 “Endo-, phyto- and synthetic cannabinoids have been proposed as promising anti-cancer agents able to impair cancer cells’ behavior without affecting their non-transformed counterparts.
“Endo-, phyto- and synthetic cannabinoids have been proposed as promising anti-cancer agents able to impair cancer cells’ behavior without affecting their non-transformed counterparts.
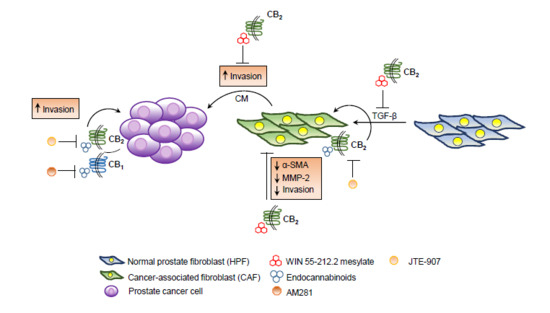
However, cancer outcome depends not only on cancer cells’ activity, but also on the stromal cells, which coevolve with cancer cells to sustain tumor progression.
Here, we show for the first time that cannabinoid treatment impairs the activation and the reactivity of cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs), the most represented stromal component of prostate tumor microenvironment.
Overall, our data strongly support the use of cannabinoids as anti-tumor agents in prostate cancer, since they are able to simultaneously strike both cancer and stromal cells.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31991773
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/3/787

 “Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) global burden is underestimated despite its high prevalence. It’s a gastrointestinal disease having obscure pathophysiology with multiple therapies yet unsatisfactory remedies.
“Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) global burden is underestimated despite its high prevalence. It’s a gastrointestinal disease having obscure pathophysiology with multiple therapies yet unsatisfactory remedies.

 “Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, the motor symptoms of which are associated classically with Lewy body formation and nigrostriatal degeneration.
“Parkinson’s disease is a neurodegenerative disorder, the motor symptoms of which are associated classically with Lewy body formation and nigrostriatal degeneration. “Osteoarticular equine disease is a common cause of malady; in general, its therapy is supported on steroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories. Nevertheless, many side effects may develop when these drugs are administered. Nowadays, the use of new alternatives for this pathology attention is demanded; in that sense,
“Osteoarticular equine disease is a common cause of malady; in general, its therapy is supported on steroids and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatories. Nevertheless, many side effects may develop when these drugs are administered. Nowadays, the use of new alternatives for this pathology attention is demanded; in that sense,  “The aim of this review article is to summarize current knowledge about the role of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors in tumor disease modulation and to evaluate comprehensively the use of cannabinoids in cancer patients.
“The aim of this review article is to summarize current knowledge about the role of cannabinoids and cannabinoid receptors in tumor disease modulation and to evaluate comprehensively the use of cannabinoids in cancer patients.
 “Confident relationships between diabetes and liver damage have previously been established.
“Confident relationships between diabetes and liver damage have previously been established.