 “Chronic pain is highly prevalent in most of the industrialized nations around the world. Despite the documented adverse effects, opioids are widely used for pain management. Cannabinoids, and specifically Cannabidiol, is proposed as an opioid alternative, having comparable efficacy with better safety profile.
“Chronic pain is highly prevalent in most of the industrialized nations around the world. Despite the documented adverse effects, opioids are widely used for pain management. Cannabinoids, and specifically Cannabidiol, is proposed as an opioid alternative, having comparable efficacy with better safety profile.
Objectives: We aim to investigate the impact of full hemp extract cannabidiol (CBD) on opioid use and quality of life indicators among chronic pain patients.
Results: Over half of chronic pain patients (53%) reduced or eliminated their opioids within 8 weeks after adding CBD-rich hemp extract to their regimens. Almost all CBD users (94%) reported quality of life improvements. The results indicated a significant relationship between CBD and PSQI (p = 0.003), and PEG (p = 0.006). There was a trend toward improvement but no significant relationship between CBD use and PHQ and PDI.
Conclusion: CBD could significantly reduce opioid use and improve chronic pain and sleep quality among patients who are currently using opioids for pain management.
Key Message: This is a prospective, single-arm cohort study for the potential role of cannabinoids as an alternative for opioids. The results indicate that using the CBD-rich extract enabled our patients to reduce or eliminate opioids with significant improvement in their quality of life indices.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31711352
“Cannabis, the plant source of cannabinoids (CB), have been used for millennia for different purposes such as pain control and stress relief. Recent evidence highlights cannabinoids’ efficacy and safety for pain control. Besides its potential direct effects on pain, cannabinoids are suggested to have a role in reducing opioid intake. This study concludes that using CBD for chronic pain in patients using opioids has a significant effect on reducing opioid intake, reducing pain and improving quality of life (QoL). Over half of the participants who added CBD hemp extract reduced or eliminated opioids over the course of 8 weeks, and almost all CBD users reported improvements in QoL.”
https://www.tandfonline.com/doi/full/10.1080/00325481.2019.1685298

 “Accumulating evidence implicates the endocannabinoid system in the pathophysiology of psychosis.
“Accumulating evidence implicates the endocannabinoid system in the pathophysiology of psychosis. “Depression is a widespread psychological disorder that affects up to 20% of the world’s population. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), with its unique curative effect in depression treatment, is gaining increasing attention as the discovery of novel antidepressant drug has become the pursuit of pharmaceutical. This article summarizes the work done on the natural products from TCM that have been reported to conceive antidepressant effects in the past two decades, which can be classified according to various mechanisms including increasing synaptic concentrations of monoamines, alleviating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis dysfunctions, lightening the impairment of neuroplasticity, fighting towards immune and inflammatory dysregulation. The antidepressant active ingredients identified can be generally divided into saponins, flavonoids, alkaloids, polysaccharides and others. Albiflorin, Baicalein, Berberine chloride, beta-Asarone, cannabidiol, Curcumin, Daidzein, Echinocystic acid (EA), Emodin, Ferulic acid, Gastrodin, Genistein, Ginsenoside Rb1, Ginsenoside Rg1, Ginsenoside Rg3, Hederagenin, Hesperidin, Honokiol, Hyperoside, Icariin, Isoliquiritin, Kaempferol, Liquiritin, L-theanine, Magnolol, Paeoniflorin, Piperine, Proanthocyanidin, Puerarin, Quercetin, Resveratrol (trans), Rosmarinic acid, Saikosaponin A, Senegenin, Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside and Vanillic acid are Specified in this review. Simultaneously, chemical structures of the active ingredients with antidepressant activities are listed and their sources, models, efficacy and mechanisms are described. Chinese compound prescription and extracts that exert antidepressant effects are also introduced, which may serve as a source of inspiration for further development. In the view of present study, the antidepressant effect of certain TCMs are affirmative and encouraging. However, there are a lot of work needs to be done to evaluate the exact therapeutic effects and mechanisms of those active ingredients, specifically, to establish a unified standard for diagnosis and evaluation of curative effect.”
