 “The potential therapeutic use of some Cannabis sativa plant compounds has been attracting great interest, especially for managing neuropsychiatric disorders due to the relative lack of efficacy of the current treatments.
“The potential therapeutic use of some Cannabis sativa plant compounds has been attracting great interest, especially for managing neuropsychiatric disorders due to the relative lack of efficacy of the current treatments.
Numerous studies have been carried out using the main phytocannabinoids, tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). CBD displays an interesting pharmacological profile without the potential for becoming a drug of abuse, unlike THC.
In this review, we focused on the anxiolytic, antidepressant, and antipsychotic effects of CBD found in animal and human studies. In rodents, results suggest that the effects of CBD depend on the dose, the strain, the administration time course (acute vs. chronic), and the route of administration. In addition, certain key targets have been related with these CBD pharmacological actions, including cannabinoid receptors (CB1r and CB2r), 5-HT1A receptor and neurogenesis factors.
Preliminary clinical trials also support the efficacy of CBD as an anxiolytic, antipsychotic, and antidepressant, and more importantly, a positive risk-benefit profile. These promising results support the development of large-scale studies to further evaluate CBD as a potential new drug for the treatment of these psychiatric disorders.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/33228239/
https://www.mdpi.com/2218-273X/10/11/1575
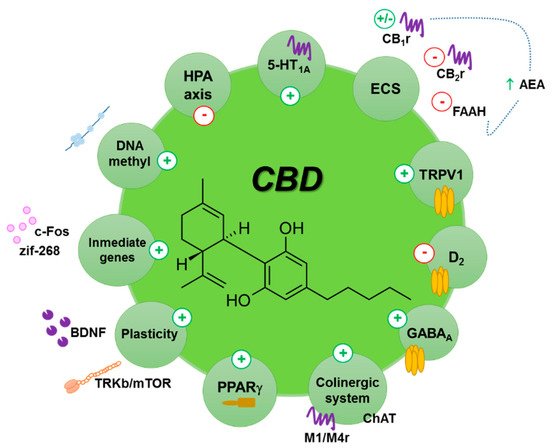

 “Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) is a non-psychoactive phytocannabinoid known for its beneficial effects including antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. Moreover, CBD is a compound with antidepressant, anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and antipsychotic effects. Thanks to all these properties, the interest of the scientific community for it has grown. “Gestational methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) treatment produces offspring with adult phenotype relevant to schizophrenia, including positive- and negative-like symptoms, cognitive deficits, dopaminergic dysfunction, structural and functional abnormalities.
“Gestational methylazoxymethanol acetate (MAM) treatment produces offspring with adult phenotype relevant to schizophrenia, including positive- and negative-like symptoms, cognitive deficits, dopaminergic dysfunction, structural and functional abnormalities.
 “Preclinical and clinical data indicate that
“Preclinical and clinical data indicate that 
 “The most recent studies published or initiated in the last 18 months, investigating cannabidiol in the treatment of symptoms of schizophrenia and related conditions are summarized, including observed tolerability and reported side-effects.
“The most recent studies published or initiated in the last 18 months, investigating cannabidiol in the treatment of symptoms of schizophrenia and related conditions are summarized, including observed tolerability and reported side-effects. “Recent evidence suggests that
“Recent evidence suggests that  “Stress is a risk factor for psychosis and treatments which mitigate its harmful effects are needed.
“Stress is a risk factor for psychosis and treatments which mitigate its harmful effects are needed.