 “Resting-state (rs) network dysfunction is a contributing factor to treatment resistance in epilepsy. In treatment-resistant epilepsy (TRE), pharmacological and nonpharmacological therapies have been shown to improve such dysfunction.
“Resting-state (rs) network dysfunction is a contributing factor to treatment resistance in epilepsy. In treatment-resistant epilepsy (TRE), pharmacological and nonpharmacological therapies have been shown to improve such dysfunction.
In this study, our goal was to prospectively evaluate the effect of highly purified plant-derived cannabidiol (CBD; Epidiolex®) on rs functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) functional connectivity (rs-FC).
We hypothesized that CBD would change and potentially normalize the rs-FC in TRE.
Results: Participants with TRE showed average decrease of 71.7% in SF (p < 0.0001) and improved CSSS, AEP, and POMS confusion, depression, and fatigue subscores (all p < 0.05) on-CBD with POMS scores becoming similar to those of HCs. Paired t-tests showed significant pre-/on-CBD changes in rs-FC in cerebellum, frontal areas, temporal areas, hippocampus, and amygdala with some of them correlating with improvement in behavioral measures. Significant differences in rs-FC between pre-CBD and HCs were found in cerebellum, frontal, and occipital regions. After controlling for changes in SF with CBD, these differences were no longer present when comparing on-CBD to HCs.
Significance: This study indicates that highly purified CBD modulates and potentially normalizes rs-FC in the epileptic brain. This effect may underlie its efficacy. This study provides Class III evidence for CBD’s normalizing effect on rs-FC in TRE.”
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32745959/
https://www.epilepsybehavior.com/article/S1525-5050(20)30476-5/fulltext

 “Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.
“Neurological disorders such as neurodegenerative diseases or traumatic brain injury are associated with cognitive, motor and behavioural changes that influence the quality of life of the patients. Although different therapeutic strategies have been developed and tried until now to decrease the neurological decline, no treatment has been found to cure these pathologies.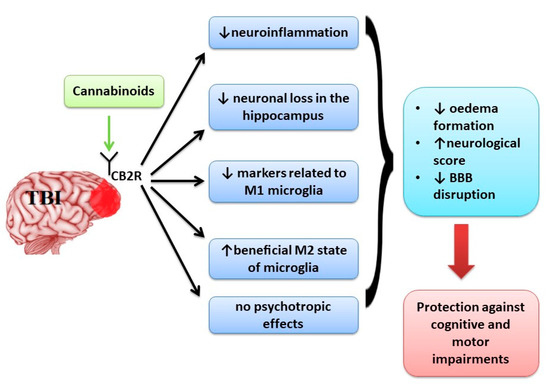
 “Cannabinoid CB2 receptor (CB2) agonists are potential analgesics void of psychotropic effects.
“Cannabinoid CB2 receptor (CB2) agonists are potential analgesics void of psychotropic effects. “Chronic ethanol abuse can lead to harmful consequences for the heart, resulting in systolic dysfunction, variability in the heart rate, arrhythmia, and cardiac remodelling. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy is poorly understood. In this regard, the present study aimed to describe the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic cell death that may be involved in ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy and characterize CBR-mediated effects on the signalling pathway and myocardial injury.
“Chronic ethanol abuse can lead to harmful consequences for the heart, resulting in systolic dysfunction, variability in the heart rate, arrhythmia, and cardiac remodelling. However, the precise molecular mechanism responsible for ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy is poorly understood. In this regard, the present study aimed to describe the RIP1/RIP3/MLKL-mediated necroptotic cell death that may be involved in ethanol-induced cardiomyopathy and characterize CBR-mediated effects on the signalling pathway and myocardial injury. “Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.
