 “Exemestane is one of the aromatase inhibitors (AI) used as first line treatment for estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer in post-menopausal women. Exemestane acts by inhibiting aromatase, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of androgens to estrogens and also by promoting apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Nevertheless, despite its therapeutic success, this AI, after prolonged treatment, can induce acquired resistance, which causes tumor relapse. Therefore, it is important to find new strategies to overcome resistance in order to improve breast cancer treatment.
“Exemestane is one of the aromatase inhibitors (AI) used as first line treatment for estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer in post-menopausal women. Exemestane acts by inhibiting aromatase, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of androgens to estrogens and also by promoting apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Nevertheless, despite its therapeutic success, this AI, after prolonged treatment, can induce acquired resistance, which causes tumor relapse. Therefore, it is important to find new strategies to overcome resistance in order to improve breast cancer treatment.
Considering that the development of resistance is the main reason for endocrine treatment failure, our group decided to explore the ability of three cannabinoids, Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and anandamide (AEA), to reverse resistance to exemestane. The THC and CBD are phytocannabinoids derived from the plant Cannabis sativa (marijuana) whereas AEA is an endocannabinoid. For that, it was used LTEDaro cells, a long-term estrogen deprived ER+ breast cancer cell line that mimics resistance to exemestane. These cells were treated with exemestane in combination with two phytocannabinoids, CBD and THC, and the endocannabinoid AEA.
The presence of CB1 and CB2 in LTEDaro cells was confirmed by Western blot analysis and the effects of the combination of cannabinoids with exemestane were evaluated by MTT and LDH assays. Cell morphology was analyzed by Giemsa and Hoechst staining.
Results: Our results demonstrate that all the cannabinoids induce a decrease in viability of exemestane-resistant cells, in a dose- and time-dependent manner, without LDH release. These results indicate that the studied cannabinoids, mainly THC and AEA, revert the resistance to exemestane, probably by inducing apoptosis, as observed in Giemsa/Hoechst stain by the presence of typical morphological features of apoptosis.
Conclusion: This study highlights the efficacy of using cannabinoids as a potential adjuvant treatment to revert resistance to AIs.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/32258721
https://journals.lww.com/pbj/fulltext/2017/09000/The_effects_of_cannabinoids_in.118.aspx
 “The inhibitor of DNA binding (Id) proteins are regulators of cell cycle and cell differentiation. Of all Id family proteins, Id1 is mostly linked to tumorigenesis, cellular senescence as well as cell proliferation and survival.
“The inhibitor of DNA binding (Id) proteins are regulators of cell cycle and cell differentiation. Of all Id family proteins, Id1 is mostly linked to tumorigenesis, cellular senescence as well as cell proliferation and survival.
 “The intraperitoneal administration of chemotherapeutics has emerged as a potential route in ovarian cancer treatment. Nanoparticles as carriers for these agents could be interesting by increasing the retention of chemotherapeutics within the peritoneal cavity. Moreover, nanoparticles could be internalised by cancer cells and let the drug release near the biological target, which could increase the anticancer efficacy.
“The intraperitoneal administration of chemotherapeutics has emerged as a potential route in ovarian cancer treatment. Nanoparticles as carriers for these agents could be interesting by increasing the retention of chemotherapeutics within the peritoneal cavity. Moreover, nanoparticles could be internalised by cancer cells and let the drug release near the biological target, which could increase the anticancer efficacy.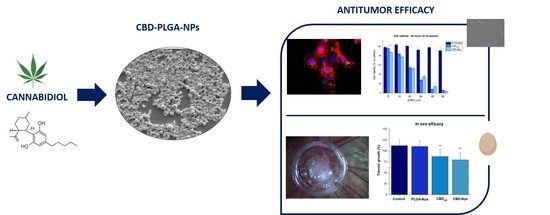
 “Colorectal cancer (CRC) has a high mortality rate and is one of the most difficult diseases to manage due to tumour resistance and metastasis. The treatment of choice for CRC is reliant on the phase and time of diagnosis. Despite several conventional treatments available to treat CRC (surgical excision, chemo-, radiation- and immune-therapy), resistance is a major challenge, especially if it has metastasized. Additionally, these treatments often cause unwanted adverse side effects and so it remains imperative to investigate, alternative combination therapies.
“Colorectal cancer (CRC) has a high mortality rate and is one of the most difficult diseases to manage due to tumour resistance and metastasis. The treatment of choice for CRC is reliant on the phase and time of diagnosis. Despite several conventional treatments available to treat CRC (surgical excision, chemo-, radiation- and immune-therapy), resistance is a major challenge, especially if it has metastasized. Additionally, these treatments often cause unwanted adverse side effects and so it remains imperative to investigate, alternative combination therapies. “Cannabis sativa produces hundreds of phytocannabinoids and terpenes.
