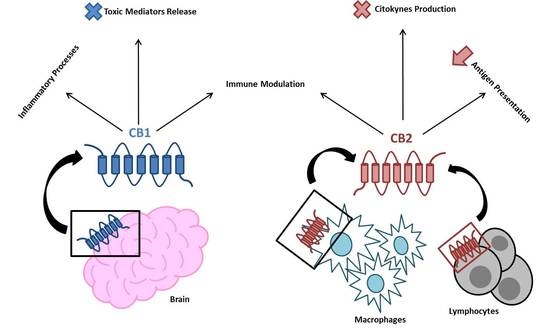
 “Endocannabinoid system consists of cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid type 2 (CB2) receptors, their endogenous ligands, and the enzymes responsible for their synthesis and degradation. CB2, to a great extent, and CB1, to a lesser extent, are involved in regulating the immune response. They also regulate the inflammatory processes by inhibiting pro-inflammatory mediator release and immune cell proliferation. This review provides an overview on the role of the endocannabinoid system with a major focus on cannabinoid receptors in the pathogenesis and onset of inflammatory and autoimmune pediatric diseases, such as immune thrombocytopenia, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, obesity, neuroinflammatory diseases, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. These disorders have a high social impact and represent a burden for the healthcare system, hence the importance of individuating more innovative and effective treatments. The endocannabinoid system could address this need, representing a possible new diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.”
“Endocannabinoid system consists of cannabinoid type 1 (CB1) and cannabinoid type 2 (CB2) receptors, their endogenous ligands, and the enzymes responsible for their synthesis and degradation. CB2, to a great extent, and CB1, to a lesser extent, are involved in regulating the immune response. They also regulate the inflammatory processes by inhibiting pro-inflammatory mediator release and immune cell proliferation. This review provides an overview on the role of the endocannabinoid system with a major focus on cannabinoid receptors in the pathogenesis and onset of inflammatory and autoimmune pediatric diseases, such as immune thrombocytopenia, juvenile idiopathic arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, celiac disease, obesity, neuroinflammatory diseases, and type 1 diabetes mellitus. These disorders have a high social impact and represent a burden for the healthcare system, hence the importance of individuating more innovative and effective treatments. The endocannabinoid system could address this need, representing a possible new diagnostic marker and therapeutic target.”
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/31771129
https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/20/23/5875

 “As we learn more about the endocannabinoid system (ECS), our understanding and grasp of the system’s ubiquitous presence is expanding. In light of this, there is also a growing body of evidence for the therapeutic potential of ECS modulation in a range of clinical situations. Strategies include for example manipulation of the
“As we learn more about the endocannabinoid system (ECS), our understanding and grasp of the system’s ubiquitous presence is expanding. In light of this, there is also a growing body of evidence for the therapeutic potential of ECS modulation in a range of clinical situations. Strategies include for example manipulation of the  “Excessive binge alcohol drinking may adversely affect cardiovascular function. In this study we characterize the detailed hemodynamic effects of an acute alcohol binge in mice using multiple approaches and investigate the role of the endocannabinoid-
“Excessive binge alcohol drinking may adversely affect cardiovascular function. In this study we characterize the detailed hemodynamic effects of an acute alcohol binge in mice using multiple approaches and investigate the role of the endocannabinoid-
 “Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening complication of end-stage liver disease characterized by the rapid decline of kidney function. Herein, we explored the therapeutic potential of targeting the
“Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) is a life-threatening complication of end-stage liver disease characterized by the rapid decline of kidney function. Herein, we explored the therapeutic potential of targeting the 
 “Uncontrolled infection and increased inflammatory mediators might cause systemic inflammatory response. It is already known that
“Uncontrolled infection and increased inflammatory mediators might cause systemic inflammatory response. It is already known that  “Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder disorder with unclear etiology.
“Interstitial cystitis (IC) is a chronic bladder disorder with unclear etiology. “The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is comprised of cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (CB1R and CB2R), endogenous ligands, and regulatory enzymes, and serves to regulate several important physiological functions throughout the brain and body.
“The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is comprised of cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (CB1R and CB2R), endogenous ligands, and regulatory enzymes, and serves to regulate several important physiological functions throughout the brain and body.
 “Delayed neurologic sequelae (DNS) are among the most serious complications of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning caused partly by elevated neuroinflammation.
“Delayed neurologic sequelae (DNS) are among the most serious complications of carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning caused partly by elevated neuroinflammation.