“Depression is a widespread psychological disorder that affects up to 20% of the world’s population. Traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), with its unique curative effect in depression treatment, is gaining increasing attention as the discovery of novel antidepressant drug has become the pursuit of pharmaceutical. This article summarizes the work done on the natural products from TCM that have been reported to conceive antidepressant effects in the past two decades, which can be classified according to various mechanisms including increasing synaptic concentrations of monoamines, alleviating the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis dysfunctions, lightening the impairment of neuroplasticity, fighting towards immune and inflammatory dysregulation. The antidepressant active ingredients identified can be generally divided into saponins, flavonoids, alkaloids, polysaccharides and others. Albiflorin, Baicalein, Berberine chloride, beta-Asarone, cannabidiol, Curcumin, Daidzein, Echinocystic acid (EA), Emodin, Ferulic acid, Gastrodin, Genistein, Ginsenoside Rb1, Ginsenoside Rg1, Ginsenoside Rg3, Hederagenin, Hesperidin, Honokiol, Hyperoside, Icariin, Isoliquiritin, Kaempferol, Liquiritin, L-theanine, Magnolol, Paeoniflorin, Piperine, Proanthocyanidin, Puerarin, Quercetin, Resveratrol (trans), Rosmarinic acid, Saikosaponin A, Senegenin, Tetrahydroxystilbene glucoside and Vanillic acid are Specified in this review. Simultaneously, chemical structures of the active ingredients with antidepressant activities are listed and their sources, models, efficacy and mechanisms are described. Chinese compound prescription and extracts that exert antidepressant effects are also introduced, which may serve as a source of inspiration for further development. In the view of present study, the antidepressant effect of certain TCMs are affirmative and encouraging. However, there are a lot of work needs to be done to evaluate the exact therapeutic effects and mechanisms of those active ingredients, specifically, to establish a unified standard for diagnosis and evaluation of curative effect.”


 “According to recent studies,
“According to recent studies, 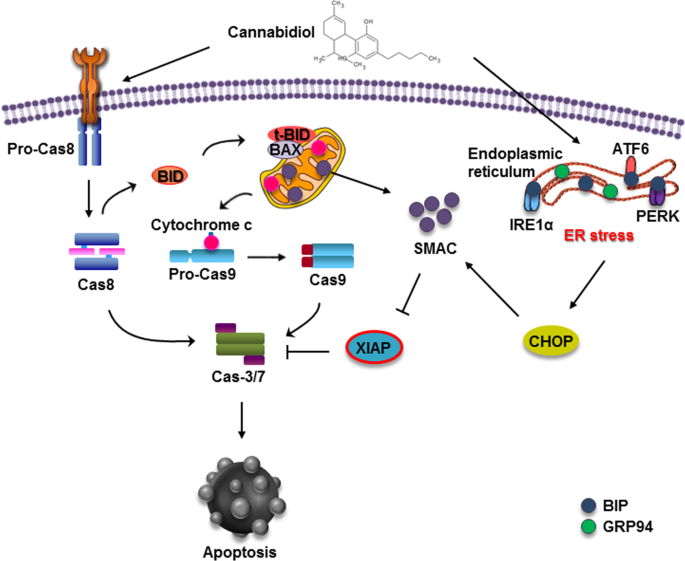
 “The healing properties of
“The healing properties of  “EpidiolexTM , a form of highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) derived from
“EpidiolexTM , a form of highly purified cannabidiol (CBD) derived from  “Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown by our laboratory to attenuate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS).
“Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown by our laboratory to attenuate experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE), an animal model of multiple sclerosis (MS). “The symptomatic treatment of myotonia and myalgia in patients with dystrophic and non-dystrophic myotonias is often not satisfactory.
“The symptomatic treatment of myotonia and myalgia in patients with dystrophic and non-dystrophic myotonias is often not satisfactory.