“Cannabis sativa produces hundreds of phytocannabinoids and terpenes. “Exemestane is one of the aromatase inhibitors (AI) used as first line treatment for estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer in post-menopausal women. Exemestane acts by inhibiting aromatase, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of androgens to estrogens and also by promoting apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Nevertheless, despite its therapeutic success, this AI, after prolonged treatment, can induce acquired resistance, which causes tumor relapse. Therefore, it is important to find new strategies to overcome resistance in order to improve breast cancer treatment.
“Exemestane is one of the aromatase inhibitors (AI) used as first line treatment for estrogen-receptor positive breast cancer in post-menopausal women. Exemestane acts by inhibiting aromatase, the enzyme responsible for the conversion of androgens to estrogens and also by promoting apoptosis of breast cancer cells. Nevertheless, despite its therapeutic success, this AI, after prolonged treatment, can induce acquired resistance, which causes tumor relapse. Therefore, it is important to find new strategies to overcome resistance in order to improve breast cancer treatment. “The recent announcement of marijuana legalization in Canada spiked many discussions about potential health benefits of Cannabis sativa.
“The recent announcement of marijuana legalization in Canada spiked many discussions about potential health benefits of Cannabis sativa.  “Over the last decades a renewed interest in n-3 very long polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), derived mainly from fish oils in the human diet, has been observed because of their potential effects against cancer diseases, including breast carcinoma. These n-3 PUFAs mainly consist of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) that, alone or in combination with anticancer agents, induce cell cycle arrest, autophagy, apoptosis, and tumor growth inhibition. A large number of molecular targets of n-3 PUFAs have been identified and multiple mechanisms appear to underlie their antineoplastic activities. Evidence exists that EPA and DHA also elicit anticancer effects by the conversion to their corresponding ethanolamide derivatives in cancer cells, by binding and activation of different receptors and distinct signaling pathways. Other conjugates with serotonin or dopamine have been found to exert anti-inflammatory activities in breast tumor microenvironment, indicating the importance of these compounds as modulators of tumor epithelial/stroma interplay. The objective of this review is to provide a general overview and an update of the current n-3 PUFA derivative research and to highlight intriguing aspects of the potential therapeutic benefits of these low-toxicity compounds in breast cancer treatment and care.”
“Over the last decades a renewed interest in n-3 very long polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs), derived mainly from fish oils in the human diet, has been observed because of their potential effects against cancer diseases, including breast carcinoma. These n-3 PUFAs mainly consist of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) that, alone or in combination with anticancer agents, induce cell cycle arrest, autophagy, apoptosis, and tumor growth inhibition. A large number of molecular targets of n-3 PUFAs have been identified and multiple mechanisms appear to underlie their antineoplastic activities. Evidence exists that EPA and DHA also elicit anticancer effects by the conversion to their corresponding ethanolamide derivatives in cancer cells, by binding and activation of different receptors and distinct signaling pathways. Other conjugates with serotonin or dopamine have been found to exert anti-inflammatory activities in breast tumor microenvironment, indicating the importance of these compounds as modulators of tumor epithelial/stroma interplay. The objective of this review is to provide a general overview and an update of the current n-3 PUFA derivative research and to highlight intriguing aspects of the potential therapeutic benefits of these low-toxicity compounds in breast cancer treatment and care.” “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) comprises the canonical receptor subtypes CB1R and CB2R and endocannabinoids (anandamide, AEA and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, 2-AG), and a “non-canonical” extended signaling network consisting of: (i) other fatty acid derivatives; (ii) the defined “ionotropic cannabinoid receptors” (TRP channels); other GPCRs (GPR55, PPARα); (iii) enzymes involved in the biosynthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids (FAAH and MAGL); and (iv) protein transporters (FABP family).The ECS is currently a hot topic due to its involvement in cancer and pain.
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) comprises the canonical receptor subtypes CB1R and CB2R and endocannabinoids (anandamide, AEA and 2-arachidonoylglycerol, 2-AG), and a “non-canonical” extended signaling network consisting of: (i) other fatty acid derivatives; (ii) the defined “ionotropic cannabinoid receptors” (TRP channels); other GPCRs (GPR55, PPARα); (iii) enzymes involved in the biosynthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids (FAAH and MAGL); and (iv) protein transporters (FABP family).The ECS is currently a hot topic due to its involvement in cancer and pain. “Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequent and aggressive malignant brain tumour, with a poor prognosis despite available surgical and radio-chemotherapy, rising the necessity for searching alternative therapies. Several preclinical studies evaluating the efficacy of
“Glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) is the most frequent and aggressive malignant brain tumour, with a poor prognosis despite available surgical and radio-chemotherapy, rising the necessity for searching alternative therapies. Several preclinical studies evaluating the efficacy of  “Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g.,
“Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) develop resistance to antitumor agents by mechanisms that involve the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT). This necessitates the development of new complementary drugs, e.g.,