 “The main aspects of severe COVID-19 disease pathogenesis include hyper-induction of proinflammatory cytokines, also known as ‘cytokine storm’, that precedes acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and often leads to death. COVID-19 patients often suffer from lung fibrosis, a serious and untreatable condition. There remains no effective treatment for these complications.
“The main aspects of severe COVID-19 disease pathogenesis include hyper-induction of proinflammatory cytokines, also known as ‘cytokine storm’, that precedes acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and often leads to death. COVID-19 patients often suffer from lung fibrosis, a serious and untreatable condition. There remains no effective treatment for these complications.
Out of all cytokines, TNFα and IL-6 play crucial roles in cytokine storm pathogenesis and are likely responsible for the escalation in disease severity. These cytokines also partake in the molecular pathogenesis of fibrosis. Therefore, new approaches are urgently needed, that can efficiently and swiftly downregulate TNFα, IL-6, and the inflammatory cytokine cascade, in order to curb inflammation and prevent fibrosis, and lead to disease remission.
Cannabis sativa has been proposed to modulate gene expression and inflammation and is under investigation for several potential therapeutic applications against autoinflammatory diseases and cancer. Here, we hypothesized that the extracts of novel C. sativa cultivars may be used to downregulate the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines and pathways involved in inflammation and fibrosis.
Novel anti-TNFα and anti-IL-6 cannabis extracts can be useful additions to the current anti-inflammatory regimens to treat COVID-19, as well as various rheumatological diseases and conditions, and ‘inflammaging’ – the inflammatory underpinning of aging and frailty.”

 “Inflammasomes are cytoplasmic inflammatory signaling protein complexes that detect microbial materials, sterile inflammatory insults, and certain host-derived elements. Inflammasomes, once activated, promote caspase-1-mediated maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18, leading to pyroptosis. Current advances in inflammasome research support their involvement in the development of chronic inflammatory disorders in contrast to their role in regulating innate immunity.
“Inflammasomes are cytoplasmic inflammatory signaling protein complexes that detect microbial materials, sterile inflammatory insults, and certain host-derived elements. Inflammasomes, once activated, promote caspase-1-mediated maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin (IL)-1β and IL-18, leading to pyroptosis. Current advances in inflammasome research support their involvement in the development of chronic inflammatory disorders in contrast to their role in regulating innate immunity. “Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown to slow cancer cell growth and is toxic to human glioblastoma cell lines. Thus, CBD could be an effective therapeutic for glioblastoma.
“Cannabidiol (CBD) has been shown to slow cancer cell growth and is toxic to human glioblastoma cell lines. Thus, CBD could be an effective therapeutic for glioblastoma.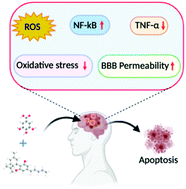
 “Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is an imbalance between the ER’s protein-folding load and capacity. It can be induced by various physiological conditions, activating the unfolded protein response to re-establish homeostasis, promoting cell survival. Under severe or chronic stress, apoptosis is induced. Normal cells generally do not experience continuous ER stress induction. The stressful conditions experienced in the tumour microenvironment facilitates chronic ER stress and UPR activation, which plays a pivotal role in tumour survival.
“Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress is an imbalance between the ER’s protein-folding load and capacity. It can be induced by various physiological conditions, activating the unfolded protein response to re-establish homeostasis, promoting cell survival. Under severe or chronic stress, apoptosis is induced. Normal cells generally do not experience continuous ER stress induction. The stressful conditions experienced in the tumour microenvironment facilitates chronic ER stress and UPR activation, which plays a pivotal role in tumour survival. “Preclinical data suggest some cannabinoids may exert antitumour effects against glioblastoma (GBM). Safety and preliminary efficacy of nabiximols oromucosal cannabinoid spray plus dose-intense temozolomide (DIT) was evaluated in patients with first recurrence of GBM.
“Preclinical data suggest some cannabinoids may exert antitumour effects against glioblastoma (GBM). Safety and preliminary efficacy of nabiximols oromucosal cannabinoid spray plus dose-intense temozolomide (DIT) was evaluated in patients with first recurrence of GBM. “Glioblastomas (GBMs) are aggressive brain tumors with frequent genetic alterations in TP53 and PTEN tumor suppressor genes rendering resistance to standard chemotherapeutics. Cannabinoid type 1 and 2 (CB1/CB2) receptor expression in GBMs and antitumor activity of cannabinoids in glioma cells and animal models, raised promises for a targeted treatment of these tumors. The susceptibility of human glioma cells to CB2-agonists and their mechanism of action are not fully elucidated. We determined CB1 and CB2 expression in 14 low-grade and 21 high-grade tumor biopsies, GBM-derived primary cultures and established cell lines. The non-selective CB receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 (but not its inactive enantiomer) or the CB2-selective agonist JWH133 induced apoptosis in patient-derived glioma cultures and five established glioma cell lines despite p53 and/or PTEN deficiency. Growth inhibitory efficacy of cannabinoids correlated with CB1/CB2 expression (EC50 WIN55,212-2: 7.36-15.70 µM, JWH133: 12.15-143.20 µM). Treatment with WIN55,212-2 or JWH133 led to activation of the apoptotic mitochondrial pathway and DNA fragmentation. Synthetic cannabinoid action was associated with the induction of autophagy and knockdown of autophagy genes augmented cannabinoid-induced apoptotic cell death. The high susceptibility of human glioblastoma cells to synthetic cannabinoids, despite genetic defects contributing to apoptosis resistance, makes cannabinoids promising anti-glioma therapeutics.”
“Glioblastomas (GBMs) are aggressive brain tumors with frequent genetic alterations in TP53 and PTEN tumor suppressor genes rendering resistance to standard chemotherapeutics. Cannabinoid type 1 and 2 (CB1/CB2) receptor expression in GBMs and antitumor activity of cannabinoids in glioma cells and animal models, raised promises for a targeted treatment of these tumors. The susceptibility of human glioma cells to CB2-agonists and their mechanism of action are not fully elucidated. We determined CB1 and CB2 expression in 14 low-grade and 21 high-grade tumor biopsies, GBM-derived primary cultures and established cell lines. The non-selective CB receptor agonist WIN55,212-2 (but not its inactive enantiomer) or the CB2-selective agonist JWH133 induced apoptosis in patient-derived glioma cultures and five established glioma cell lines despite p53 and/or PTEN deficiency. Growth inhibitory efficacy of cannabinoids correlated with CB1/CB2 expression (EC50 WIN55,212-2: 7.36-15.70 µM, JWH133: 12.15-143.20 µM). Treatment with WIN55,212-2 or JWH133 led to activation of the apoptotic mitochondrial pathway and DNA fragmentation. Synthetic cannabinoid action was associated with the induction of autophagy and knockdown of autophagy genes augmented cannabinoid-induced apoptotic cell death. The high susceptibility of human glioblastoma cells to synthetic cannabinoids, despite genetic defects contributing to apoptosis resistance, makes cannabinoids promising anti-glioma therapeutics.”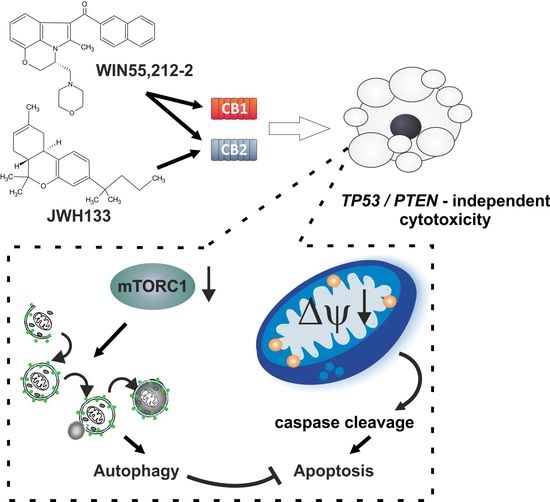
 “Glioblastoma is the most aggressive cancer among primary brain tumours. As with other cancers, the incidence of glioblastoma is increasing; despite modern therapies, the overall mean survival of patients post-diagnosis averages around 16 months, a figure that has not changed in many years. Cannabigerol (CBG) has only recently been reported to prevent the progression of certain carcinomas and has not yet been studied in glioblastoma. Here, we have compared the cytotoxic, apoptotic, and anti-invasive effects of the purified natural cannabinoid CBG together with CBD and THC on established differentiated glioblastoma tumour cells and glioblastoma stem cells. CBG and THC reduced the viability of both types of cells to a similar extent, whereas combining CBD with CBG was more efficient than with THC. CBD and CBG, both alone and in combination, induced caspase-dependent cell apoptosis, and there was no additive THC effect. Of note, CBG inhibited glioblastoma invasion in a similar manner to CBD and the chemotherapeutic temozolomide. We have demonstrated that THC has little added value in combined-cannabinoid glioblastoma treatment, suggesting that this psychotropic cannabinoid should be replaced with CBG in future clinical studies of glioblastoma therapy.”
“Glioblastoma is the most aggressive cancer among primary brain tumours. As with other cancers, the incidence of glioblastoma is increasing; despite modern therapies, the overall mean survival of patients post-diagnosis averages around 16 months, a figure that has not changed in many years. Cannabigerol (CBG) has only recently been reported to prevent the progression of certain carcinomas and has not yet been studied in glioblastoma. Here, we have compared the cytotoxic, apoptotic, and anti-invasive effects of the purified natural cannabinoid CBG together with CBD and THC on established differentiated glioblastoma tumour cells and glioblastoma stem cells. CBG and THC reduced the viability of both types of cells to a similar extent, whereas combining CBD with CBG was more efficient than with THC. CBD and CBG, both alone and in combination, induced caspase-dependent cell apoptosis, and there was no additive THC effect. Of note, CBG inhibited glioblastoma invasion in a similar manner to CBD and the chemotherapeutic temozolomide. We have demonstrated that THC has little added value in combined-cannabinoid glioblastoma treatment, suggesting that this psychotropic cannabinoid should be replaced with CBG in future clinical studies of glioblastoma therapy.” “Considering the advantages of using medicinal herbs as supplementary treatments to sensitize conventional anti-cancer drugs, studying functional mechanisms and regulatory effects of Echinacea purpurea (as a non-cannabinoid plant)
“Considering the advantages of using medicinal herbs as supplementary treatments to sensitize conventional anti-cancer drugs, studying functional mechanisms and regulatory effects of Echinacea purpurea (as a non-cannabinoid plant) 


 “Cannabis sativa contains more than 500 constituents, yet the anticancer properties of the vast majority of cannabis compounds remains unknown. We aimed to identify cannabis compounds and their combinations presenting cytotoxicity against bladder urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common urinary system cancer.
“Cannabis sativa contains more than 500 constituents, yet the anticancer properties of the vast majority of cannabis compounds remains unknown. We aimed to identify cannabis compounds and their combinations presenting cytotoxicity against bladder urothelial carcinoma (UC), the most common urinary system cancer.