“Cannabinoids (CBs), analgesic drugs used for thousands of years, were first found in Cannabis sativa, and the multiple CBs used medicinally, such as tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), cannabidiol (CBD) and dozens more, have complex structures. In addition to their production by plants, CBs are naturally present in the nerves and immune systems of humans and animals.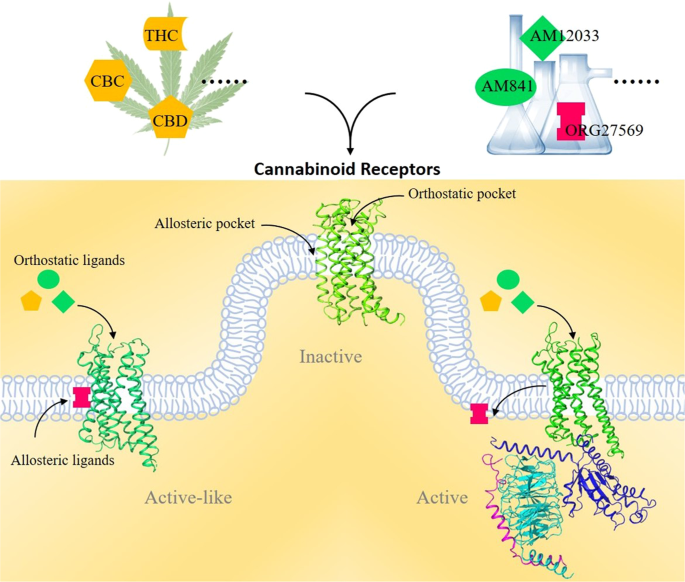
 “HIV is associated with disruptions in cognition and brain function.
“HIV is associated with disruptions in cognition and brain function. “In the last few years research into Cannabis and its constituent phytocannabinoids has burgeoned, particularly in the potential application of novel cannabis phytochemicals for the treatment of diverse illnesses related to neurodegeneration and dementia, including Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and Huntington’s disease (HD). To date, these neurological diseases have mostly relied on symptomatological management. However, with an aging population globally, the search for more efficient and disease-modifying treatments that could delay or mitigate disease progression is imperative. In this context, this review aims to present a state of art in the research with cannabinoids and novel cannabinoid-based drug candidates that have been emerged as novel promising alternatives for drug development and innovation in the therapeutics of a number of diseases, especially those related to CNS-disturbance and impairment.”
“In the last few years research into Cannabis and its constituent phytocannabinoids has burgeoned, particularly in the potential application of novel cannabis phytochemicals for the treatment of diverse illnesses related to neurodegeneration and dementia, including Alzheimer’s (AD), Parkinson’s (PD) and Huntington’s disease (HD). To date, these neurological diseases have mostly relied on symptomatological management. However, with an aging population globally, the search for more efficient and disease-modifying treatments that could delay or mitigate disease progression is imperative. In this context, this review aims to present a state of art in the research with cannabinoids and novel cannabinoid-based drug candidates that have been emerged as novel promising alternatives for drug development and innovation in the therapeutics of a number of diseases, especially those related to CNS-disturbance and impairment.” “We observed that cannabidiol supplements were highly effective in treating an infant boy with drug-resistant early infantile epileptic encephalopathy, eliminating his intractable tonic seizures.
“We observed that cannabidiol supplements were highly effective in treating an infant boy with drug-resistant early infantile epileptic encephalopathy, eliminating his intractable tonic seizures. “In this work, we evaluated, for the first time, the antitumor effect of cannabidiol (CBD) as monotherapy and in combination with conventional chemotherapeutics in ovarian cancer and developed PLGA-microparticles as CBD carriers to optimize its anticancer activity.
“In this work, we evaluated, for the first time, the antitumor effect of cannabidiol (CBD) as monotherapy and in combination with conventional chemotherapeutics in ovarian cancer and developed PLGA-microparticles as CBD carriers to optimize its anticancer activity.
 “In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids.
“In recent years, the role of the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in various cardiovascular conditions has been a subject of great interest. The ECS is composed of cannabinoid receptors, their endogenous ligands, also known as endocannabinoids, and enzymes responsible for the synthesis and degradation of endocannabinoids.