interest. Most studies of hemp seed oil were conducted in-vitro, meaning we lack information about effects and activity in vivo. In the present study, we evaluated the hypothesis that hemp seed oil at different concentrations improves the oxidative state of D. melanogaster, under non-stress as well as hydrogen-peroxide-induced stress. We analyzed the effects of hemp seed oil on oxidative stress markers and on the life cycle of D.melanogaster under non-stress and hydrogen-peroxide-induced stress conditions. D.melanogaster larvae were exposed to hemp seed oil concentrations ranging from 12.5 to 125 μL/mL. The results revealed that under non-stress conditions, oil concentrations up to 62.5 µL/mL did not induce negative effects on the life cycle of D. melanogaster and maintained the redox status of the larval cells at similar levels to the control level. Under oxidative stress conditions, biochemical parameters were significantly affected and only two oil concentrations, 18.7 and 31.2 µL/mL, provided protection against hydrogen peroxide stress effects. A higher oil concentration (125 μL/mL) exerted negative effects on the oxidative status and increased larval mortality. The tested oil was characterized chemically by NMR, transesterification, and silylation, followed by GC-MS analyses, and was shown to contain polyunsaturated fatty acid triglycerides and low levels of tocopherols. The high levels of linoleic and linolenic acids in the oil are suggested to be responsible for the observed in vivo antioxidant effects. Taken together, the results show that hemp seed oil is effective for reducing oxidative stress at the cellular level, thus supporting the hypothesis. The obtained results point to the potential of hemp seed oil for the prevention and treatment of conditions caused by the action of reactive oxygen species.”

 “The concept of neurons as irreplaceable cells does not hold true today. Experiments and evidence of neurogenesis, also, in the adult brain give hope that some compounds or drugs can enhance this process, helping to reverse the outcomes of diseases or traumas that once were thought to be everlasting.
“The concept of neurons as irreplaceable cells does not hold true today. Experiments and evidence of neurogenesis, also, in the adult brain give hope that some compounds or drugs can enhance this process, helping to reverse the outcomes of diseases or traumas that once were thought to be everlasting.  “The global incidence of respiratory diseases and complications is increasing. Therefore, new methods of treatment, as well as prevention, need to be investigated.
“The global incidence of respiratory diseases and complications is increasing. Therefore, new methods of treatment, as well as prevention, need to be investigated.  “”Medicinal cannabis” is defined as the use of cannabis-based products for the treatment of an illness. Investigations of cannabis compounds in psychiatric and neurological illnesses primarily focus on the major cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ
“”Medicinal cannabis” is defined as the use of cannabis-based products for the treatment of an illness. Investigations of cannabis compounds in psychiatric and neurological illnesses primarily focus on the major cannabinoids, cannabidiol (CBD) and Δ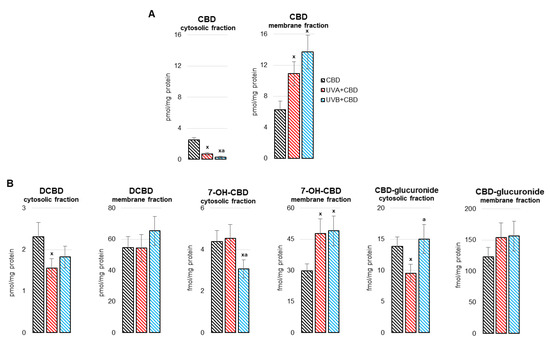
 “Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia Nigra pars compacta, leading to classical PD motor symptoms. Current therapies are purely symptomatic and do not modify disease progression.
“Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized by the loss of dopaminergic neurons in the Substantia Nigra pars compacta, leading to classical PD motor symptoms. Current therapies are purely symptomatic and do not modify disease progression.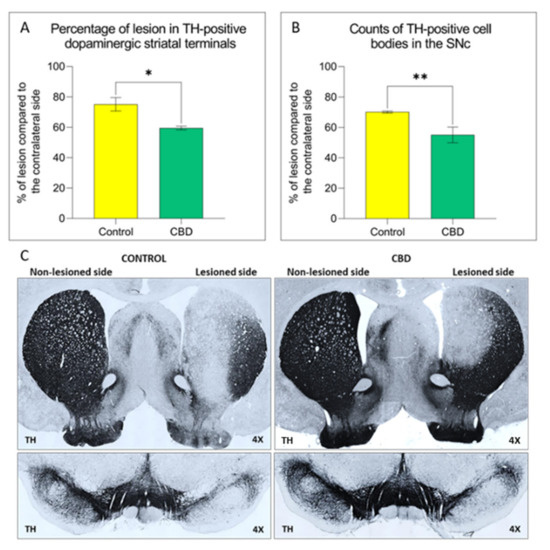
 “Obesity-related insulin resistance (IR) and attenuated brain insulin signaling are significant risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders, e.g., Alzheimer’s disease. IR and type 2 diabetes correlate with an increased concentration of sphingolipids, a class of lipids that play an essential structural role in cellular membranes and cell signaling pathways.
“Obesity-related insulin resistance (IR) and attenuated brain insulin signaling are significant risk factors for neurodegenerative disorders, e.g., Alzheimer’s disease. IR and type 2 diabetes correlate with an increased concentration of sphingolipids, a class of lipids that play an essential structural role in cellular membranes and cell signaling pathways. “Despite the high incidence of traumatic brain injury (TBI), there is no universal treatment to safely treat patients. Blunt brain injuries destroy primary neural tissue that results in impaired perfusion, excessive release of glutamate, inflammation, excitotoxicity, and progressive secondary neuronal cell death.
“Despite the high incidence of traumatic brain injury (TBI), there is no universal treatment to safely treat patients. Blunt brain injuries destroy primary neural tissue that results in impaired perfusion, excessive release of glutamate, inflammation, excitotoxicity, and progressive secondary neuronal cell death.  “Introduction:
“Introduction: