“Mutations in SYNGAP1 are associated with developmental delay, epilepsy, and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Epilepsy is often drug-resistant in this syndrome with frequent drop attacks.
“Mutations in SYNGAP1 are associated with developmental delay, epilepsy, and autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Epilepsy is often drug-resistant in this syndrome with frequent drop attacks.
In a prospective study of add-on cannabidiol (CBD), we identified three patients with SYNGAP1 mutations: two boys and one girl. Seizure onset was at 3.5, 8, and 18 months (M), respectively, with numerous atypical absences per day associated with eyelid myoclonia (2/3 patients), upper limb myoclonic jerks (2/3 patients), and drop attacks (all patients). Seizures were resistant to at least 5 antiepileptic drugs (AEDs).
After CBD introduction, two patients were responders since M2 and achieve a seizure reduction of 90% and 80%, respectively, at M9 with disappearance of drop attacks. EEGs showed an improvement regarding background activity and interictal anomalies. The last patient showed a late response at M7 of treatment with an 80% decrease in seizure frequency. Caregiver in all three evaluated as much improved the status of their children. Treatment was well-tolerated in all, and no major adverse events (AEs) were reported.
CBD showed efficacy in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy due to SYNGAP1 mutations. Other patients with rare genetic developmental and epileptic encephalopathies with drug-resistant epilepsies might benefit from CBD.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32913957/
“CBD add‐on therapy in patients with SYNGAP1 encephalopathy showed a good response in three patients with a good safety profile and a late response in one patient. This therapy should be included in the treatment algorithm of patients with SYNGAP1 mutations presenting drug resistance epilepsy and might be expanded to other rare genetic epilepsies that might not be included in formal trials.”

 “Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed contains high contents of various nutrients, including fatty acids and proteins.
“Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seed contains high contents of various nutrients, including fatty acids and proteins.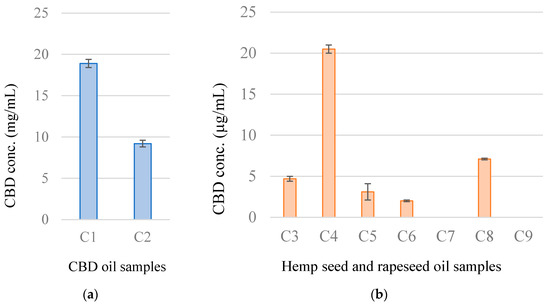


 “Recent years have seen an increase in the adoption of cannabinoid medicines, which have demonstrated effectiveness for the treatment of chronic pain.
“Recent years have seen an increase in the adoption of cannabinoid medicines, which have demonstrated effectiveness for the treatment of chronic pain. “Cannabis products have been used for centuries by humans for recreational and medical purposes. Resent research, proposed the promising therapeutic potential of cannabis and related cannabinoids for a wide range of medical conditions, including psychiatric and neurological diseases.
“Cannabis products have been used for centuries by humans for recreational and medical purposes. Resent research, proposed the promising therapeutic potential of cannabis and related cannabinoids for a wide range of medical conditions, including psychiatric and neurological diseases. “Cannabis and cannabinoid-based extracts have long been utilized for their perceived therapeutic value, and support for the legalization of cannabis for medicinal purposes continues to increase worldwide.
“Cannabis and cannabinoid-based extracts have long been utilized for their perceived therapeutic value, and support for the legalization of cannabis for medicinal purposes continues to increase worldwide. “Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.
“Cannabis is an annual plant with a long history of use as food, feed, fiber, oil, medicine, and narcotics. Despite realizing its true value, it has not yet found its true place. Cannabis has had a long history with many ups and downs, and now it is our turn to promote it.
 “The immune-suppressive effects of cannabidiol (CBD) are attributed to the modulation of essential immunological signaling pathways and receptors. Mechanistic understanding of the pharmacological effects of CBD emphasizes the therapeutic potential of CBD as a novel immune modulator.
“The immune-suppressive effects of cannabidiol (CBD) are attributed to the modulation of essential immunological signaling pathways and receptors. Mechanistic understanding of the pharmacological effects of CBD emphasizes the therapeutic potential of CBD as a novel immune modulator. “Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a multifactorial, pervasive neurodevelopmental disorder defined by the core symptoms of significant impairment in social interaction and communication as well as restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior. In addition to these core behaviors, persons with ASD frequently have associated noncore behavioral disturbance (ie, self-injury, aggression), as well as several medical comorbidities. Currently, no effective treatment exists for the core symptoms of ASD.
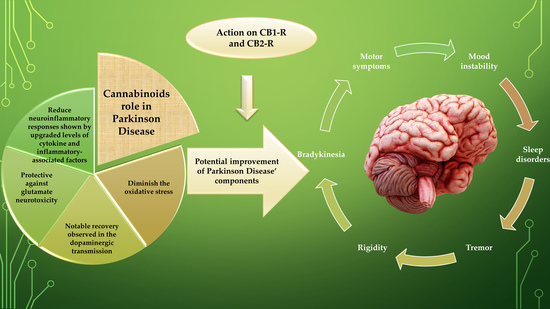
“Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a multifactorial, pervasive neurodevelopmental disorder defined by the core symptoms of significant impairment in social interaction and communication as well as restricted, repetitive patterns of behavior. In addition to these core behaviors, persons with ASD frequently have associated noncore behavioral disturbance (ie, self-injury, aggression), as well as several medical comorbidities. Currently, no effective treatment exists for the core symptoms of ASD. “Current pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is symptomatic and palliative, with levodopa/carbidopa therapy remaining the prime treatment, and nevertheless, being unable to modulate the progression of the neurodegeneration. No available treatment for PD can enhance the patient’s life-quality by regressing this diseased state.
“Current pharmacotherapy of Parkinson’s disease (PD) is symptomatic and palliative, with levodopa/carbidopa therapy remaining the prime treatment, and nevertheless, being unable to modulate the progression of the neurodegeneration. No available treatment for PD can enhance the patient’s life-quality by regressing this diseased state.